Jacquemart-André — A Wonderful Little Museum in Paris
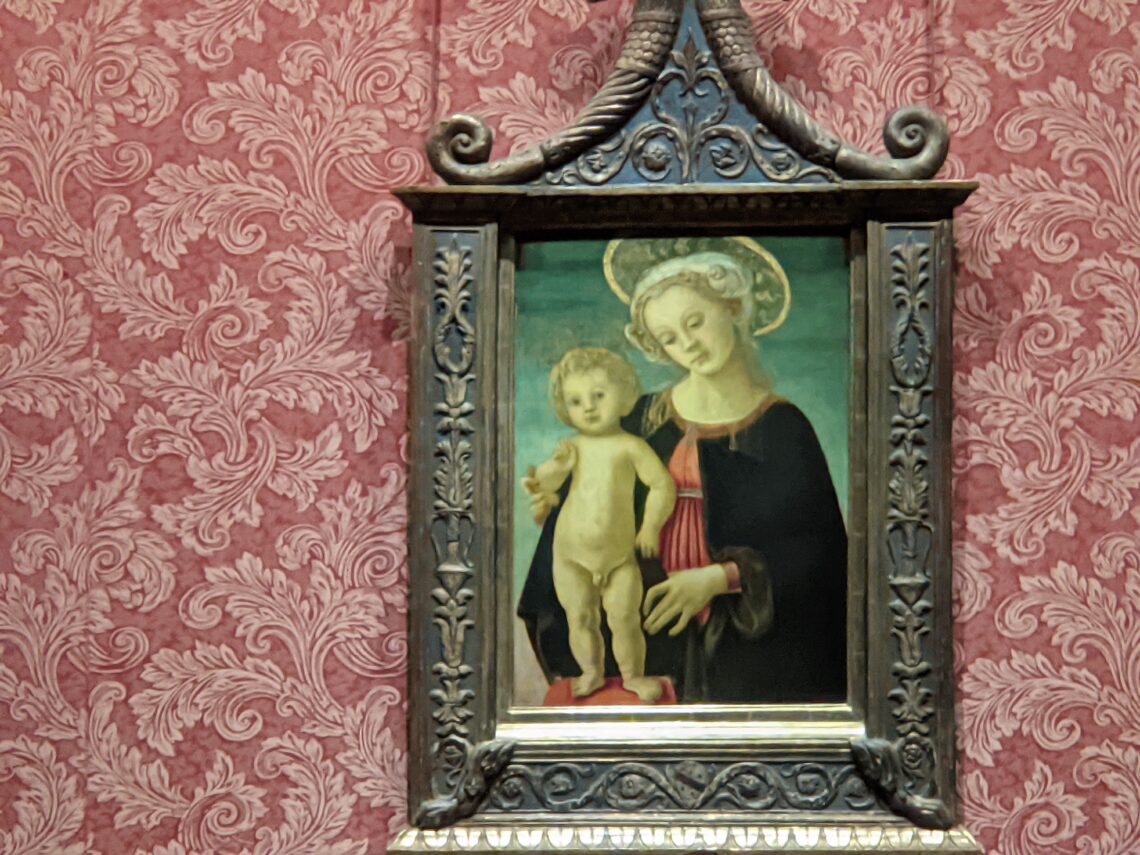
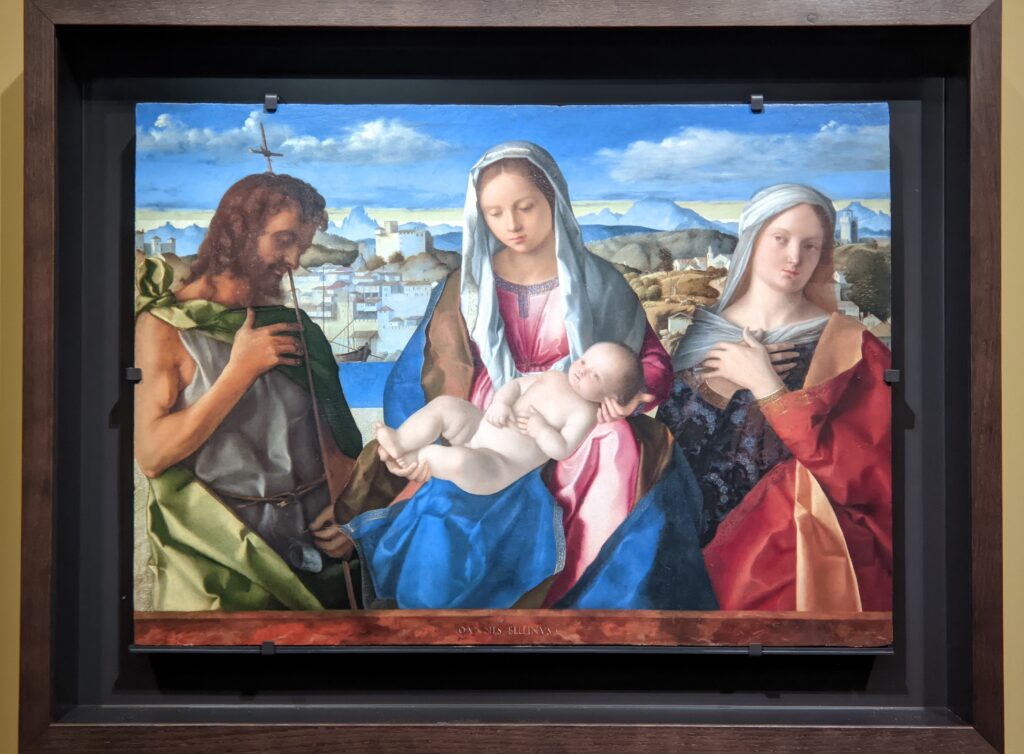
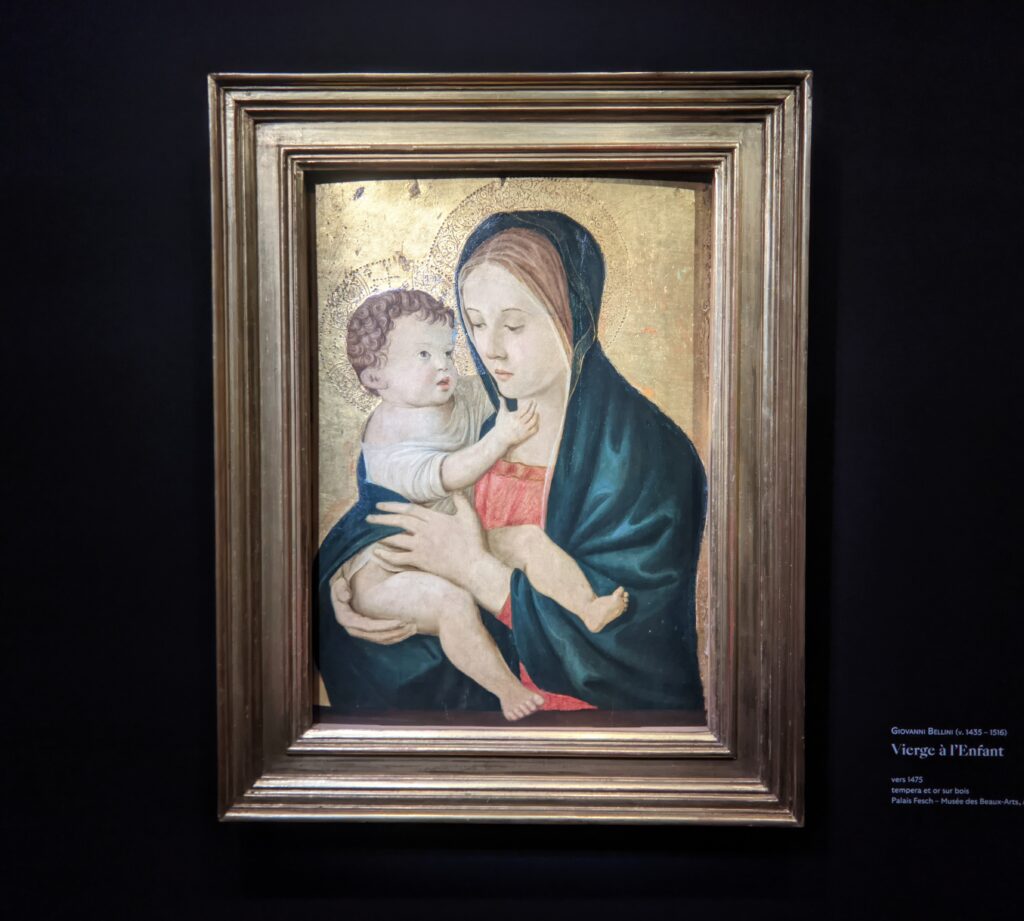
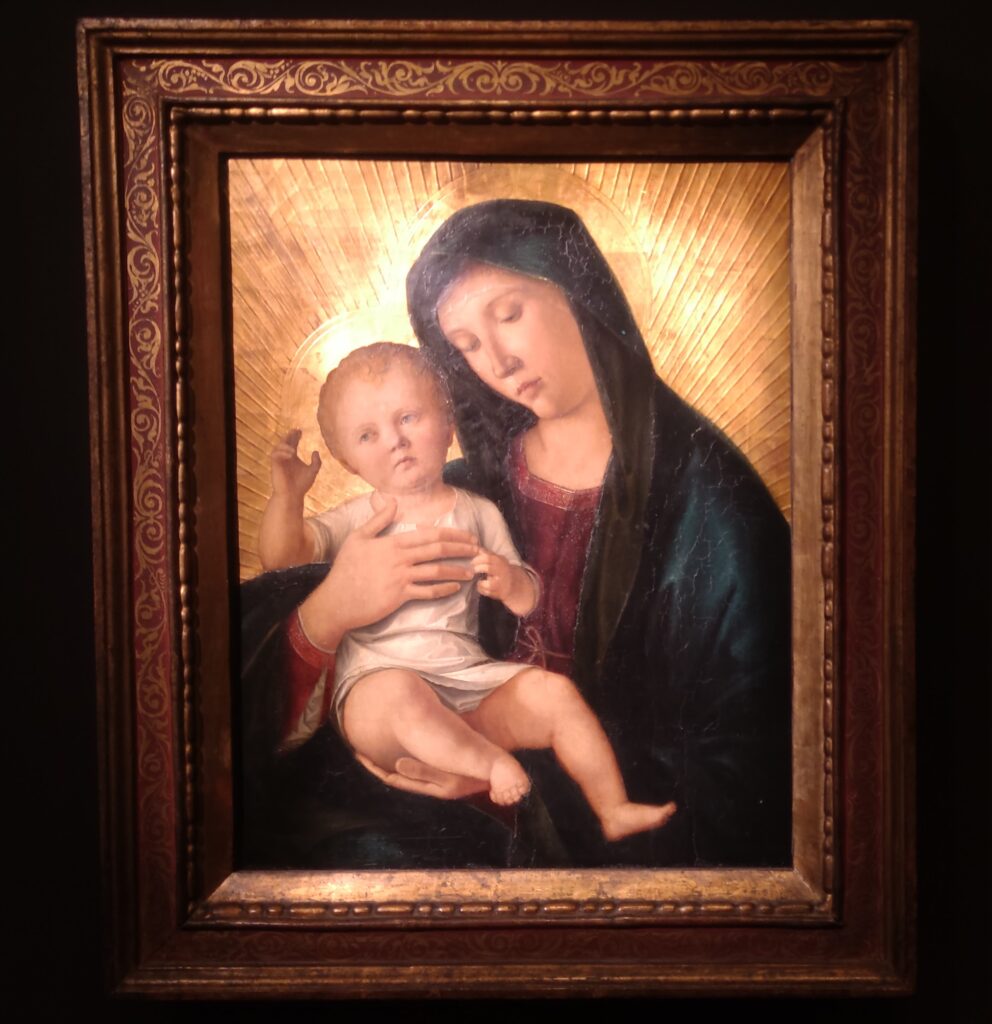
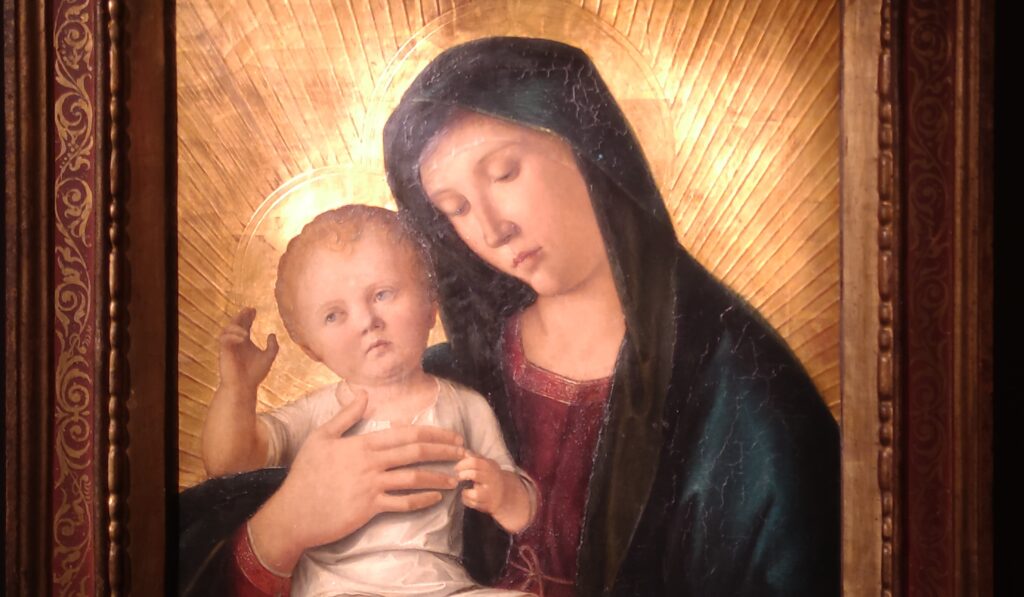
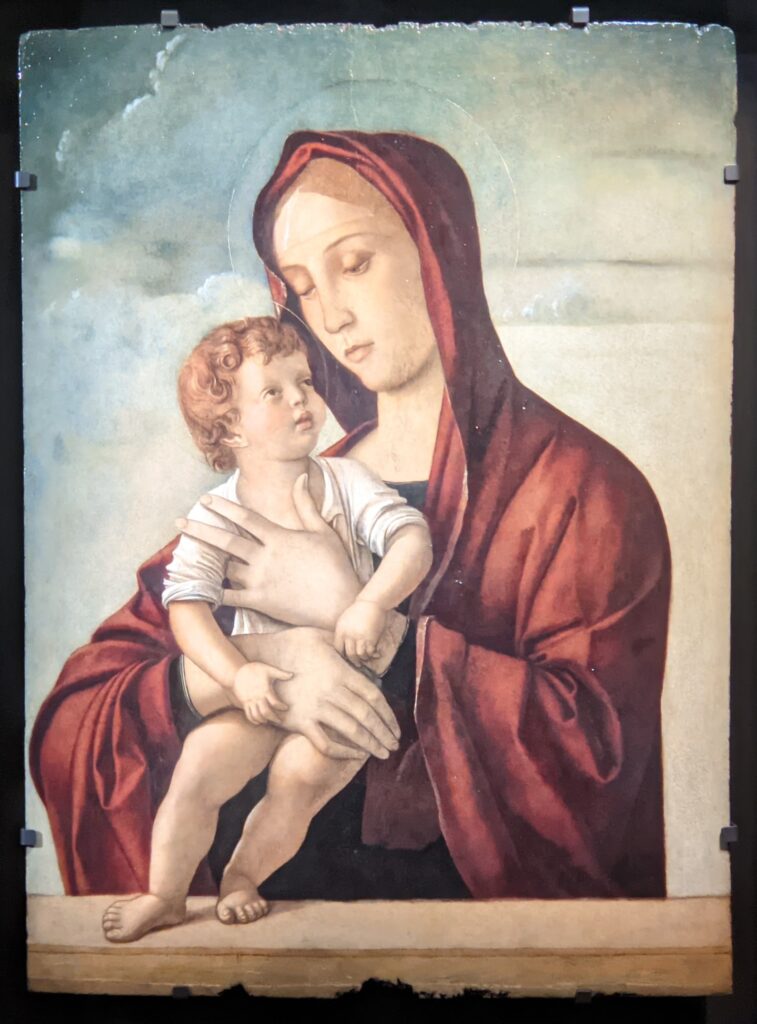
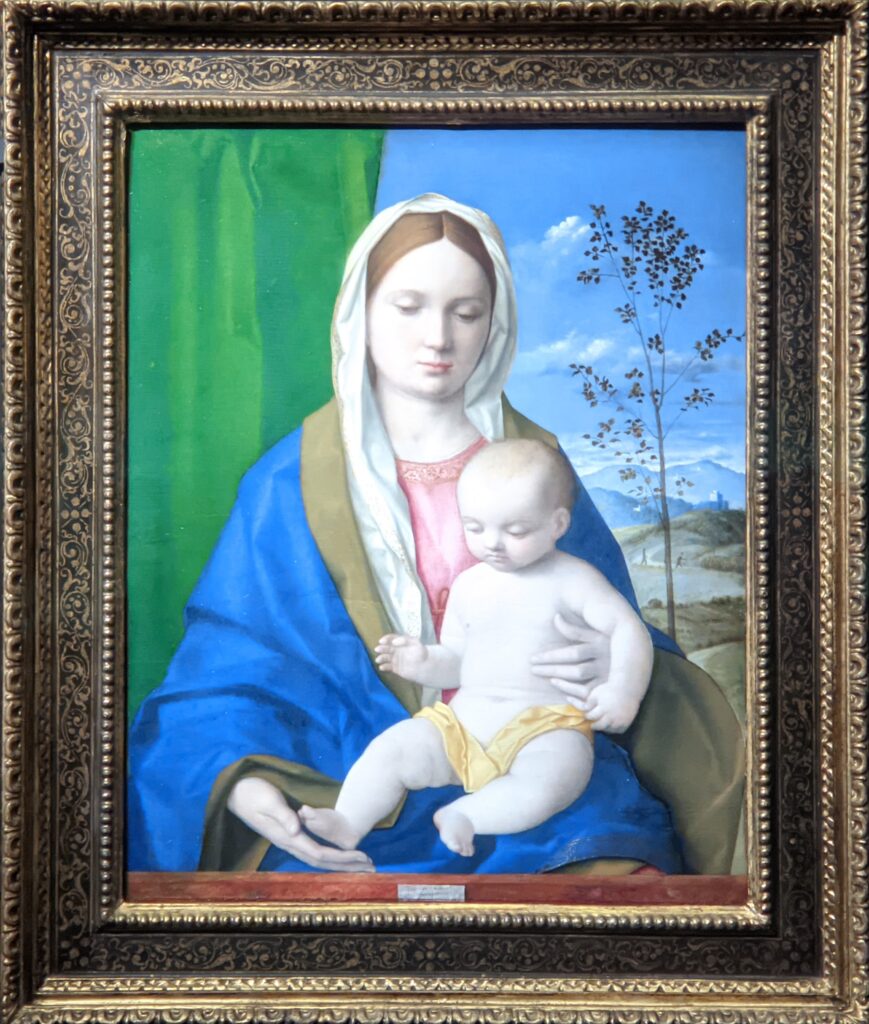
When Nélie Jacquemart acquired “Virgin and Child on a Throne” (pictured below) at the end of the 19th century she did not know who had created this important painting — for it was only in the 1930s that this masterpiece was attributed to Giovanni Bellini.
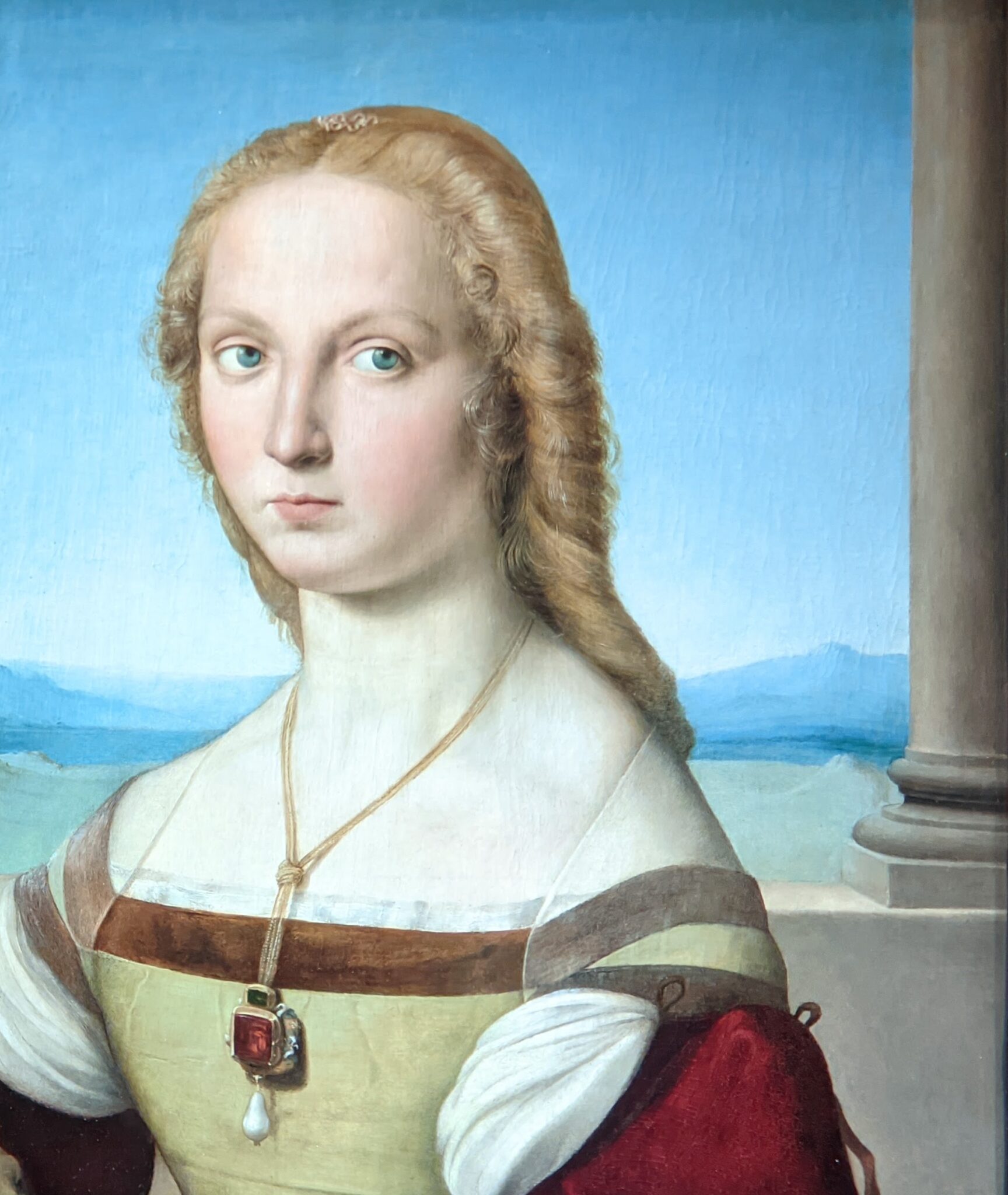




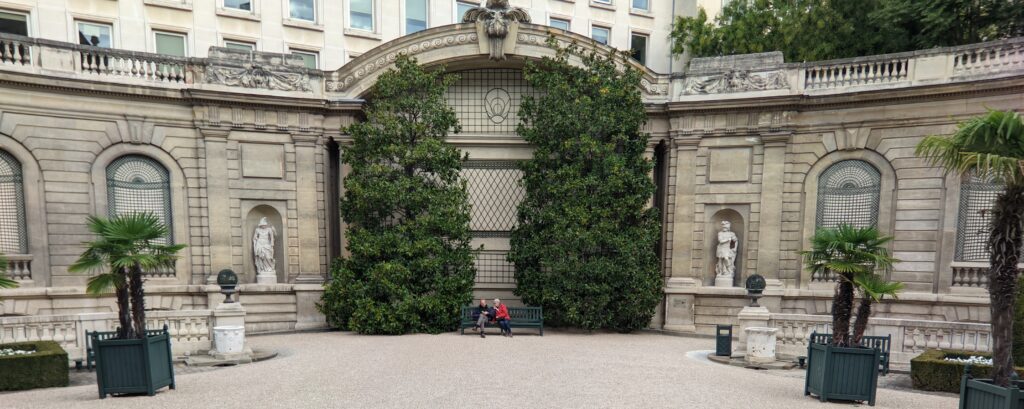
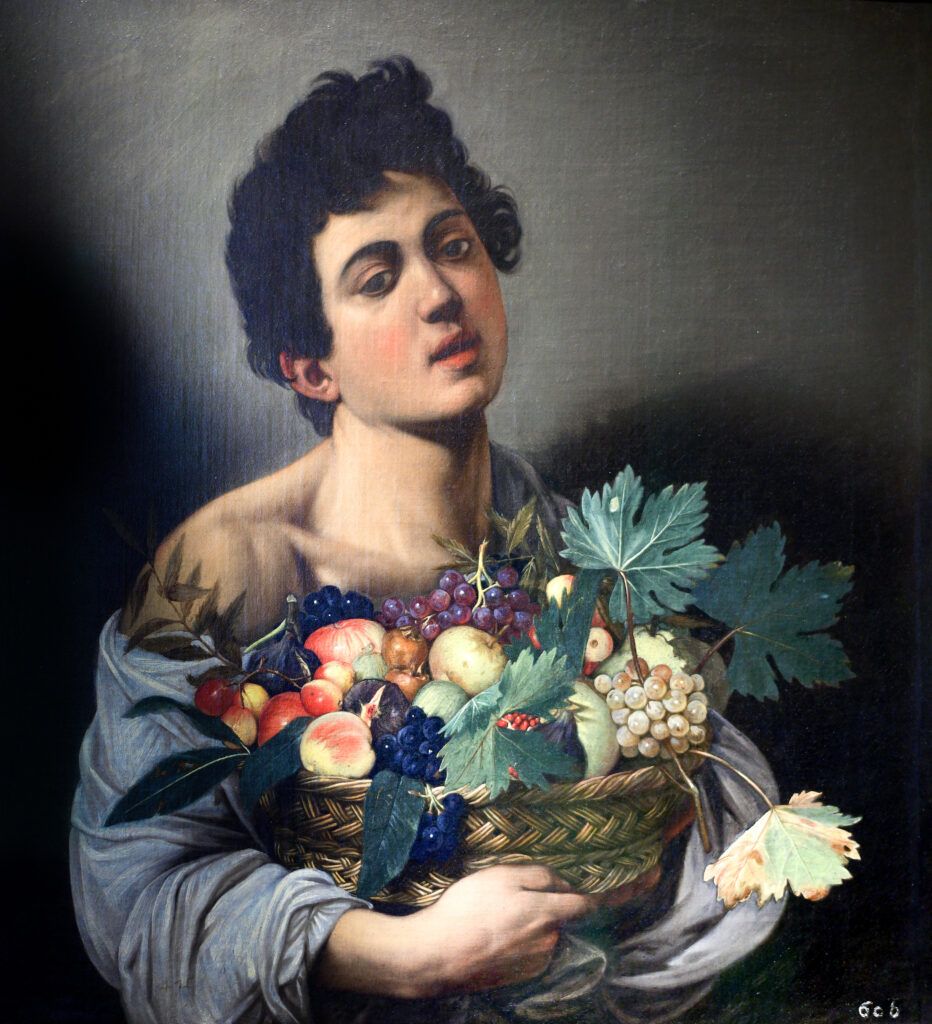
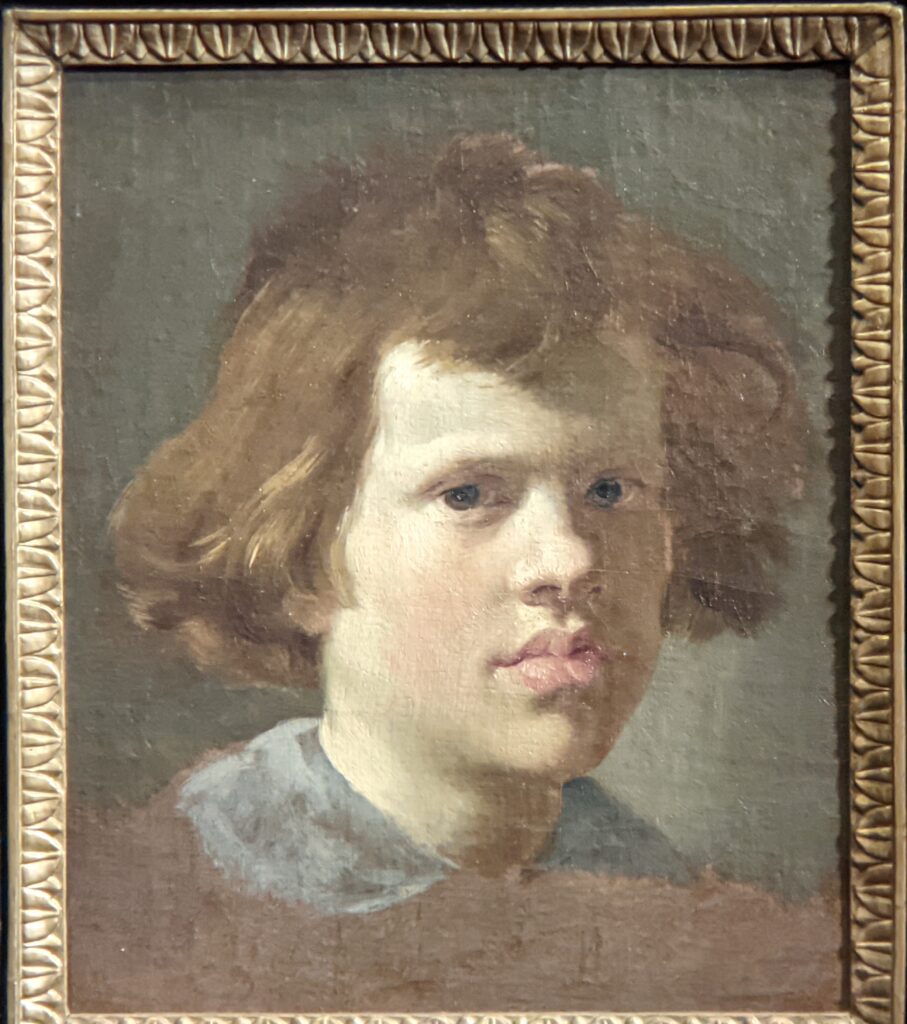
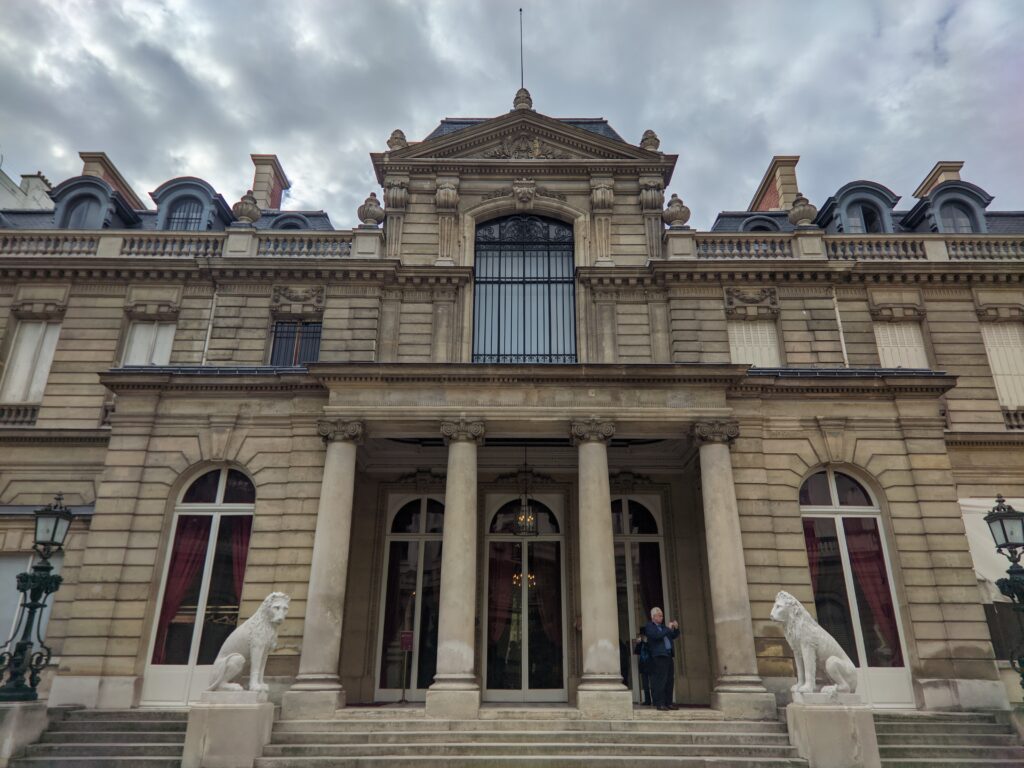
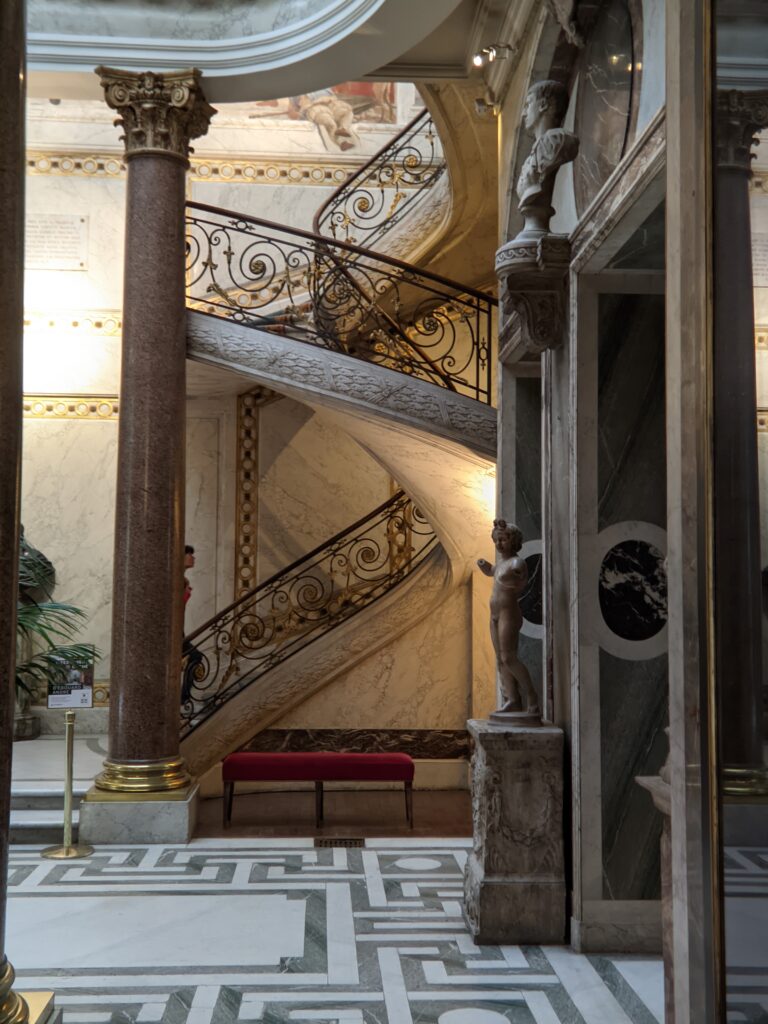
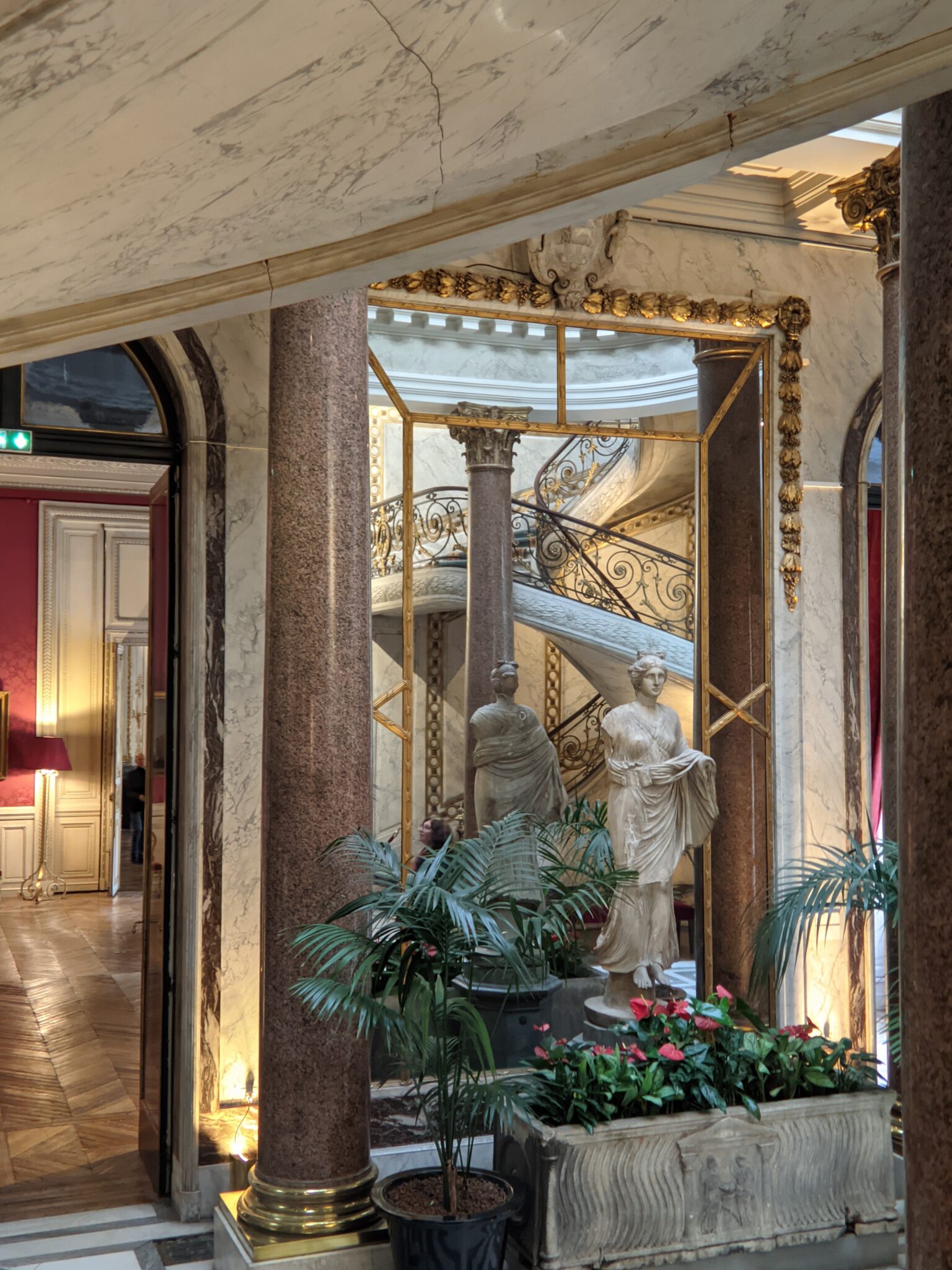
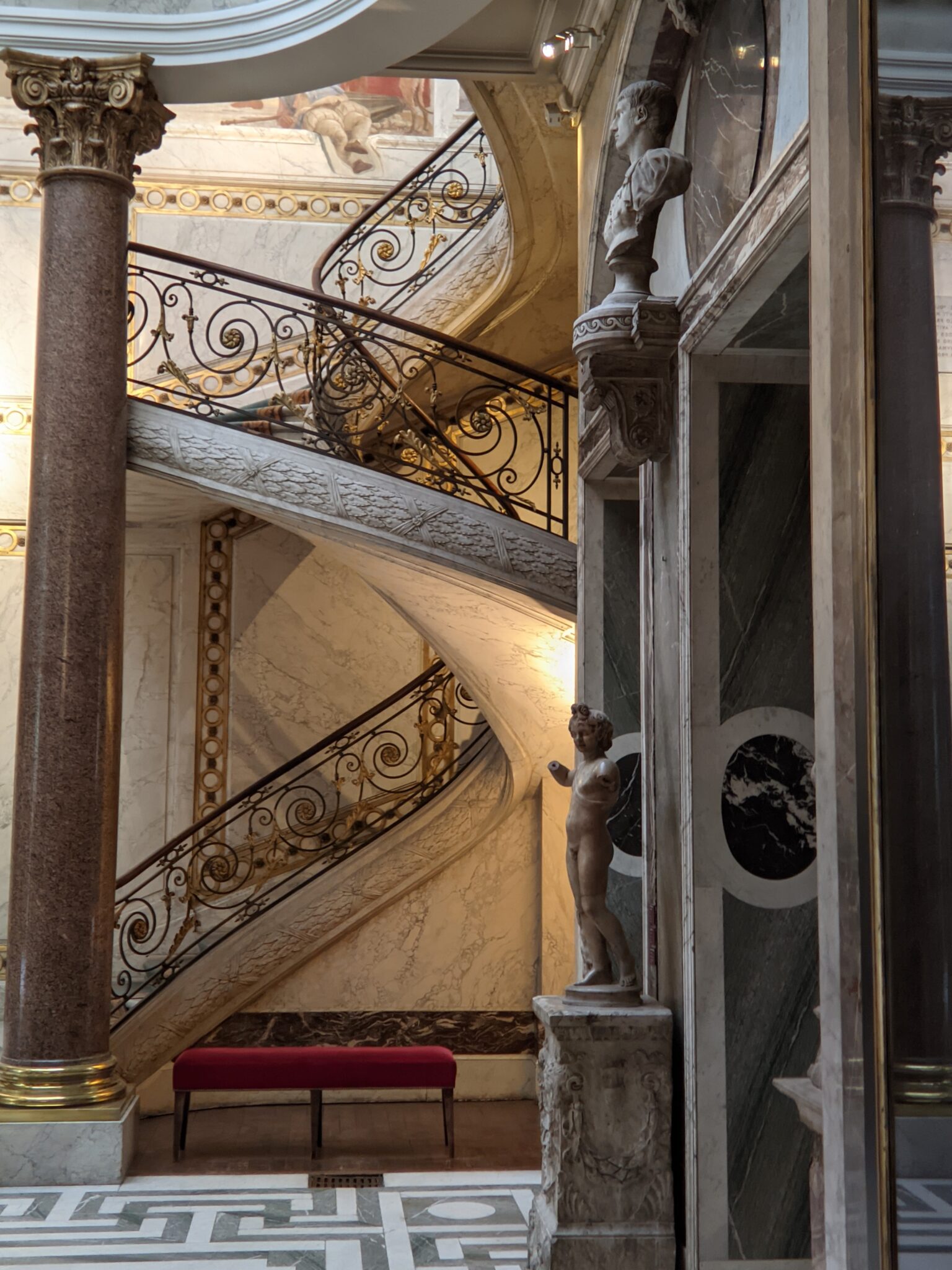
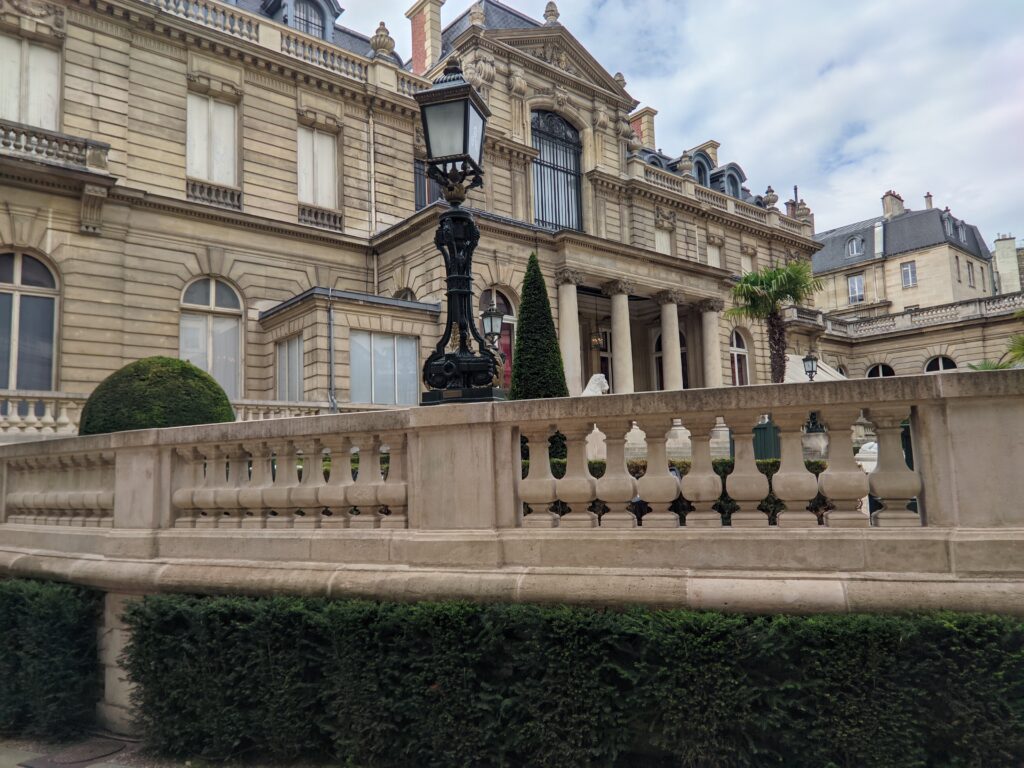
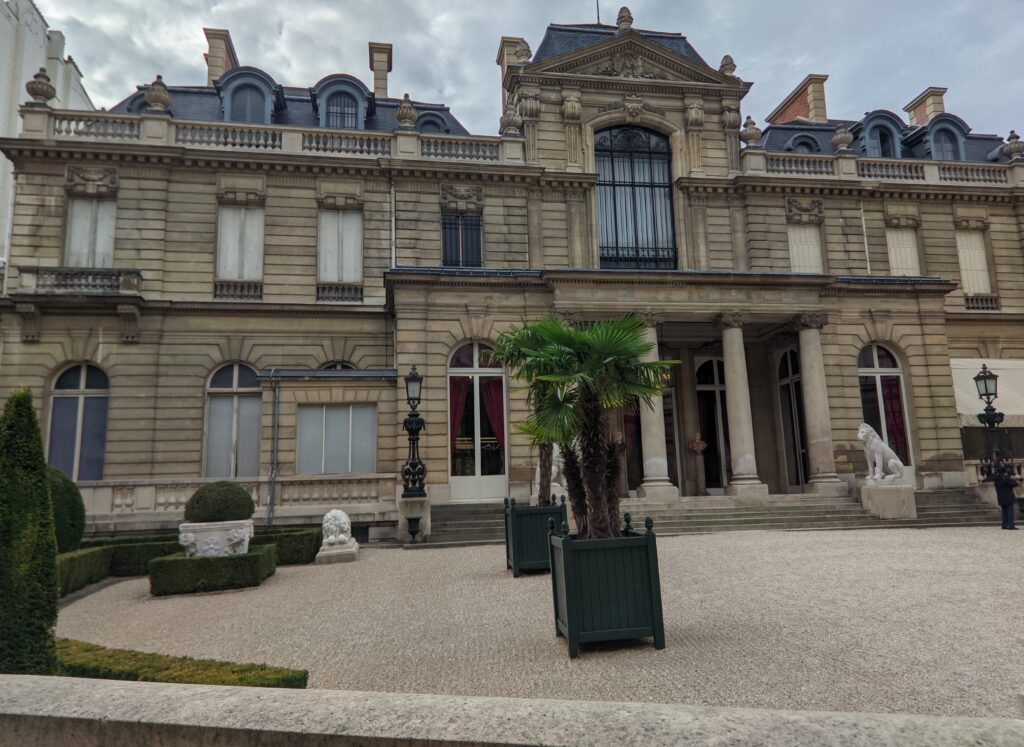
The Musee Jacquemart-André on Boulevard Haussmann was created from the private home of Nélie and her husband Édouard André to show the art they collected. After closing for one year for major restoration work, the museum reopened in September 2024 for the presentation of the exhibit “Masterpieces from the Borghese Gallery” in Rome. Incredible paintings by Raphael (above left), Titian, Lotto and Garofalo — in addition to “Boy with a Basket of Fruit” (below) — were on view in Paris through February 9, 2025.

If you are attracted to the rare atmosphere and experience found at the Gardner Museum in Boston and the Frick Collection in New York, you will definitely want to find time to visit the Jacquemart-André Museum in Paris.
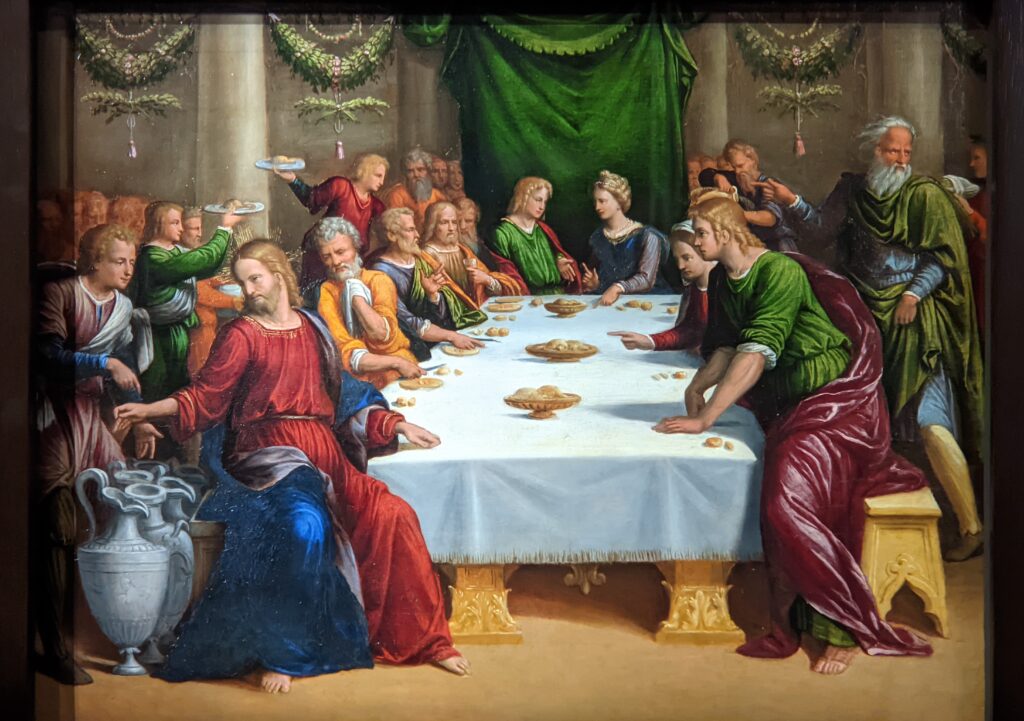
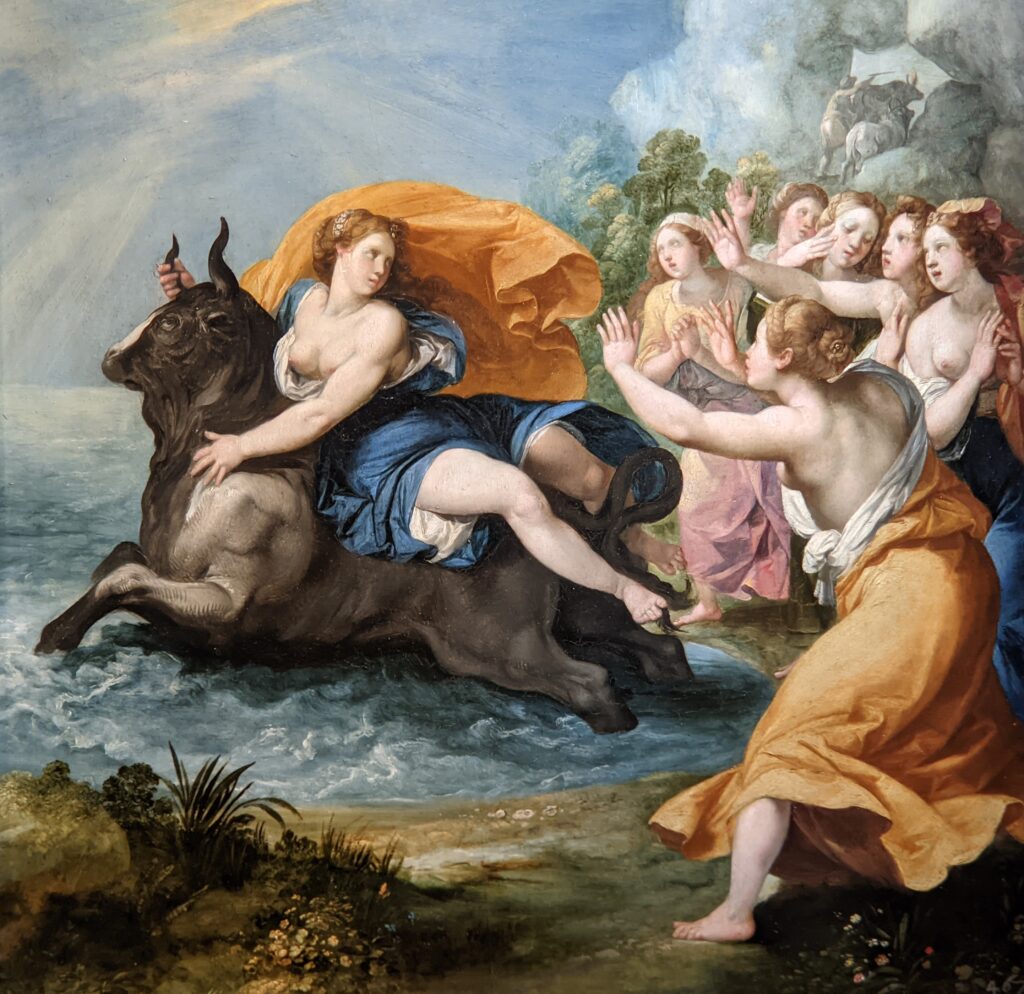
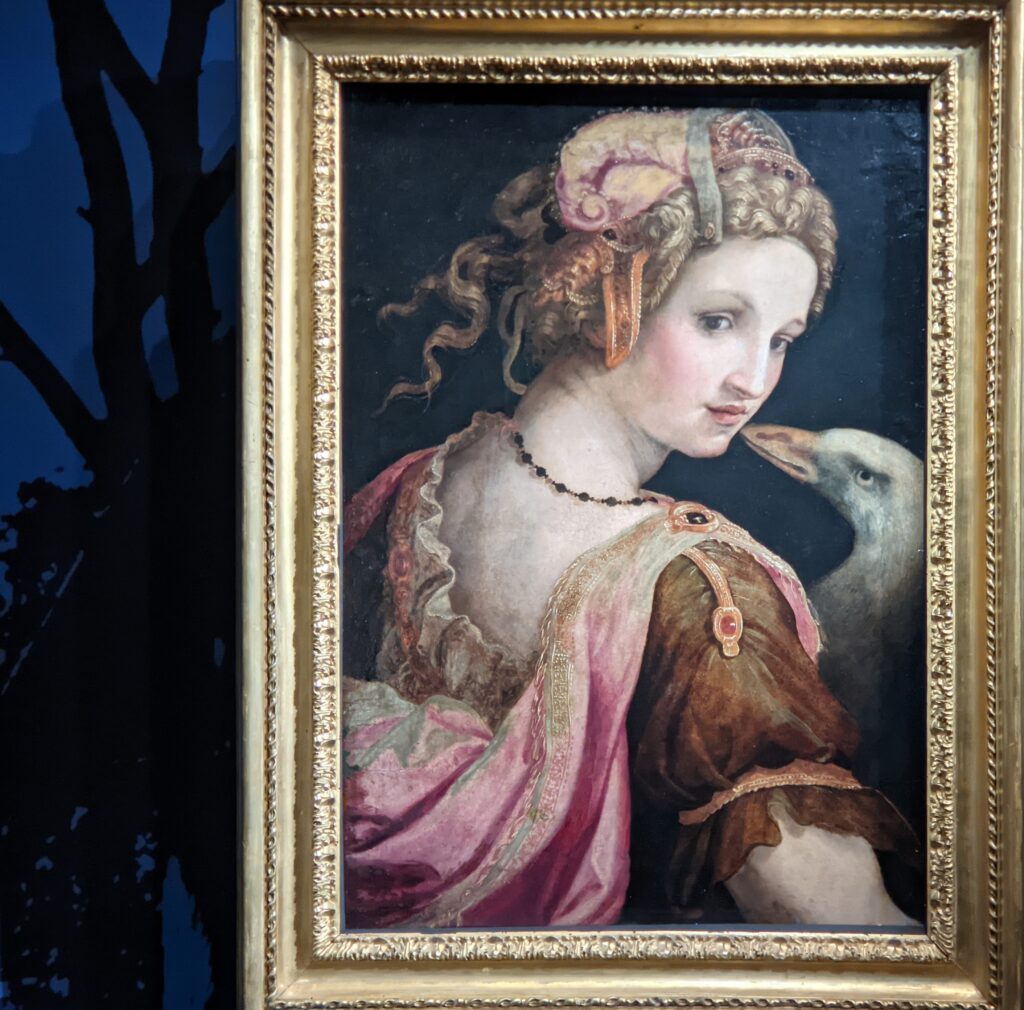
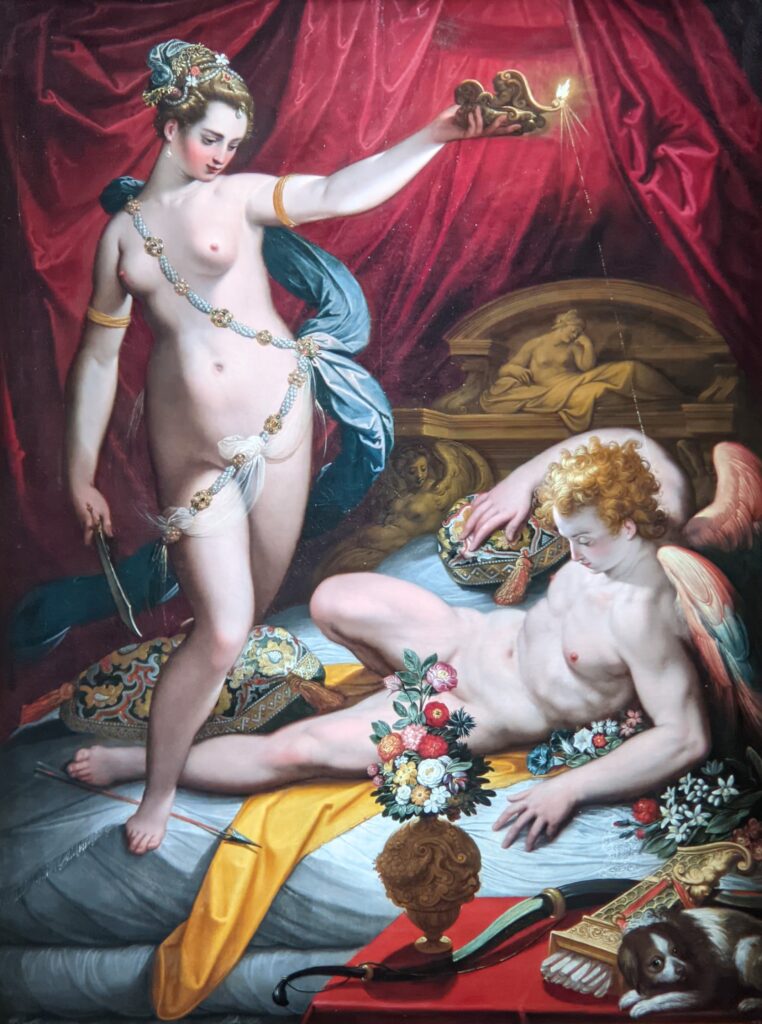
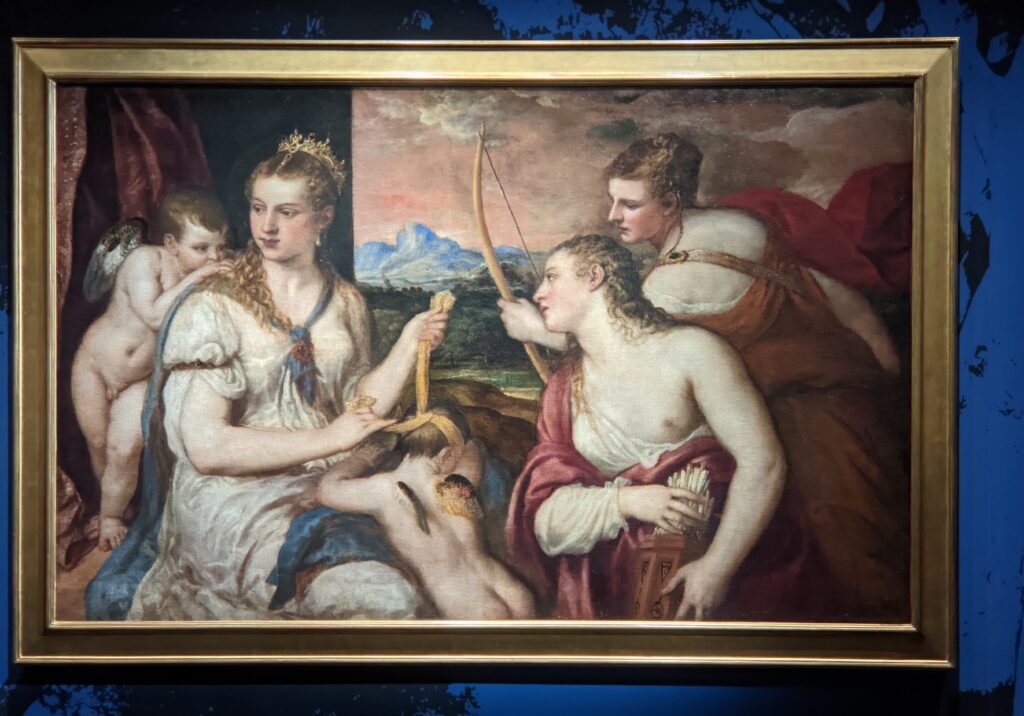
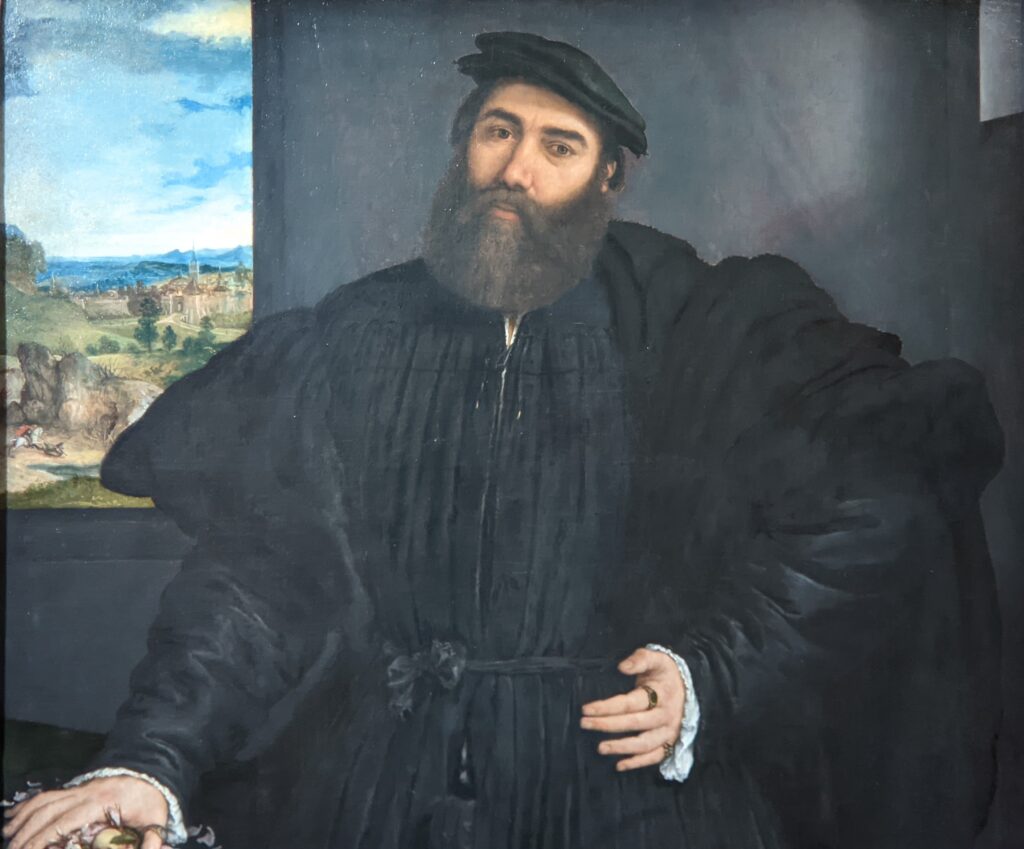
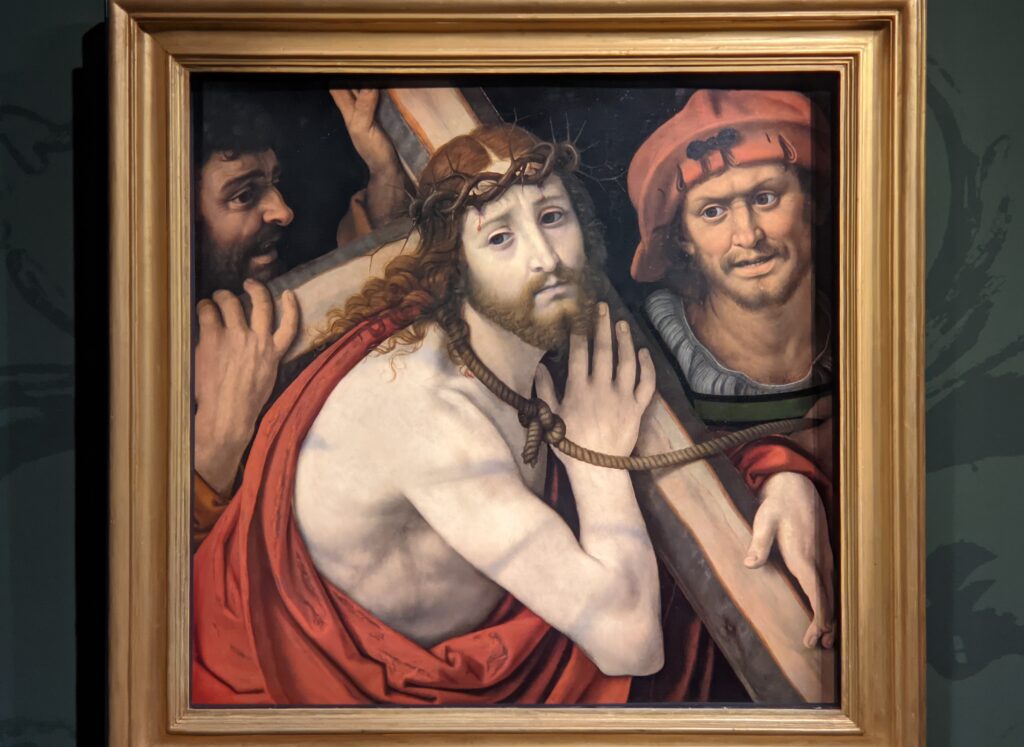
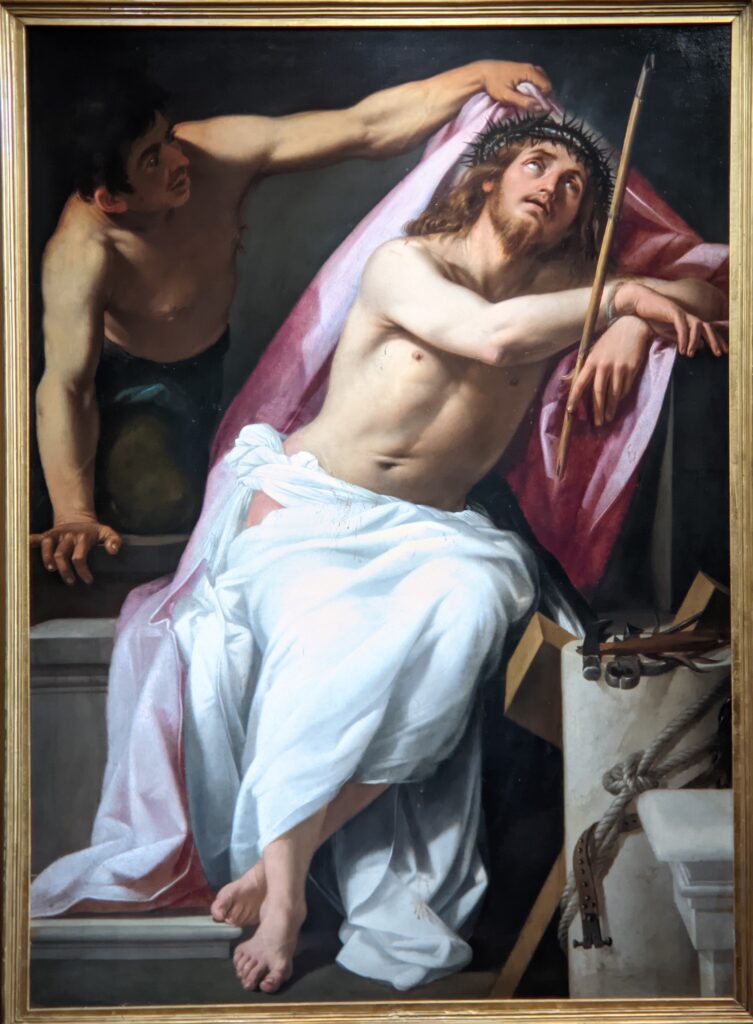
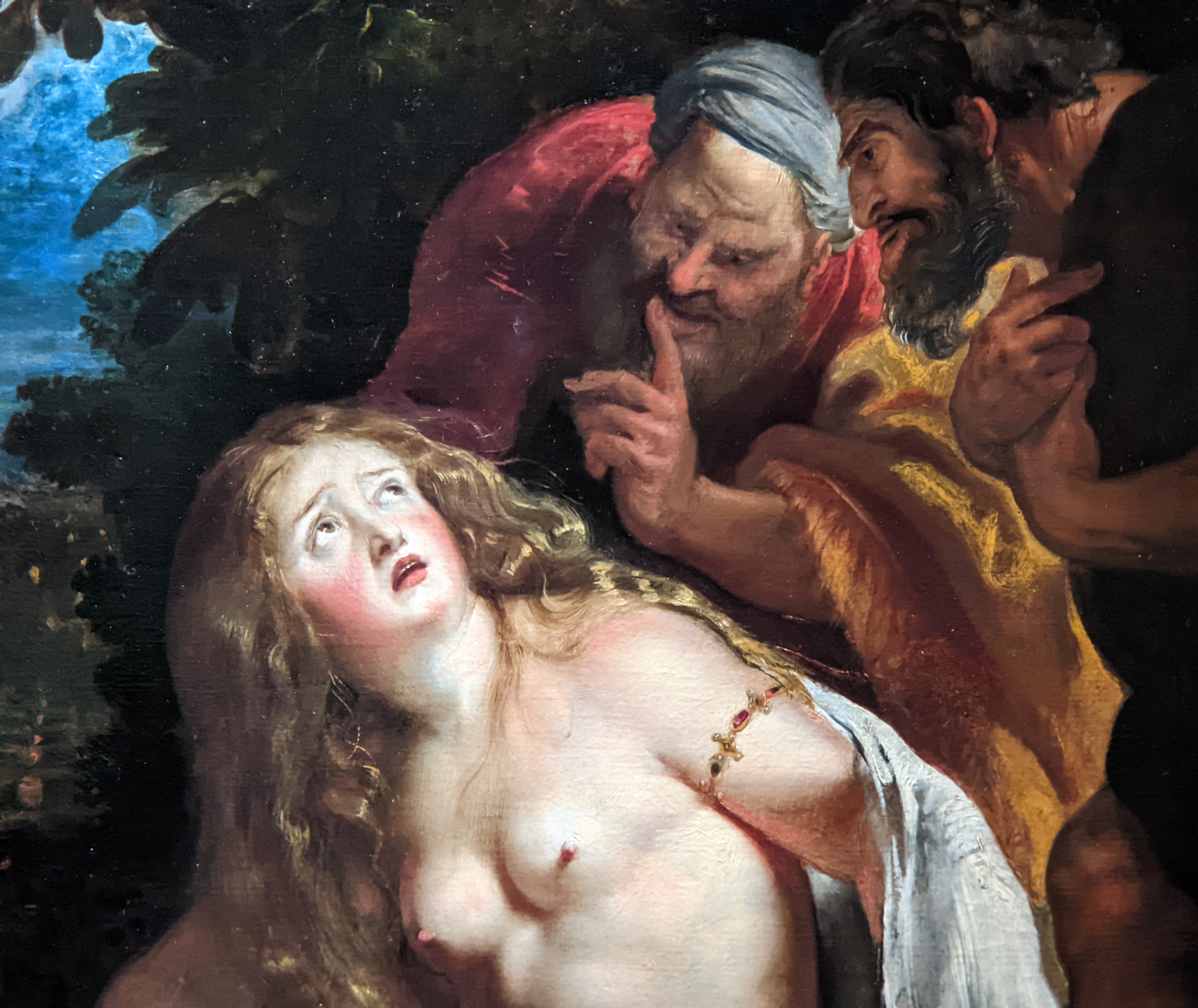
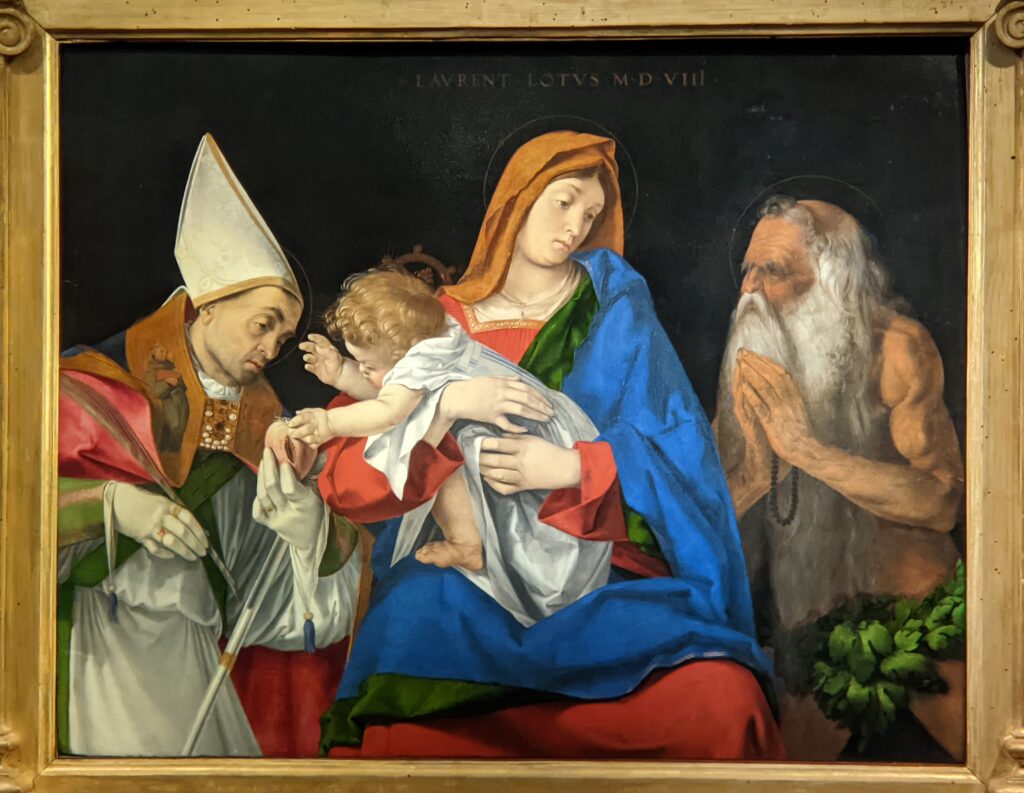
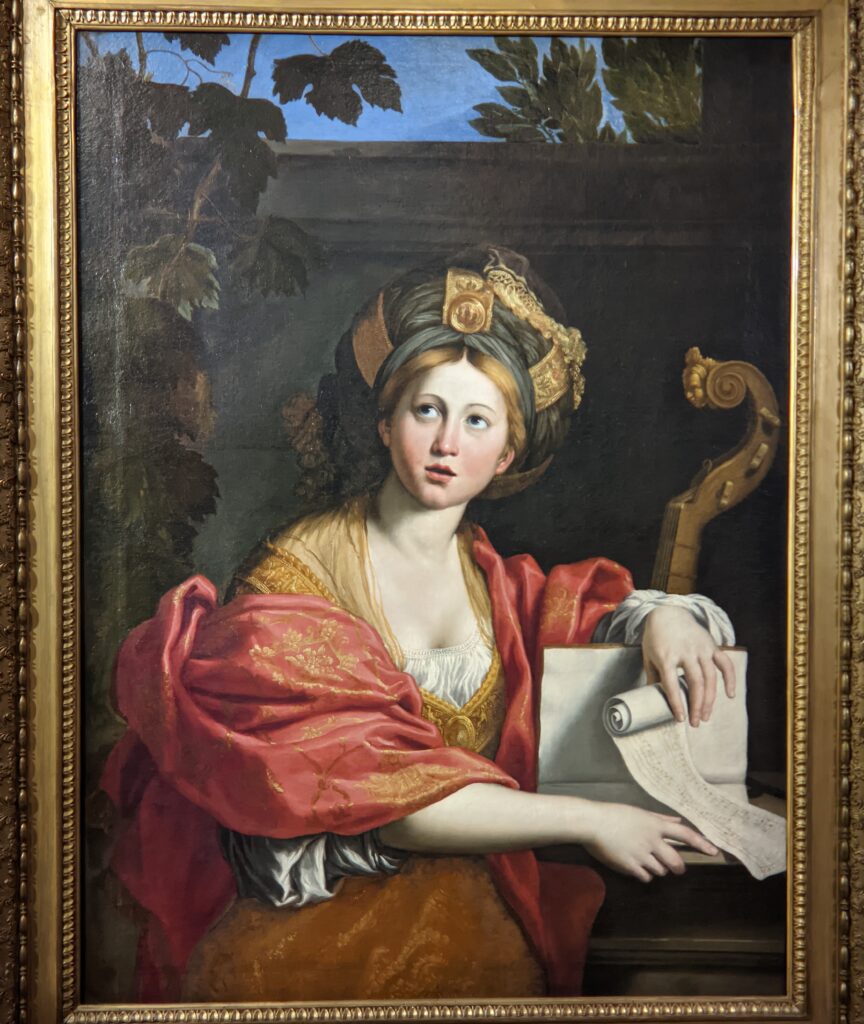
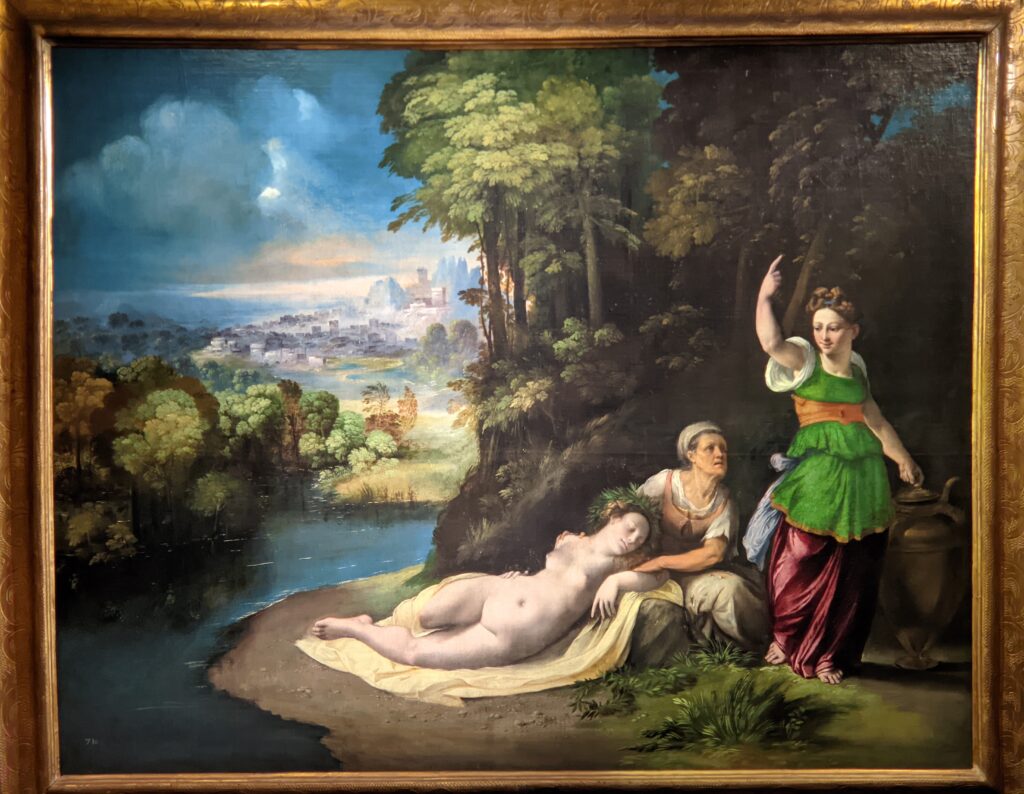
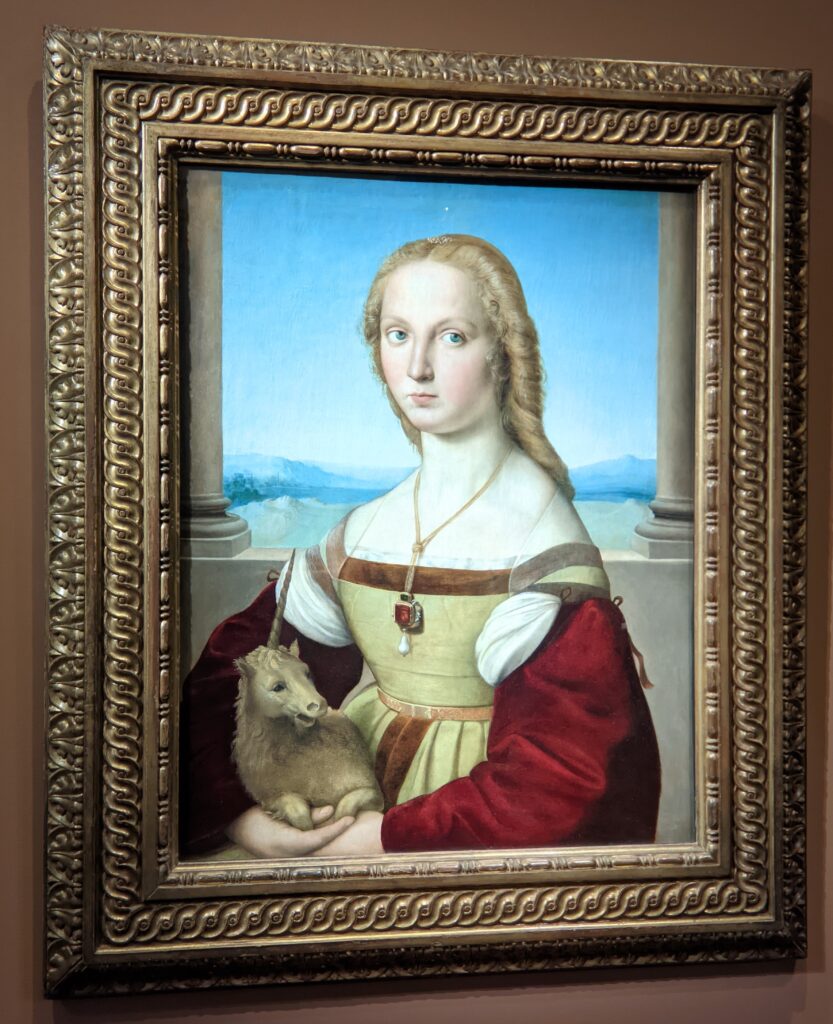






















The previous special exhibiti at the Jacquemart-André, on display during 2023, was entitled “GIOVANNI BELLINI Cross Influences.”
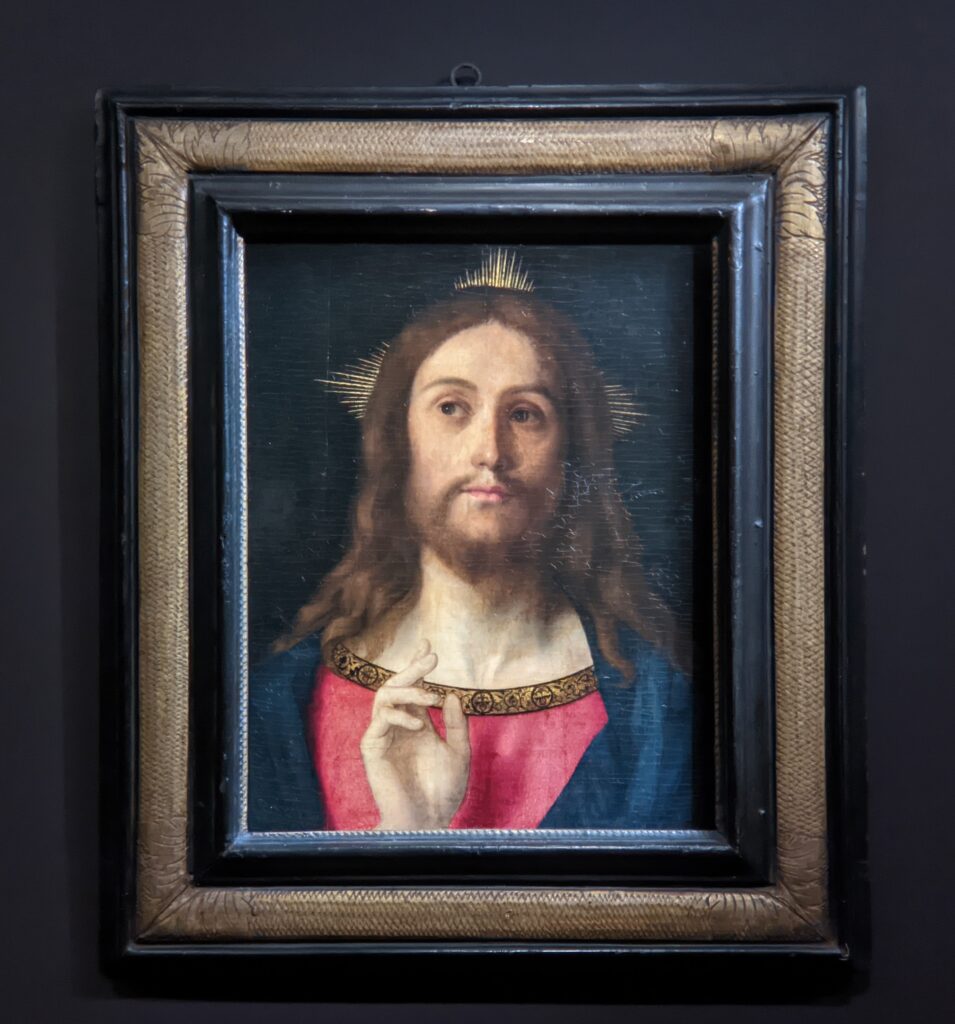



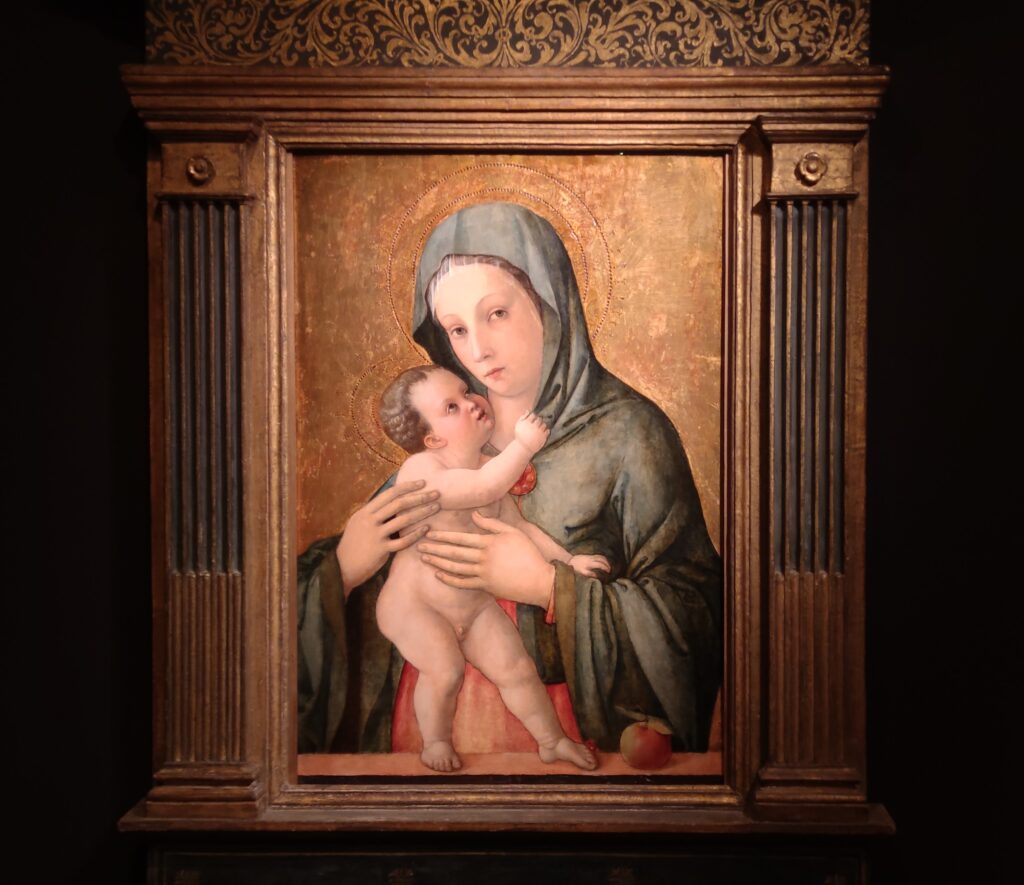
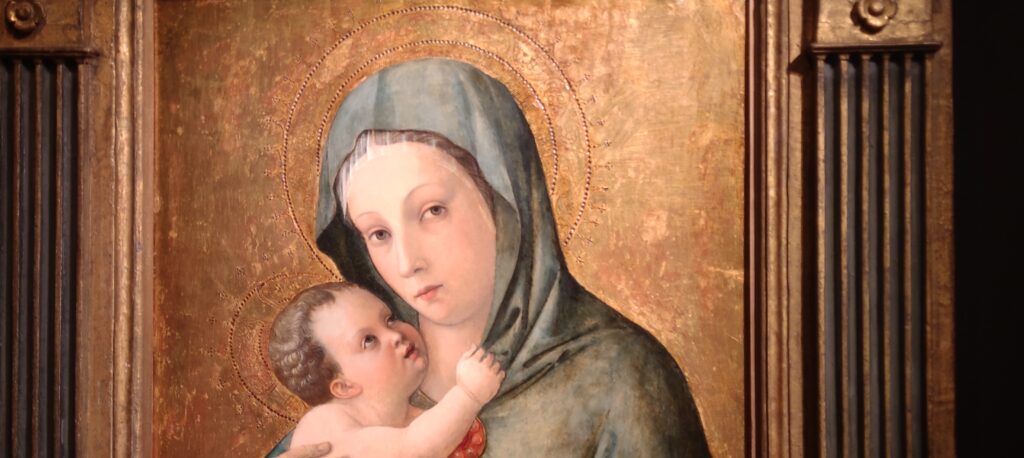
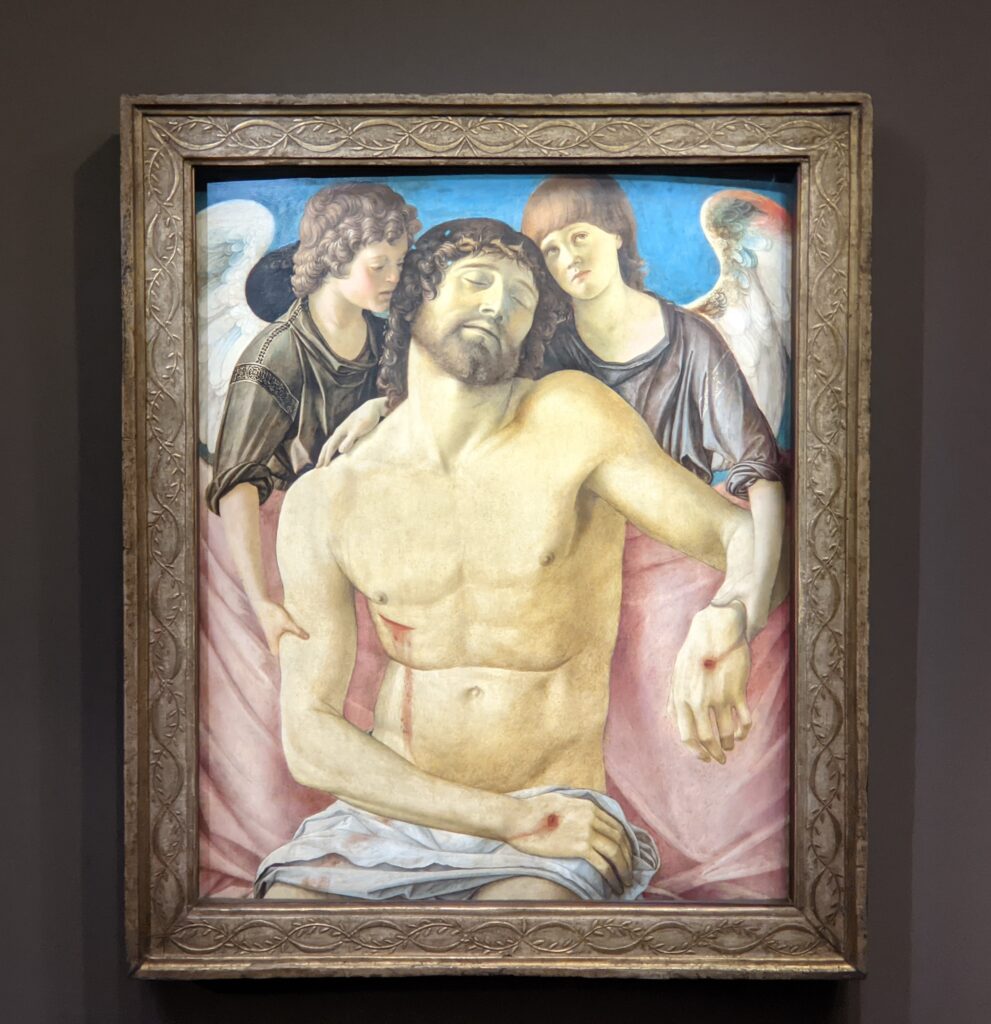
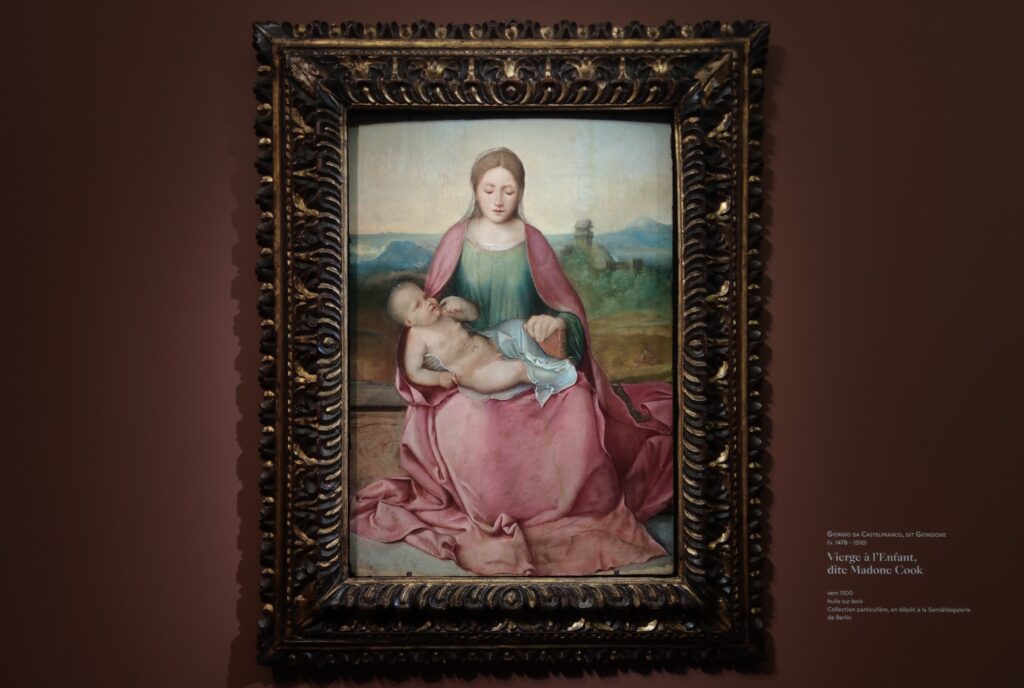
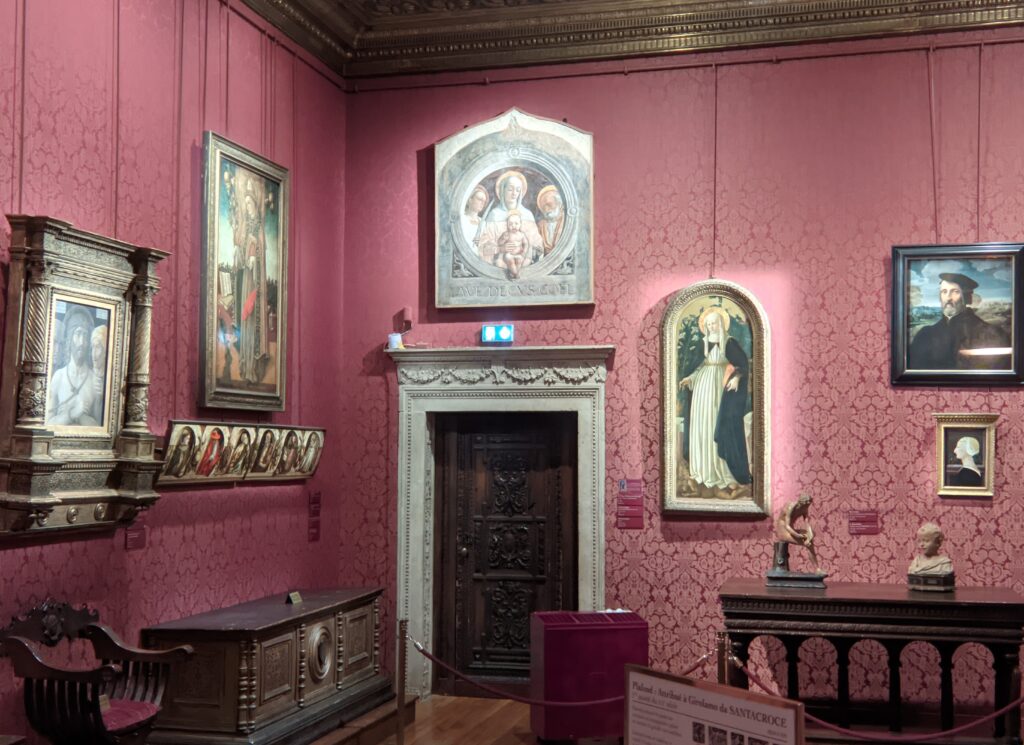
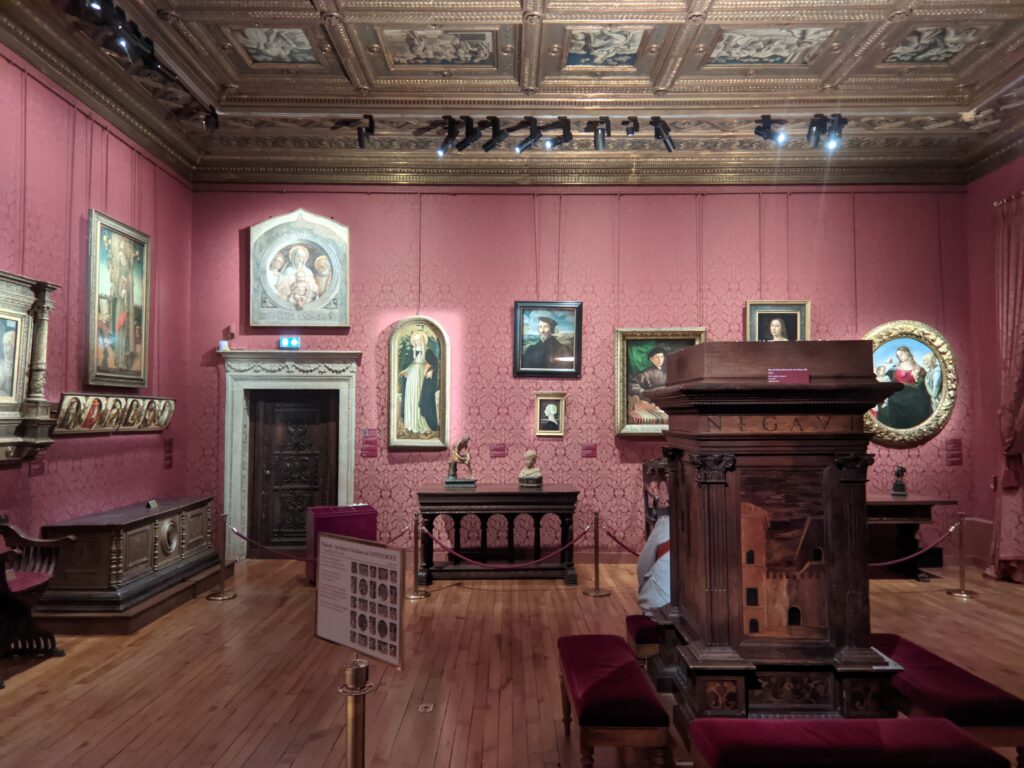
The 50 works displayed at the Jacquemart-André in 2023 paid tribute to the master painter Giovanni Bellini (circa 1435 — 1516), father of the Venetian school during the Italian Renaissance to which his pupils Titian and Giorgione belonged. Born into a family of artists, Bellini embraced various artistic influences — from the Florentine school of his father’s day to styles from the farthest regions in the Eastern Mediterranean controlled by the Republic of Venice during the 15th century.
Giovanni Bellini was born in Venice during the era of Francesco Foscari, the 65th and longest-serving Doge who was elected to hold power from 1423 — 1457, when the city was at the height of its territorial extent and power. By the end of the 15th century, Venice with its 180,000 inhabitants was the 2nd largest city in Europe (after Paris) and presumably the richest in the world.
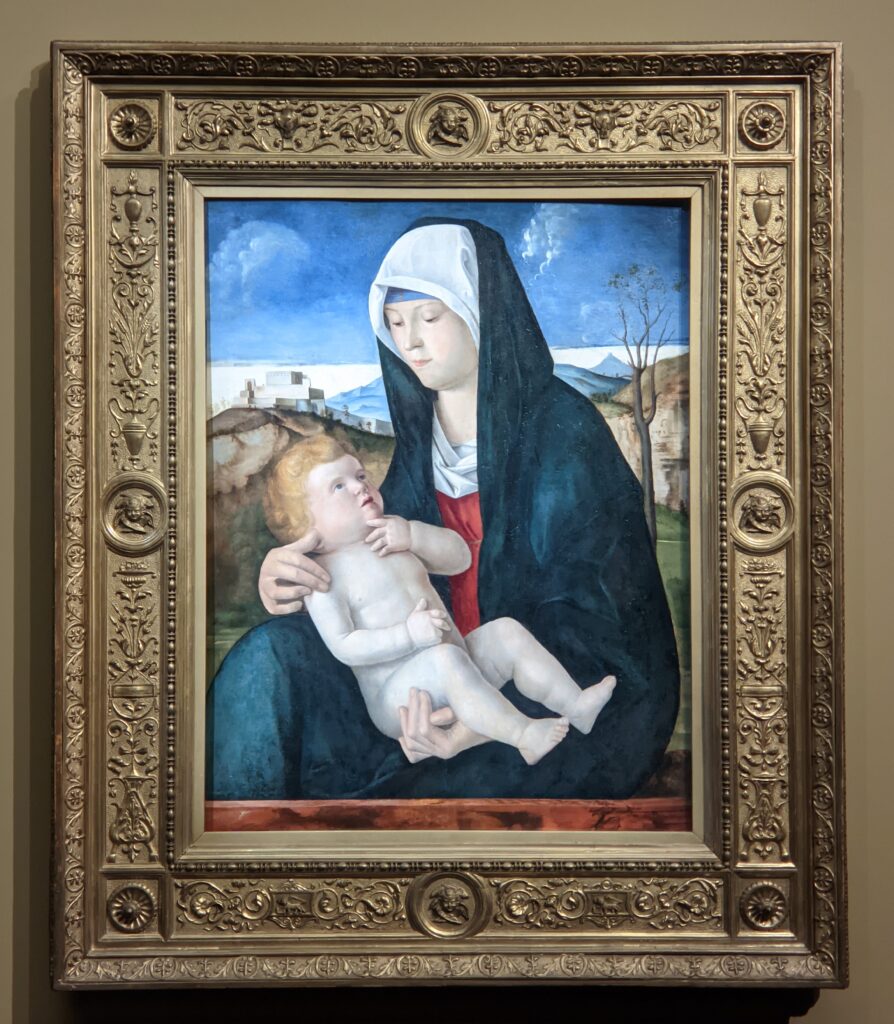
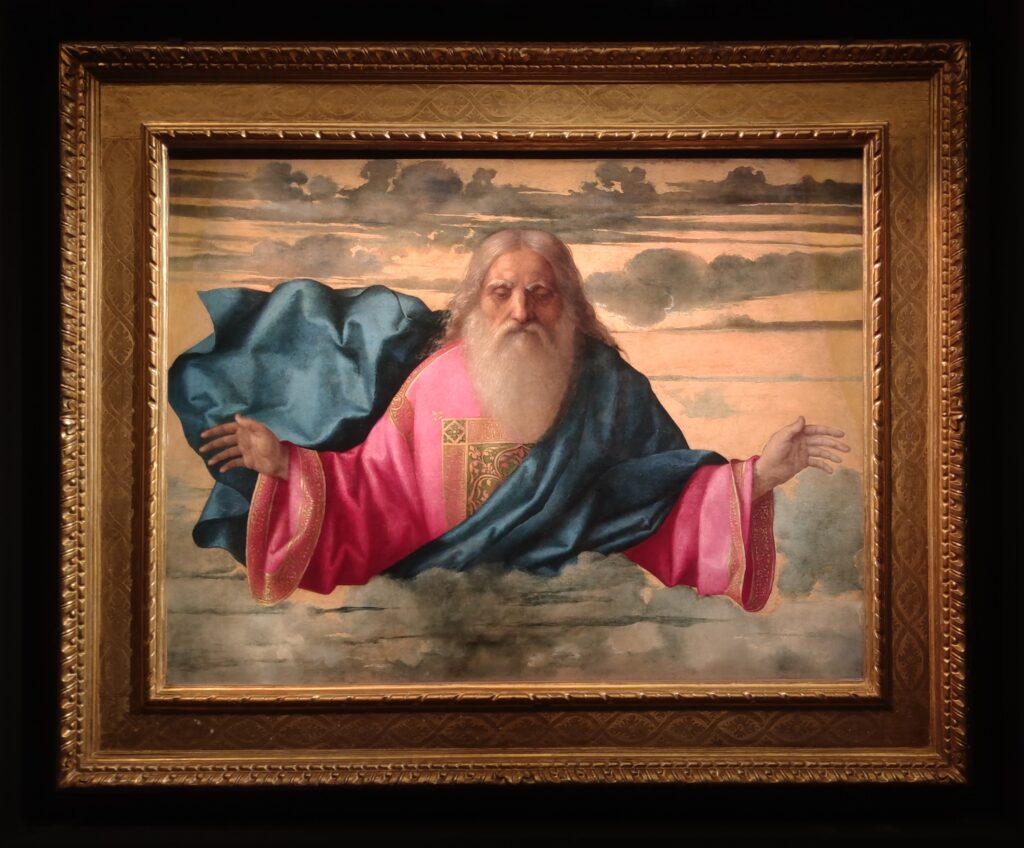
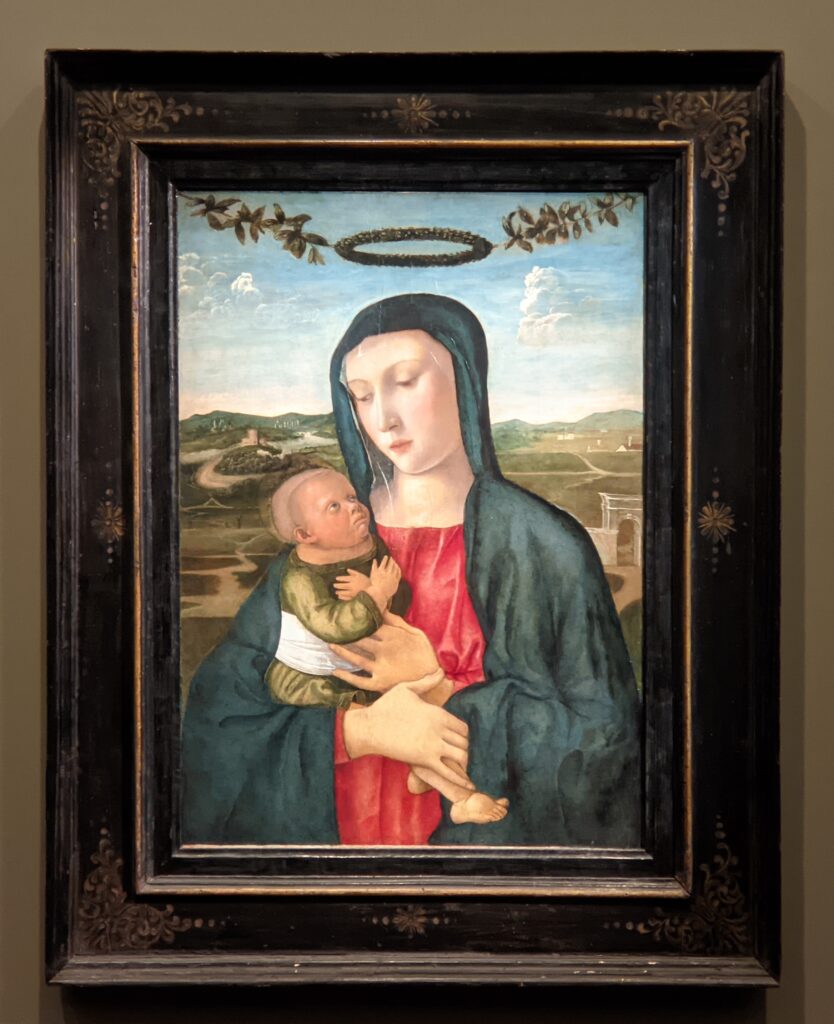
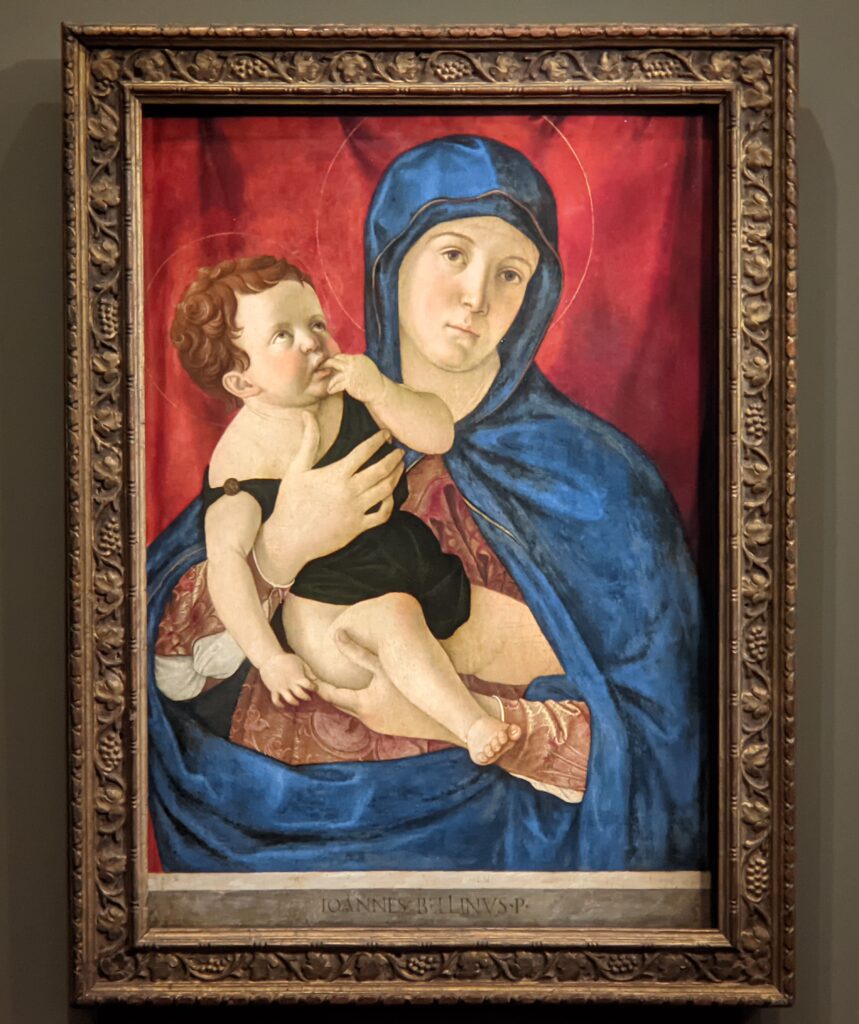

















Jacopo Bellini (1400 — 1471) & Gentile Bellini (1429 — 1507)
Giovanni Bellini was raised in a household of painters. His father Jacopo Bellini worked in the style now known as International Gothic, which was then all the rage from Northern Italy across Western Europe. His older brother Gentile also worked in Jacopo’s workshop.
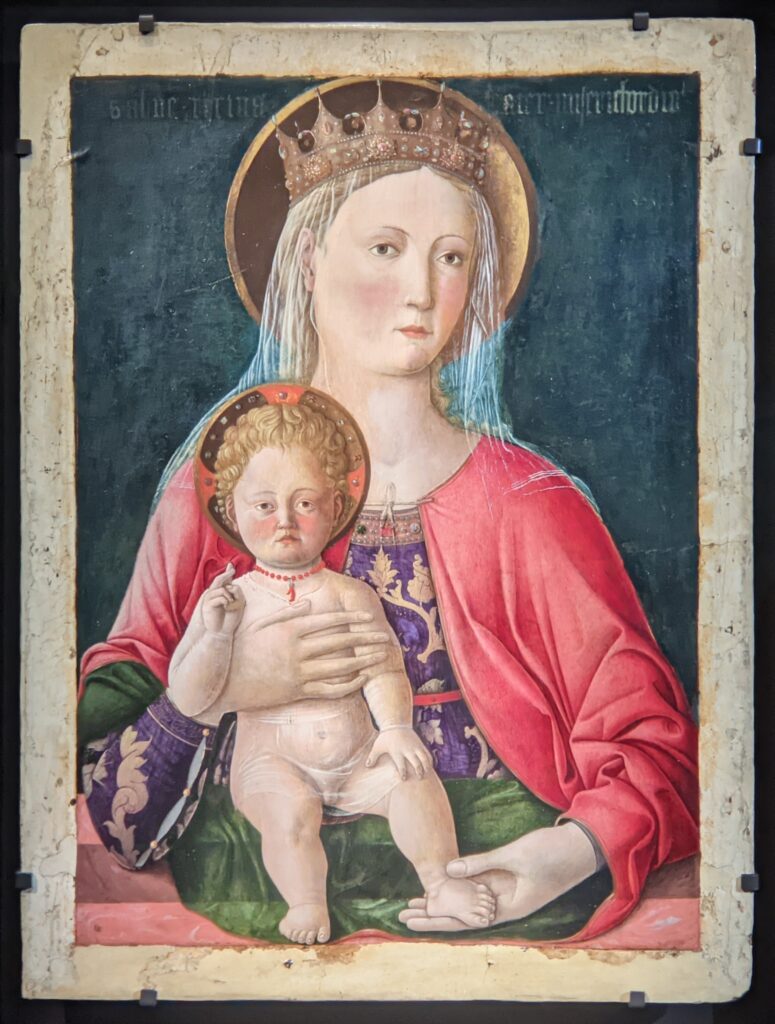
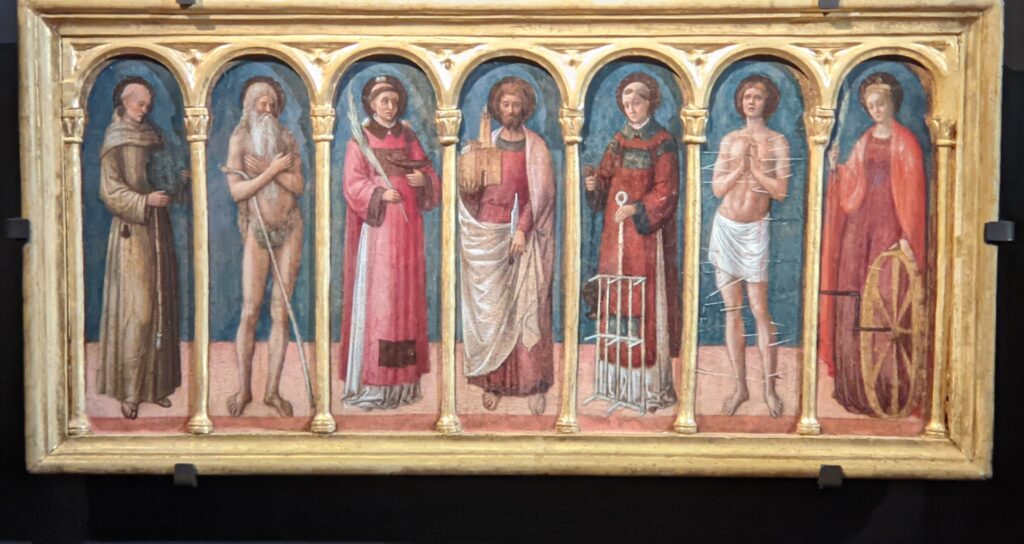





Andrea Mantegna (1431 — 1506)
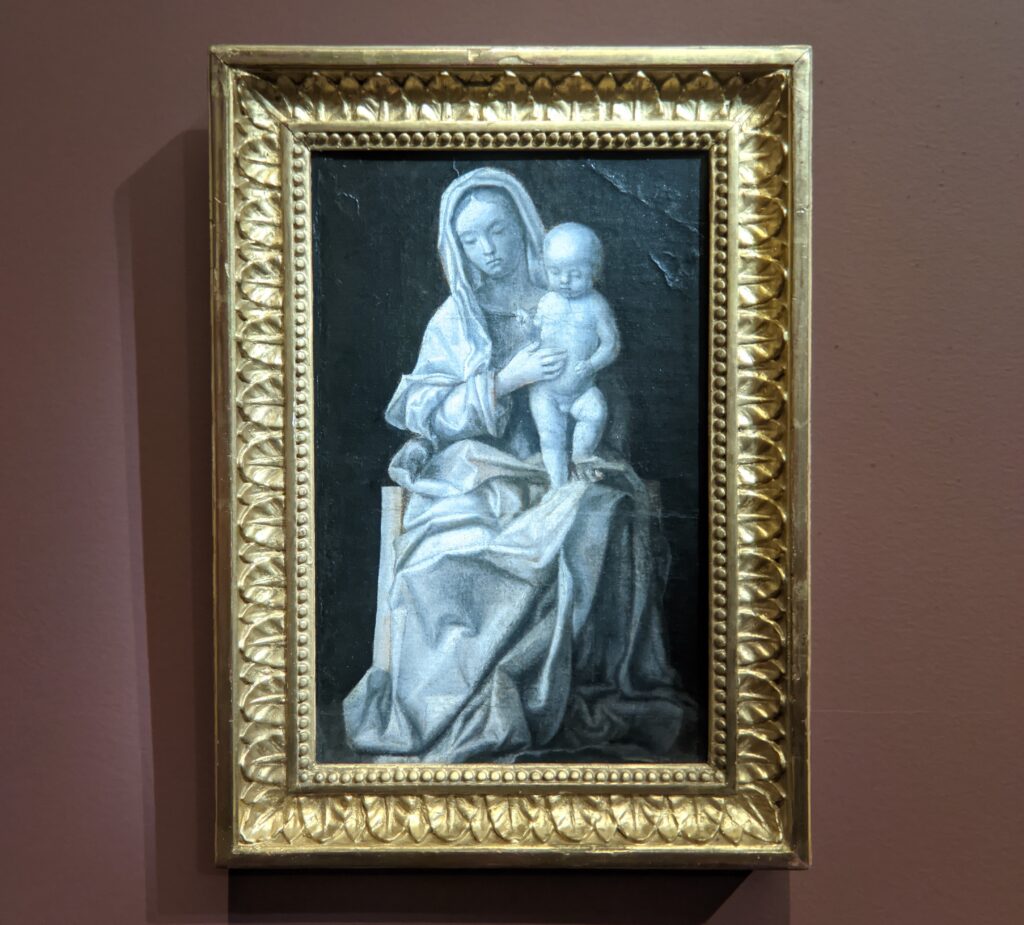
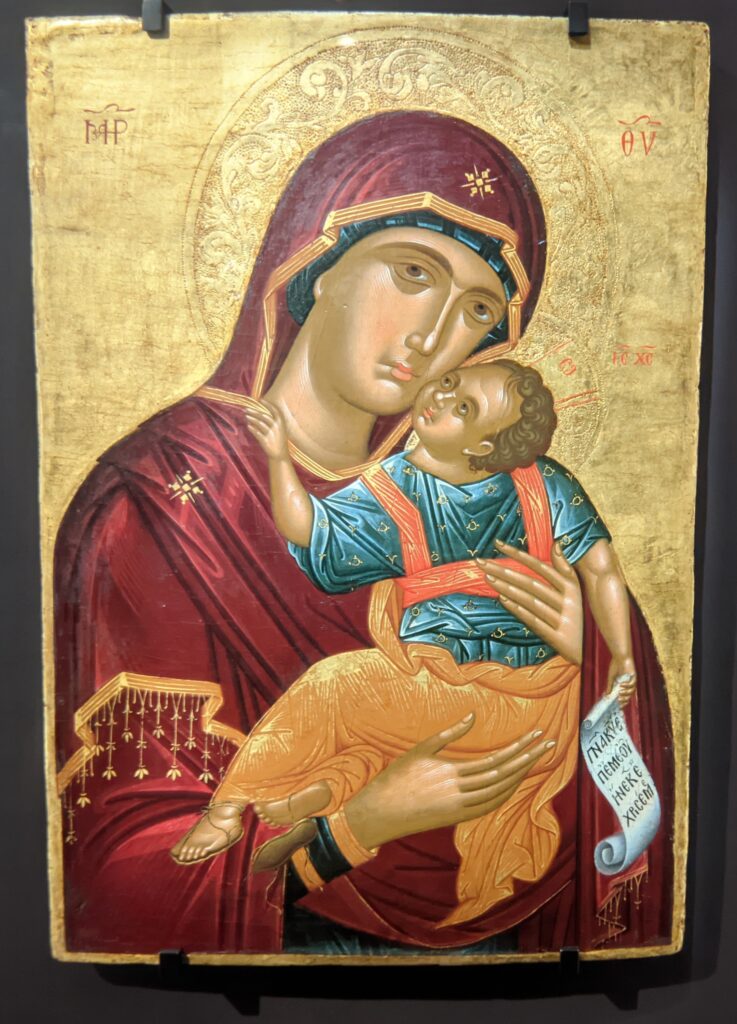
This exhibit traced the individuals and styles of art that influenced the creative genius of Giovanni Bellini, including “Madonna and Child” (below, center) from the Cretan School during the post-Byzantine period when Crete was under Venetian control. Venice, at first a colony of Byzantium, became a privileged trading partner of the Eastern Roman Empire due to its strategic geography. When Constantinople fell to the Ottomans, in 1453, thousands of refugees flooded Venice, bringing with them relics and icons. Even though Giovanni Bellini was most interested in modern painting, his Madonnas often express the gestures familiar to him from Byzantine icons. 1453 proved to be a watershed year for Bellini because his sister married Andrea Mantegna, a successful and talented painter interested in following in the footsteps of Donatello, the great Florentine sculptor.
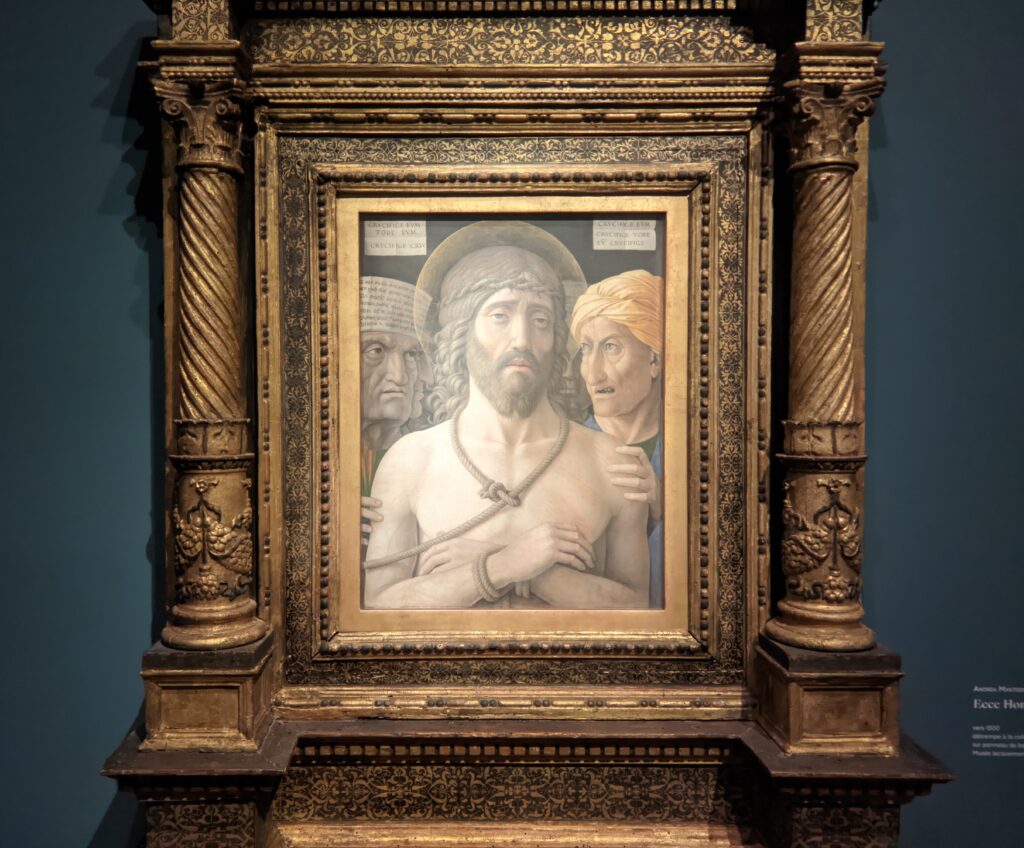




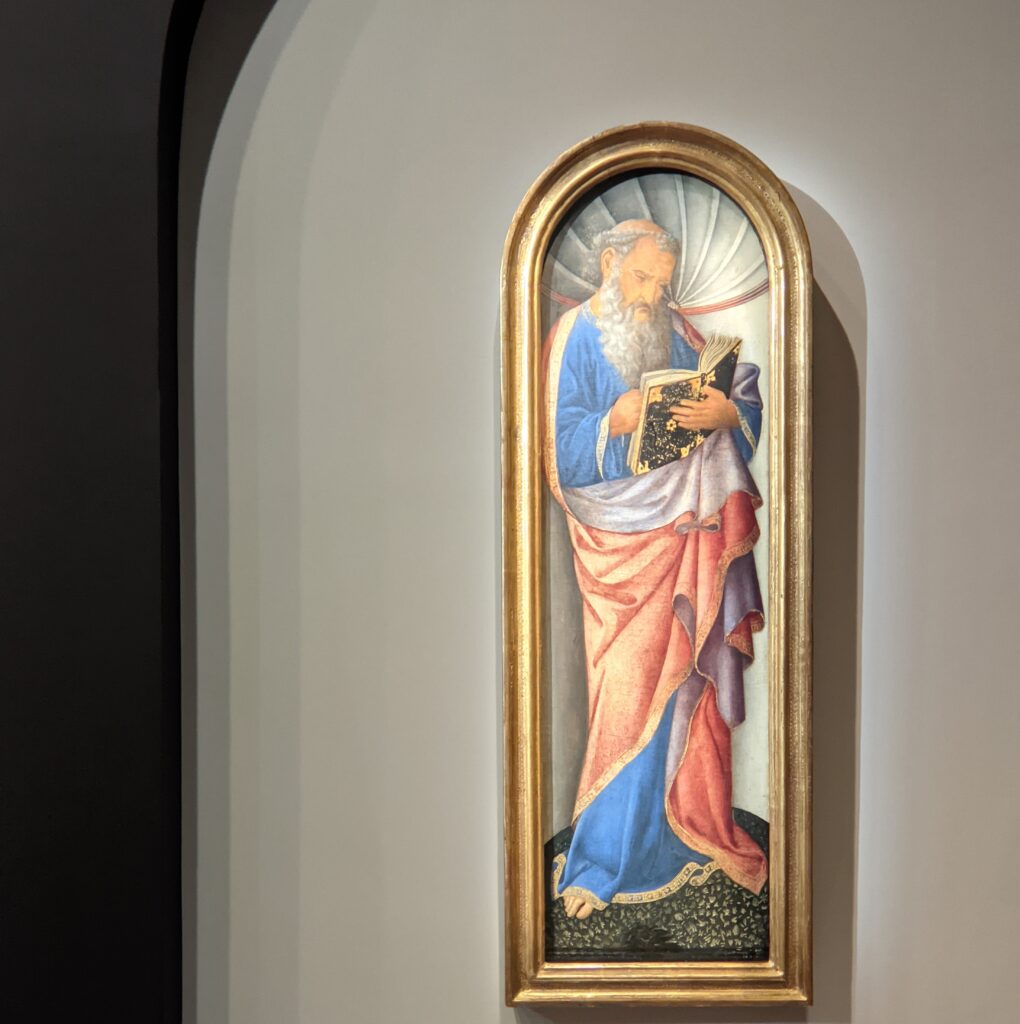
Hans Memling (1430 — 1494)
Giovanni Bellini expanded his creativity by transposing the sculpted “Virgins with Child” of Donatello into two dimensions and replicating the Mantegnesque style of his brother-in-law; however, Bellini was most interested in a new technique produced in Flanders: oil painting.
Painting with oils enabled artists in the 15th century to achieve unprecedented realism in details, and this new art form from the Low Countries became a favorite for Giovanni Bellini. Even though Bellini never traveled to the region we know today as the Netherlands and Belgium, living in Venice — the center of world trade — meant that paintings by Jan van Eyck and Hans Memling made their way to him in La Serenissima. This Giovanni Bellini exhibition at the Jacquemart-André has brought amazing works of art by Memling to Paris, and in visual terms makes it is easy to understand how Bellini incorporated this Flemish technique of painting into his own aesthetic to create transparent glazes in flesh tones and fabrics, making figures and landscapes both realistic and poetic.
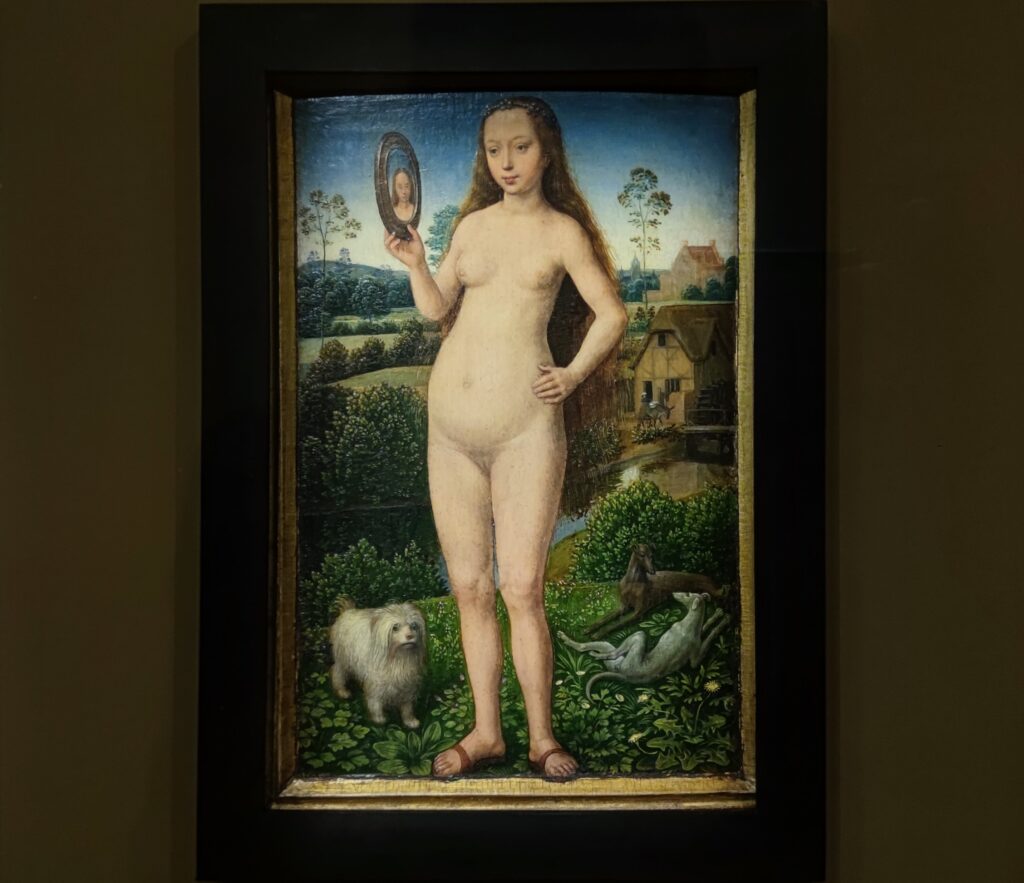






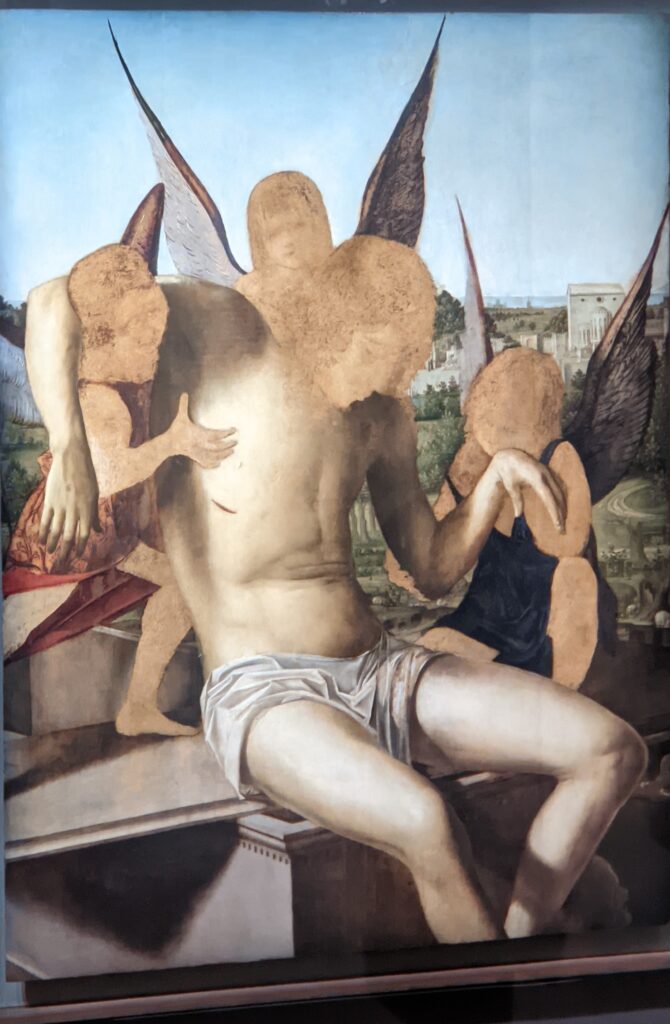
Giovanni Battista Cima (1459 — 1517) & Giorgione (1473 — 1510)
The Jacquemart-André’s exhibition illuminated how Giovanni Bellini departed from the more linear style practiced by his father, then adopted the Paduan model introduced to him by Mantegna, and finally began to assert his own creative personality in 1460 when his brother-in-law departed Venice to become the official court painter in Mantua. Later in life, Bellini was inspired by the mastery of oil painting by Memling and Antonello da Messina (who arrived in Venice in 1475) to explore and develop a unique, more colorful palette.
Giovanni Bellini’s growth over time and ascendance to become the official painter of the Republic of Venice meant that members of the following generation of great artists such as Giovanni Battista Cima fell under the influence of Bellini. Titian became a pupil of Bellini and it is also believed that Giorgione served his apprenticeship in the workshop of Bellini. Cima was one of the first Italian painters to assign prominence to landscape depiction, and to formulate laws of atmosphere and of the distribution of light and shade. Giorgione, together with his younger contemporary Titian (1488 — 1576), founded the Venetian school of Italian Renaissance painting known for its use of mood and color.
With the ablest successors such as Cima, Giorgione and Titian, and the development of a groundbreaking style that contrasted with the more linear disegno-led methodology of Florentine painting, Giovanni Bellini established the pathway that indisputably links his oeuvre to Titian and the golden age of Venetian painting.
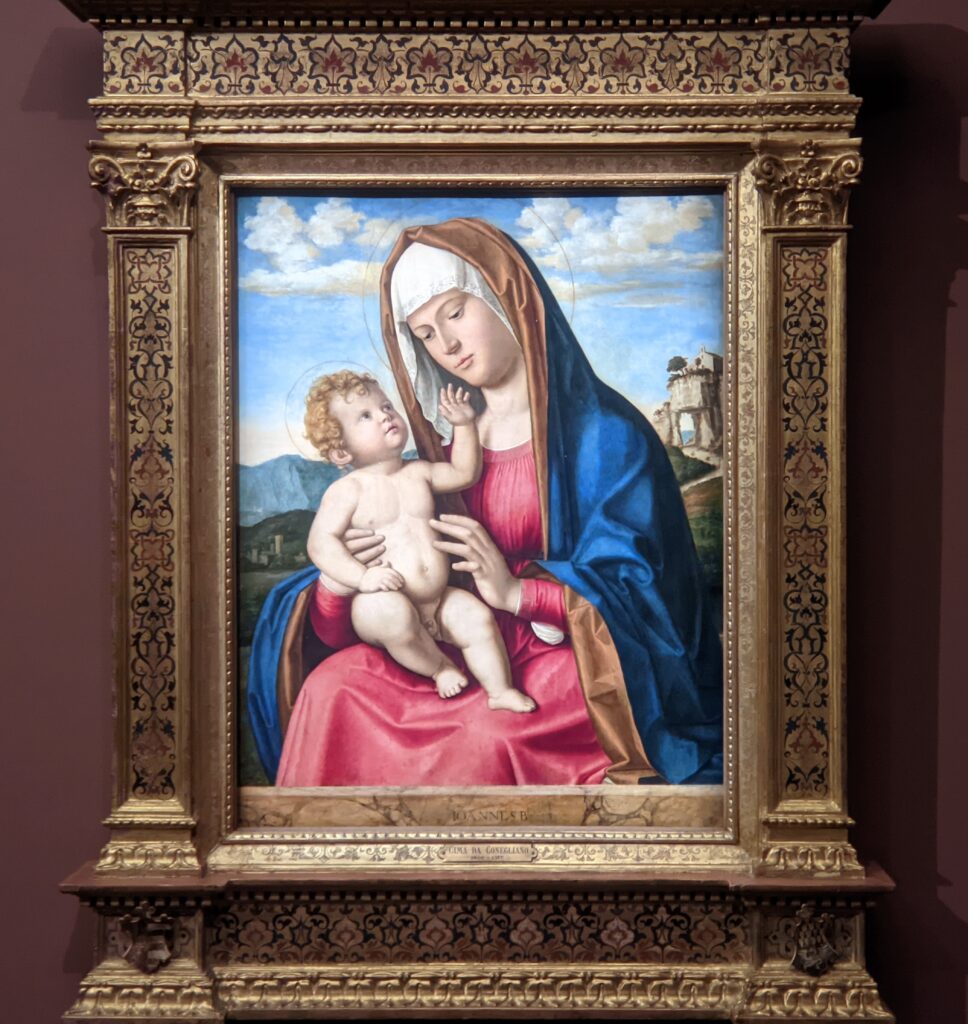
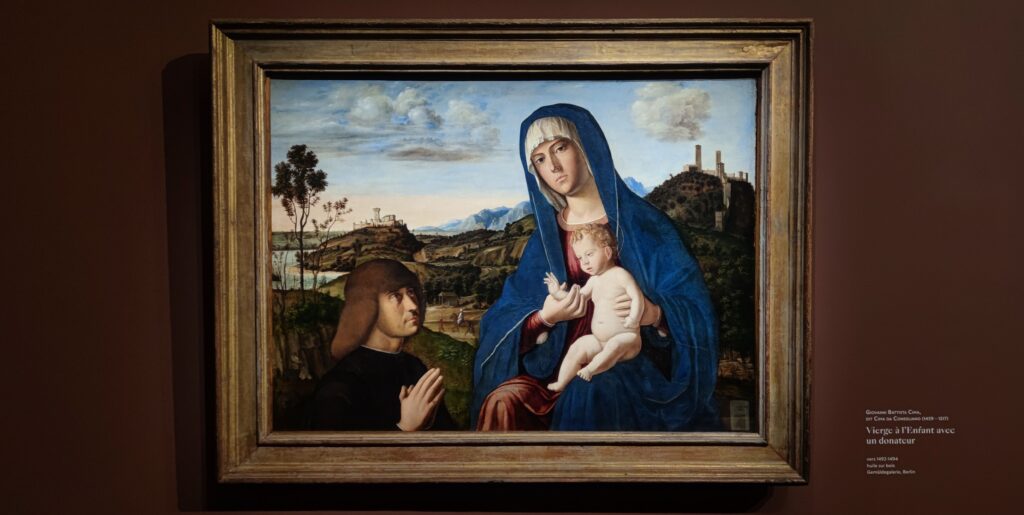
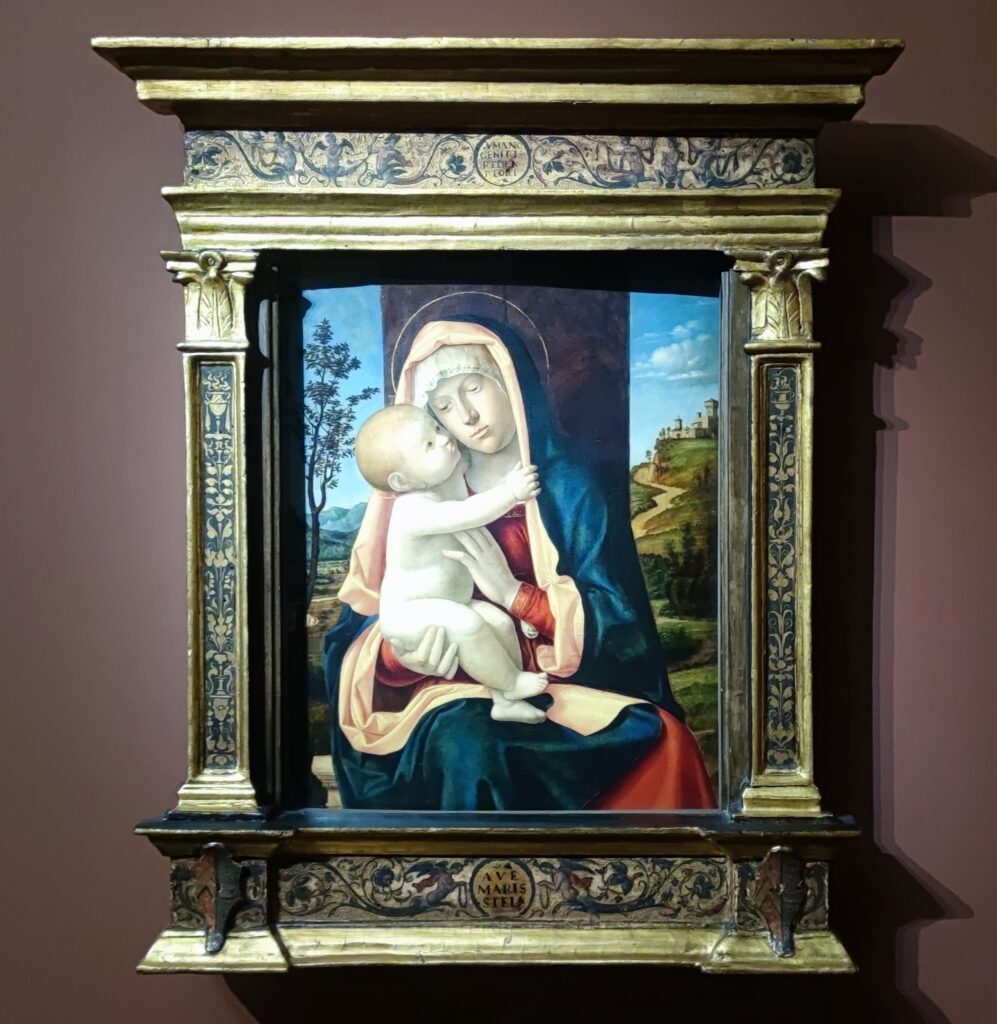





The Jacquemart-André Museum Reopened in September 2024
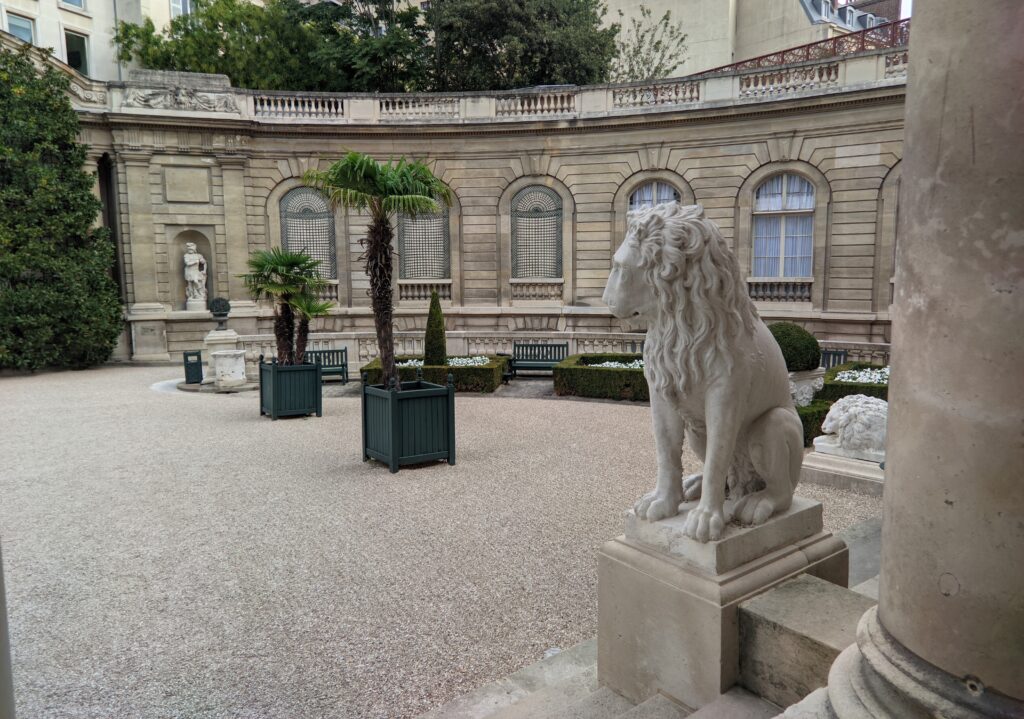


In addition to temporary exhibits, you will enjoy the oval-shaped garden and 19th-century mansion that houses the permanent collection of the museum. Nélie Jacquemart was a talented painter in her own right whose first showing at the Salon came in 1863 when she was only 22. She and her husband were collectors of art before they married; altogether, they acquired 207 sculptures and 97 paintings.
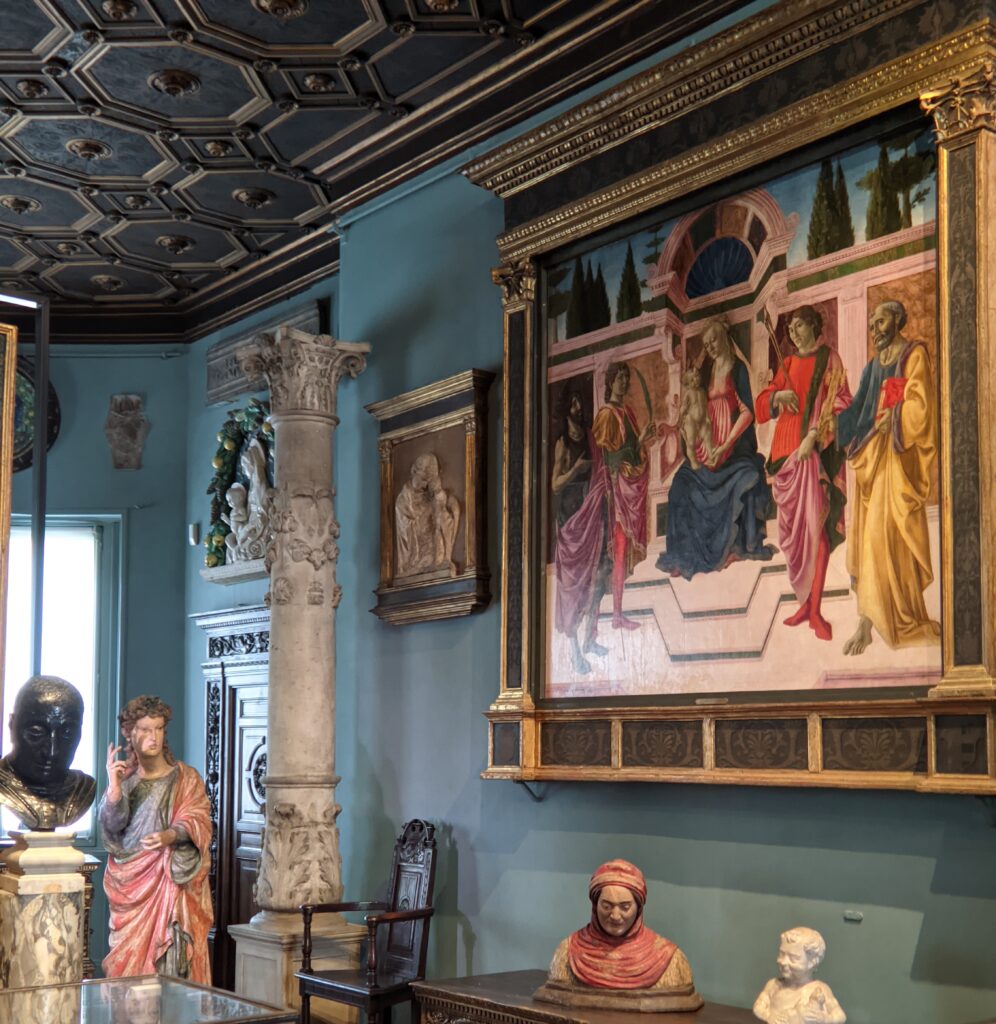


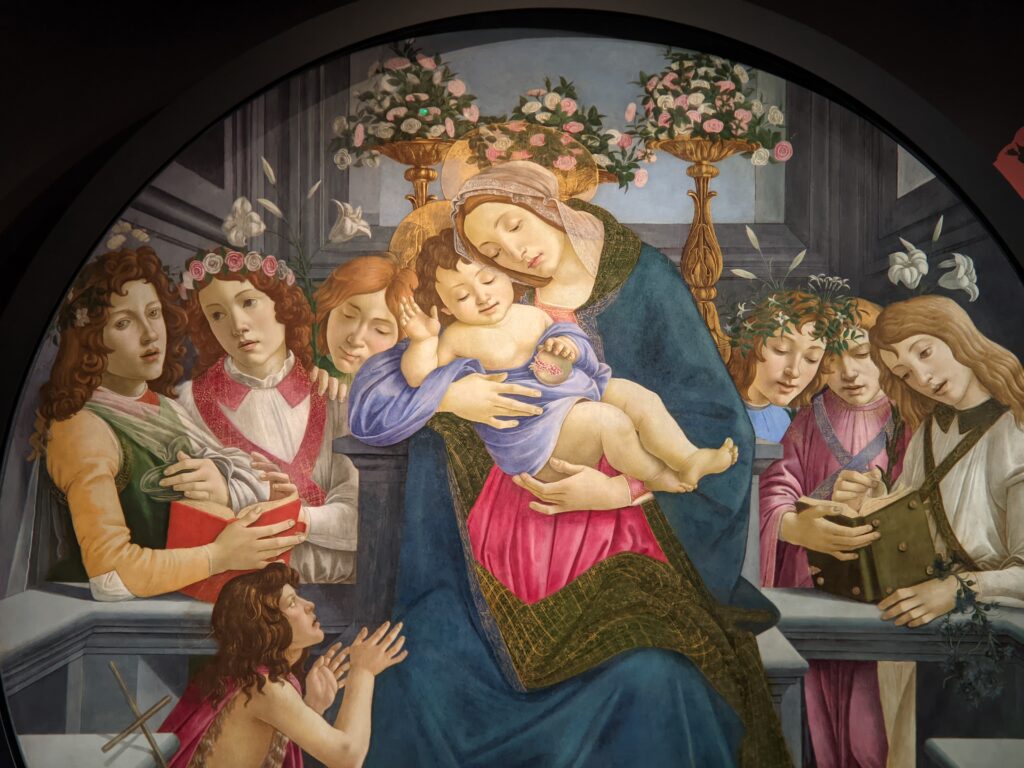
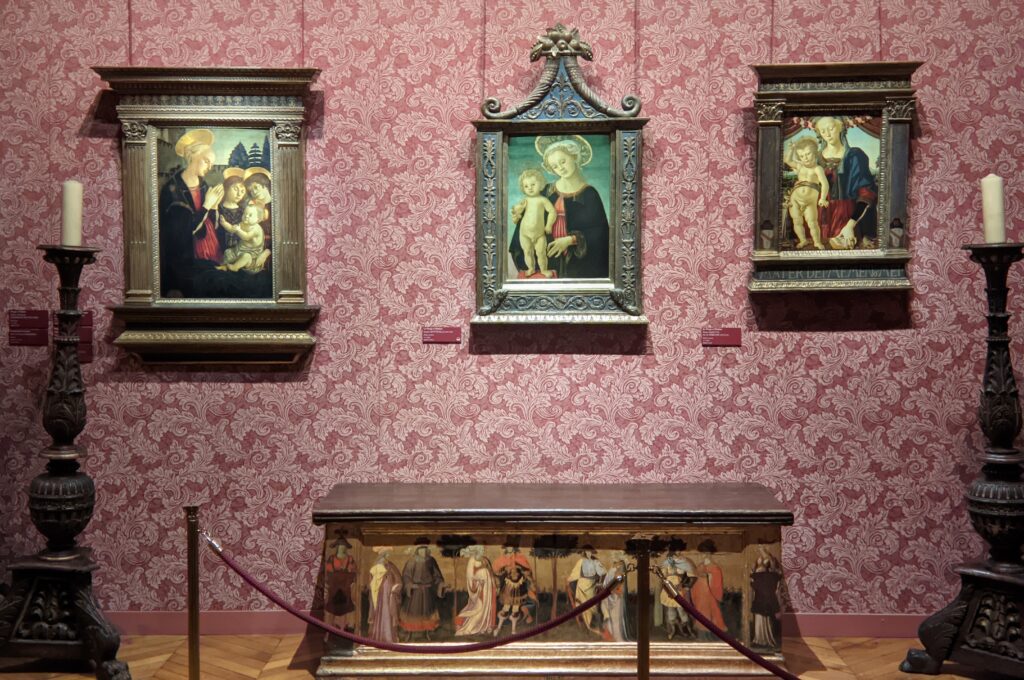
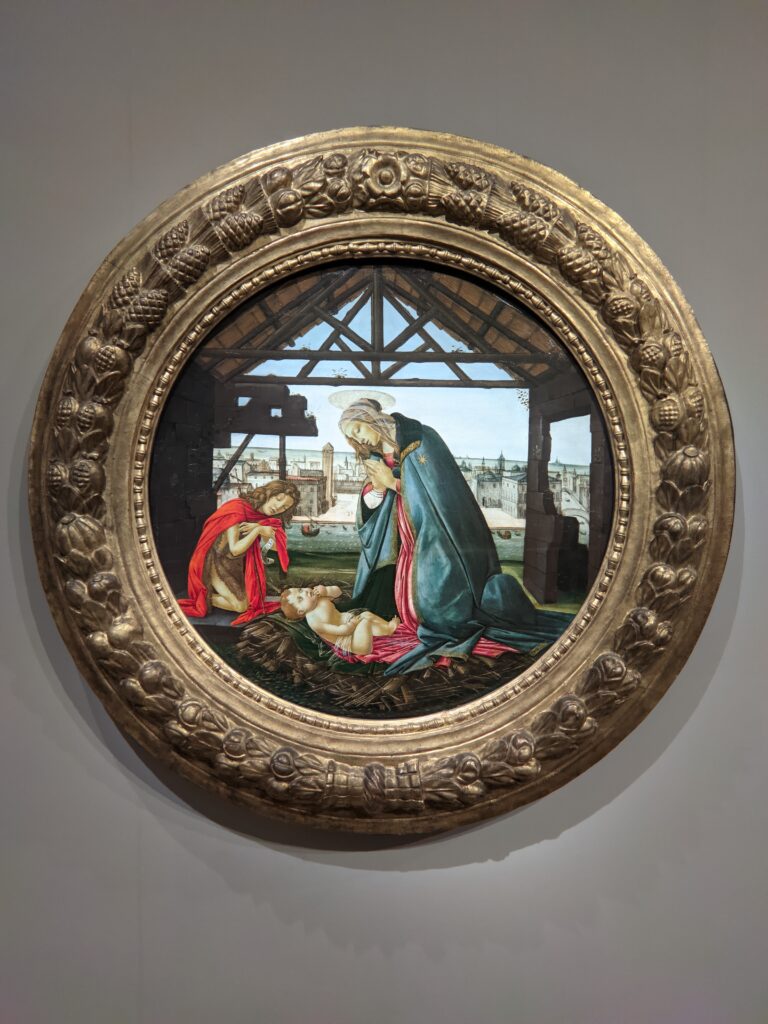
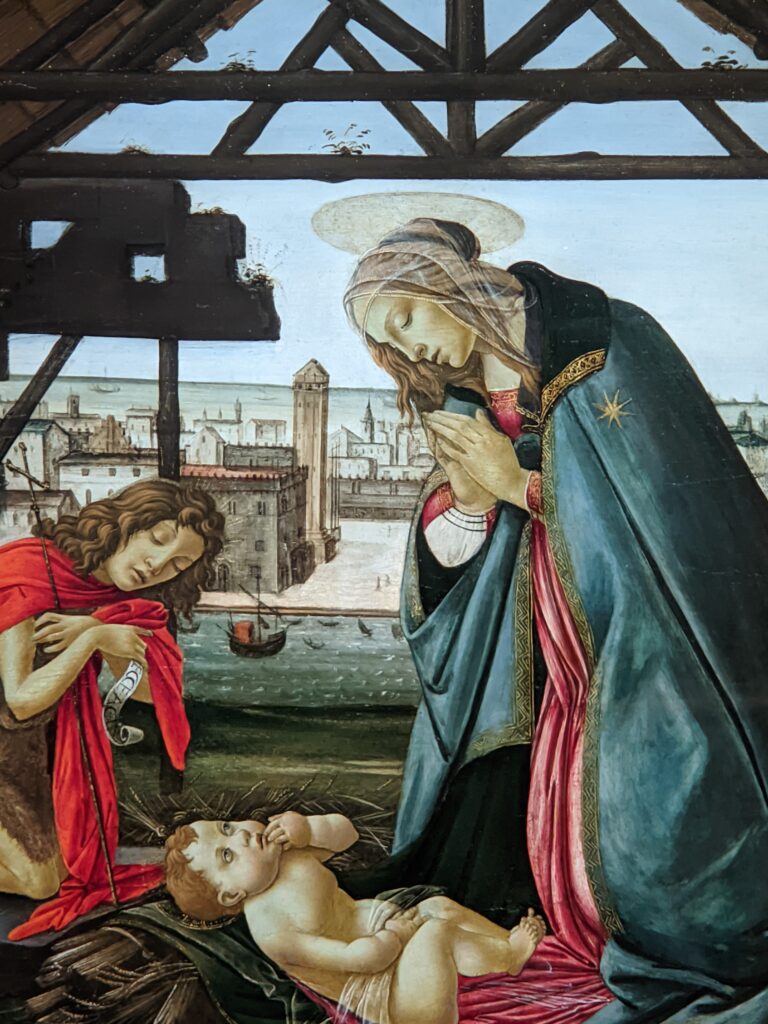
Beginning September 6, 2024, the Jacquemart-André Museum will be open every day from 10:00 in the morning until 18:00 (6:00 p.m.), and on Fridays from 10:00 until 22:00 (10:00 p.m.) during exhibition periods. When Nélie Jacquemart acquired the painting of the Madonna (below center) in Florence, it was covered with repaints and thick layers of varnish; she was told it was painted by Andrea del Verrocchio. In-depth study revealed that it was painted by Sandro Botticelli (1445 — 1510) in 1470.
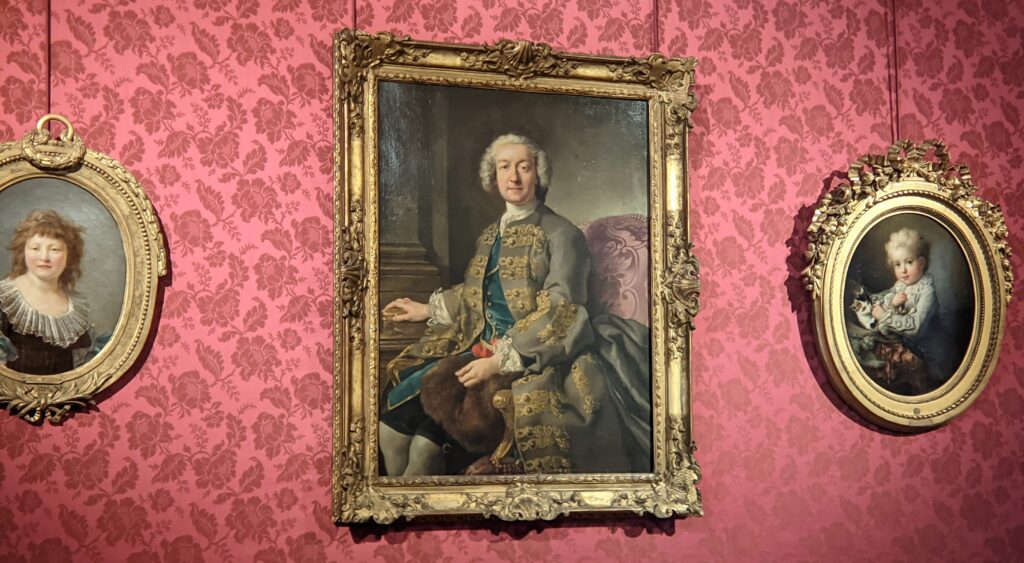








Exhibits Presented at the Jacquemart-André between 2021 & 2023
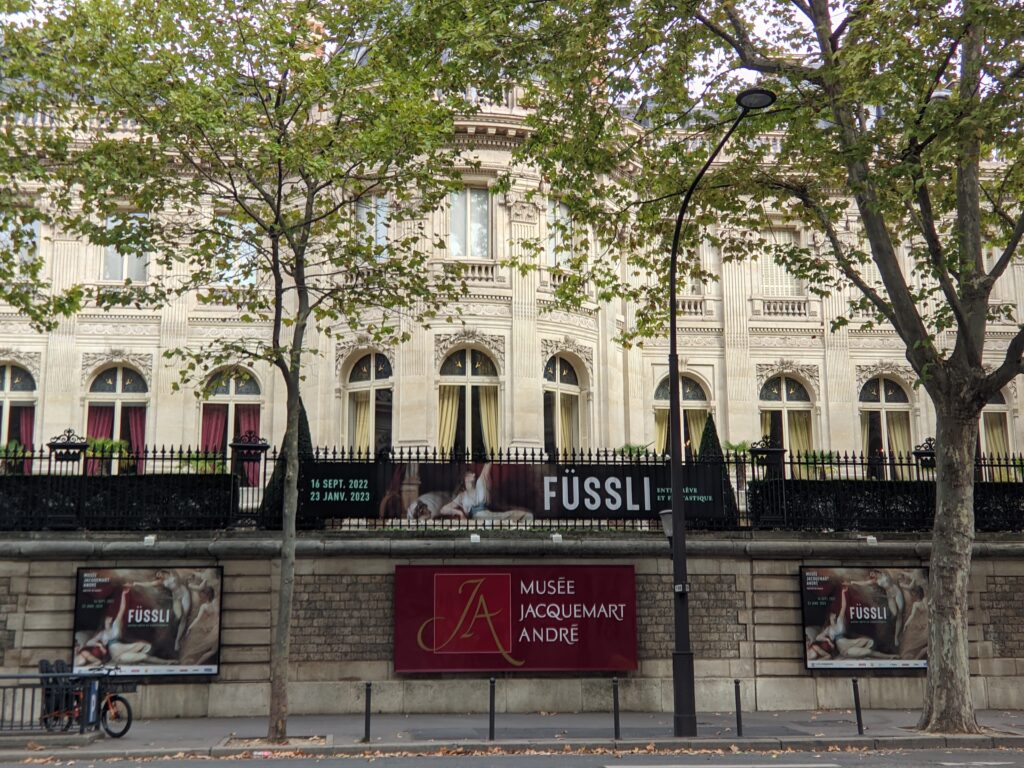
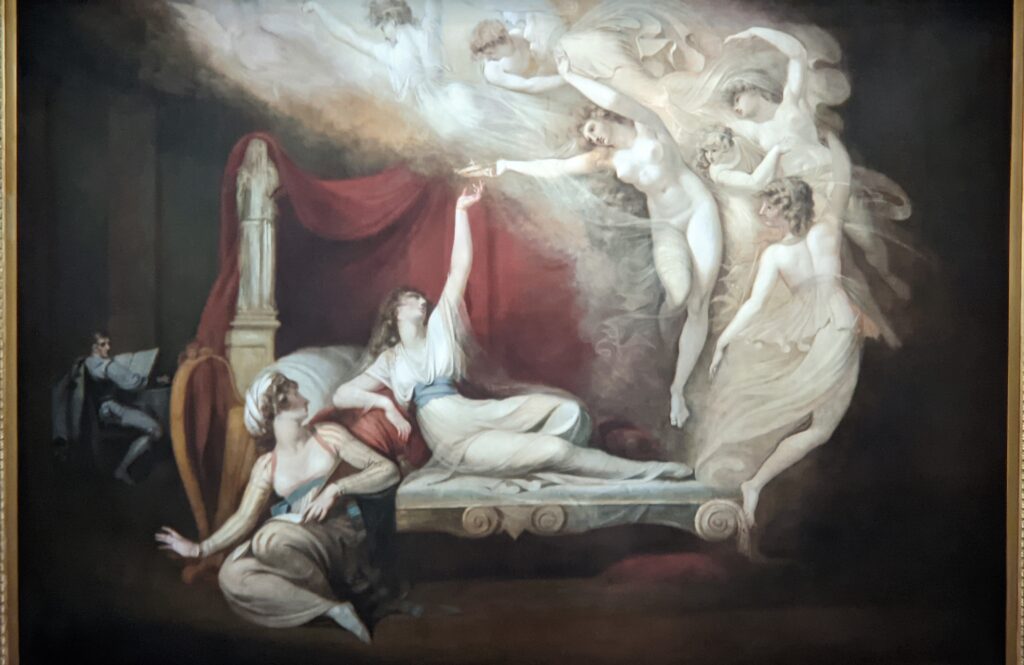


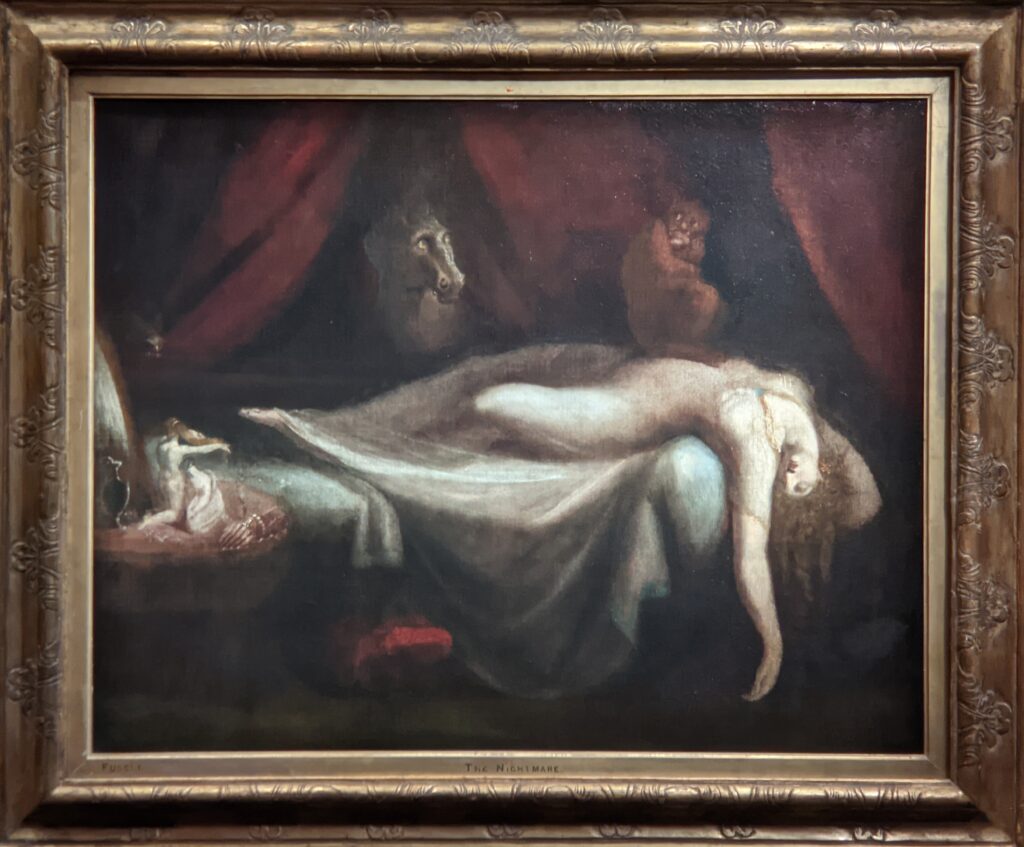
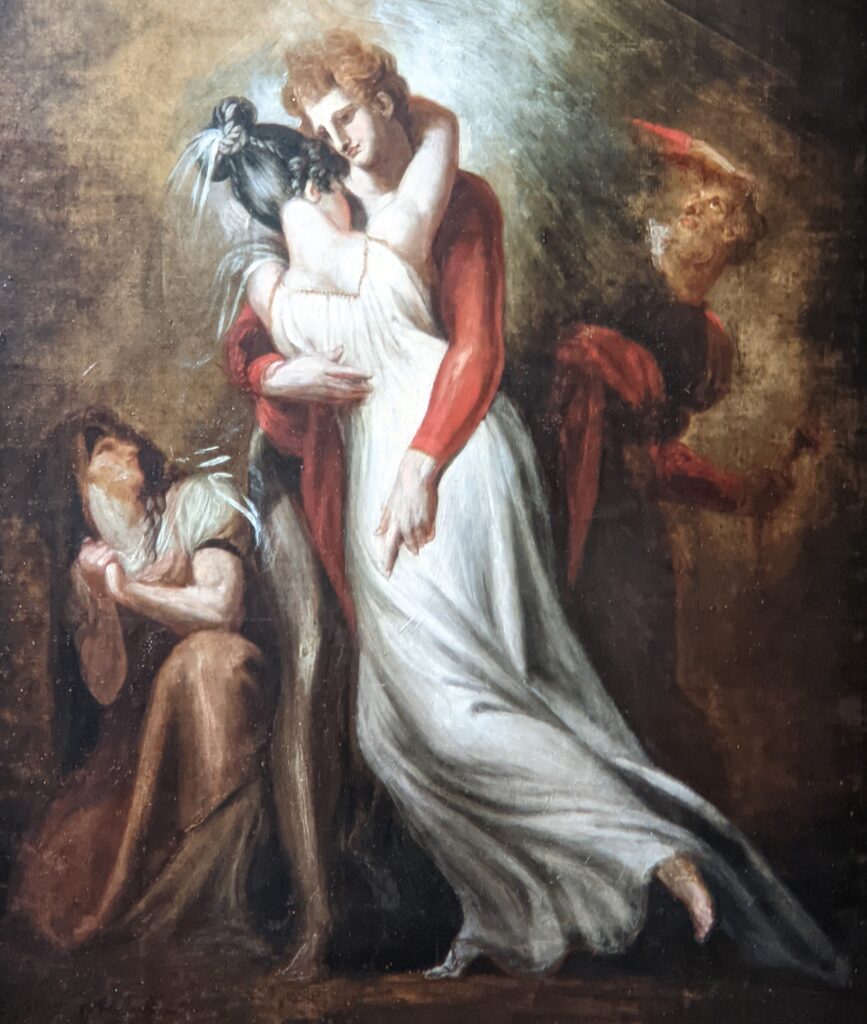
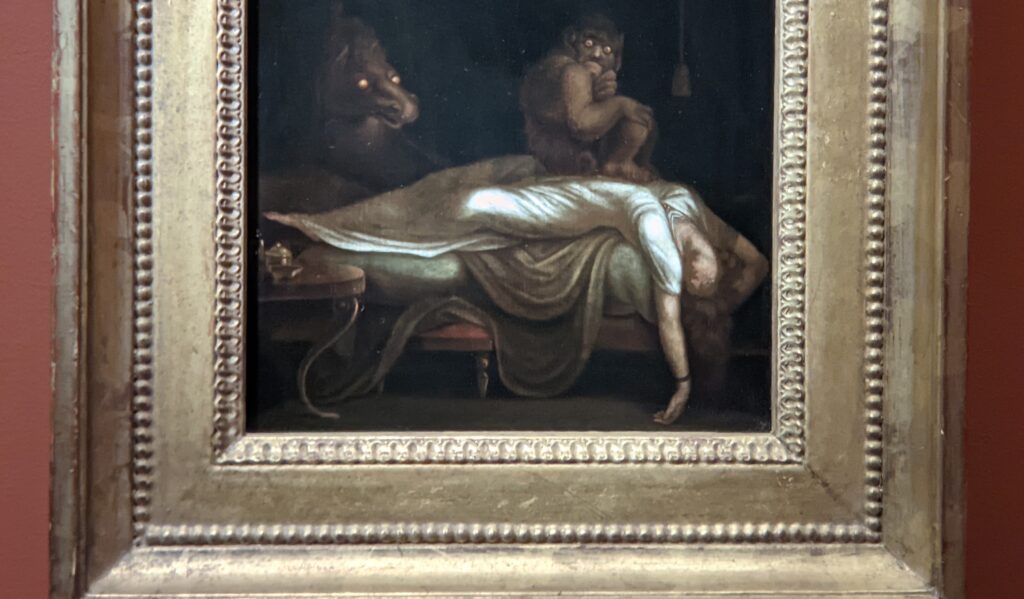
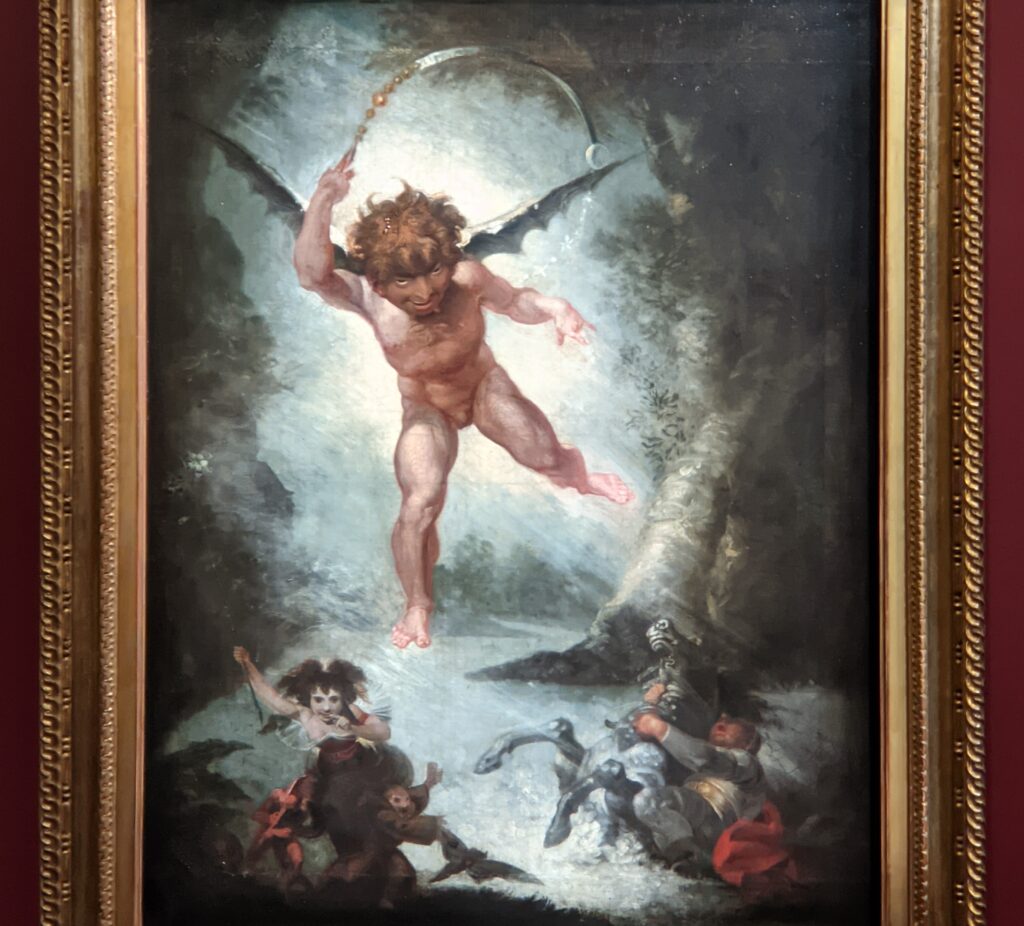
Johann Heinrich Füssli at the Jacquemart-André
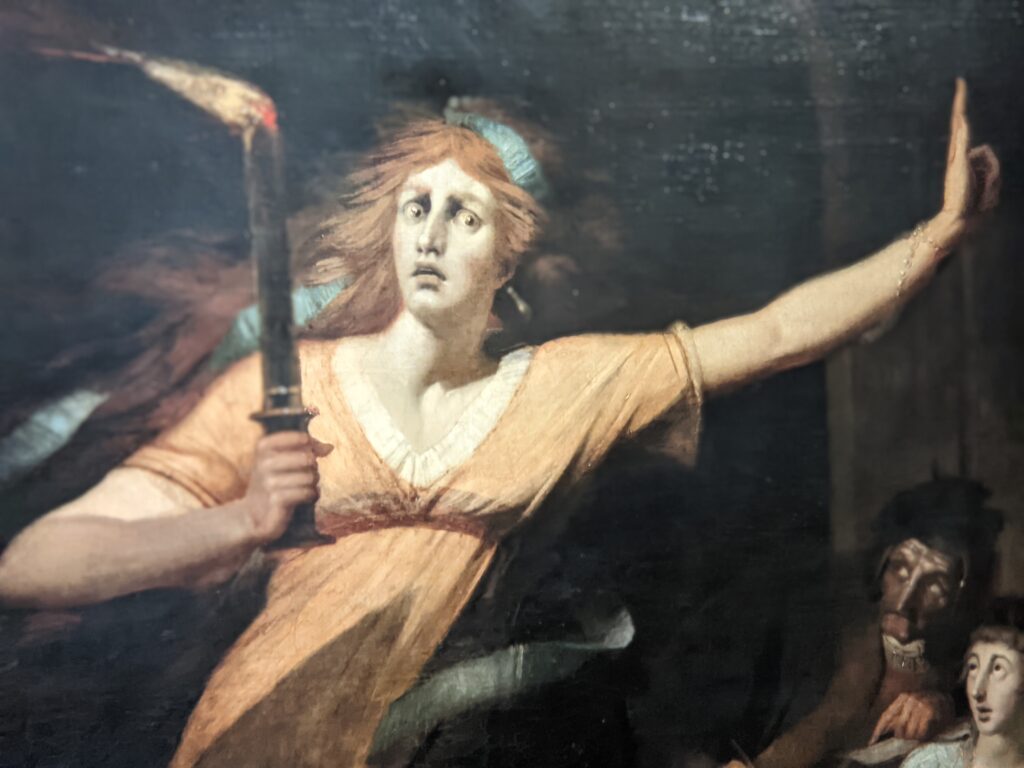

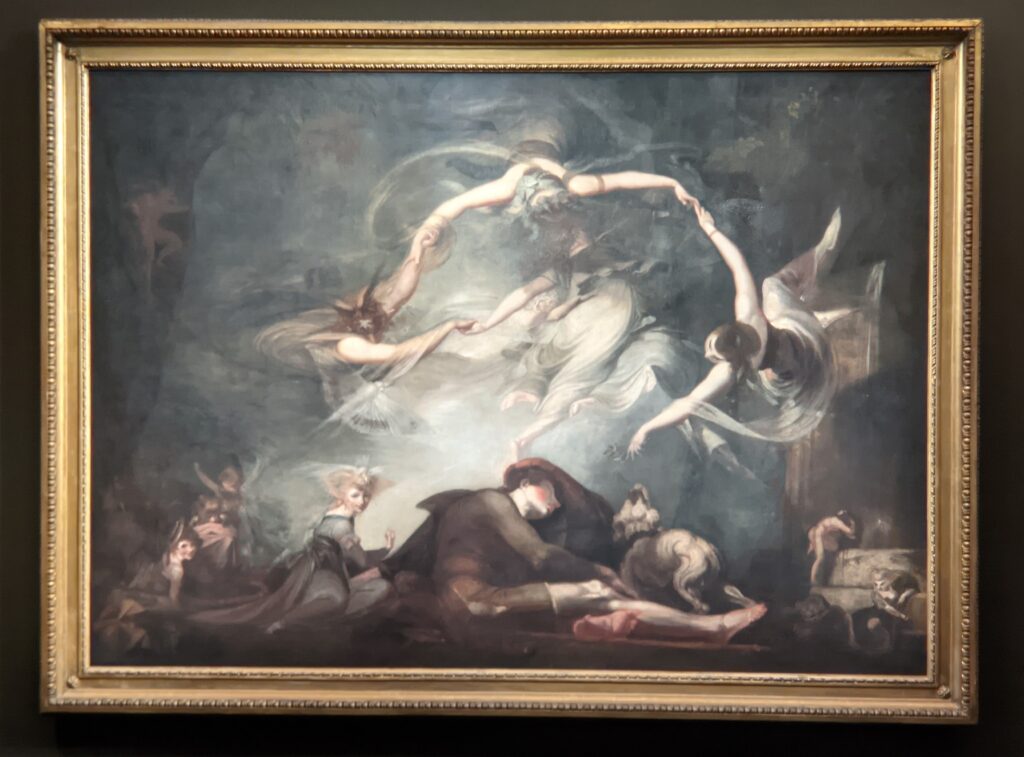
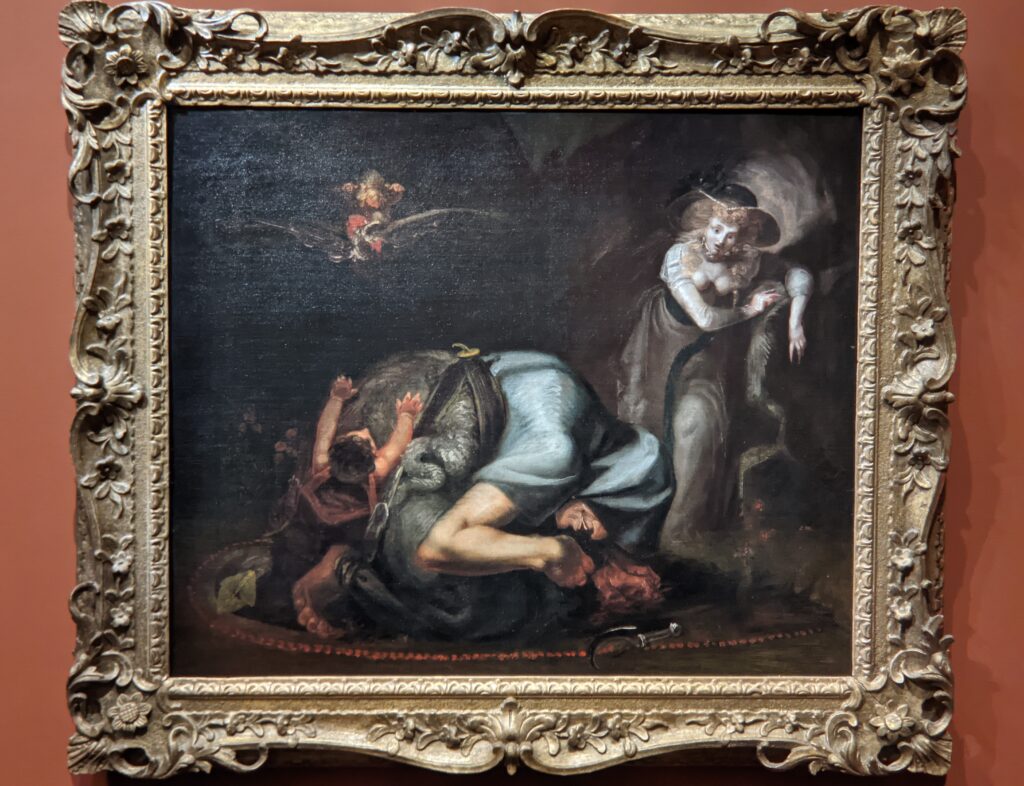
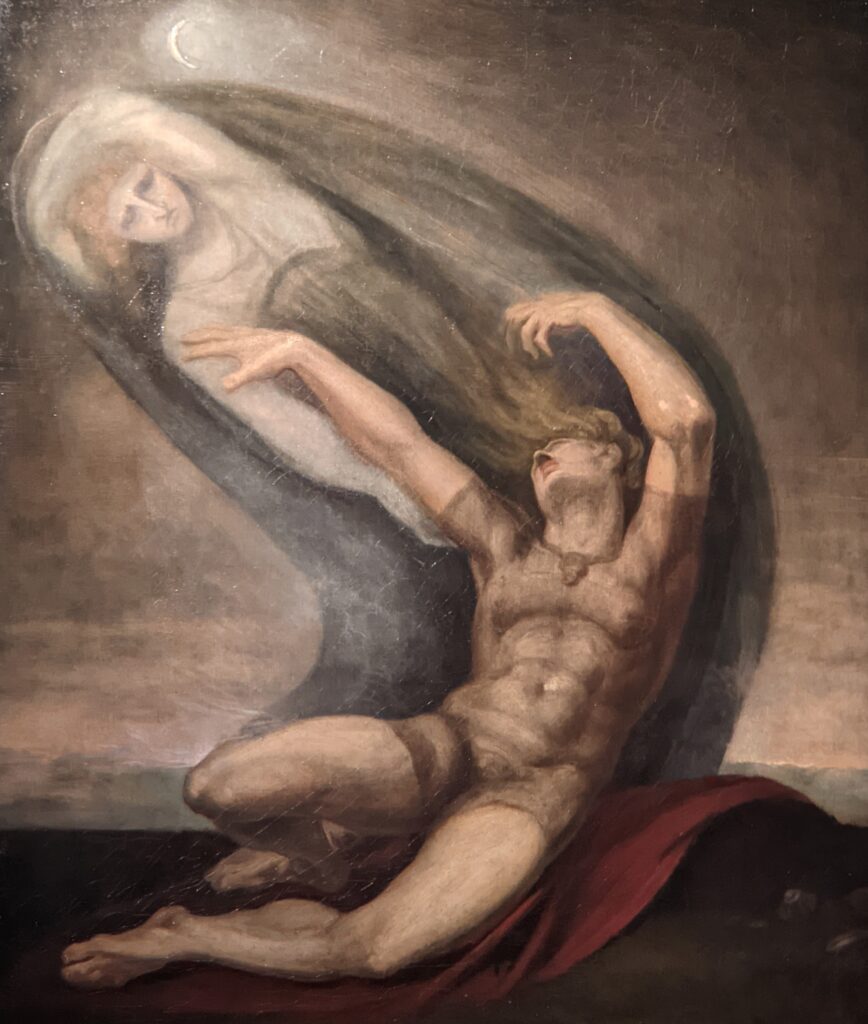
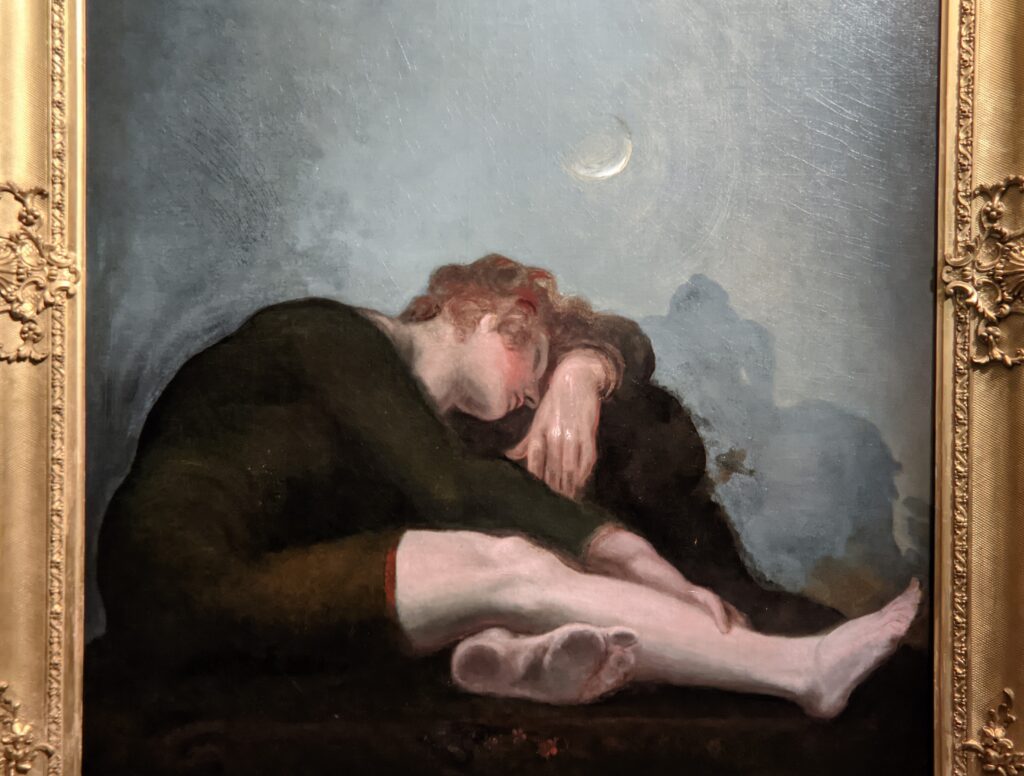
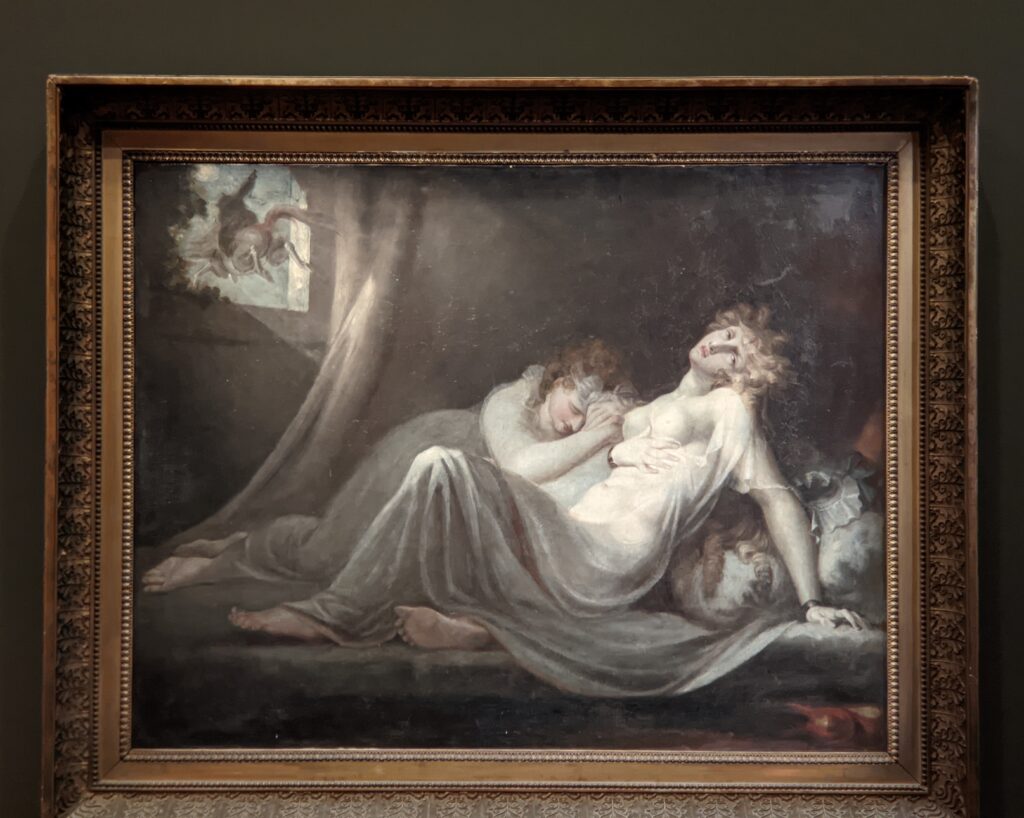
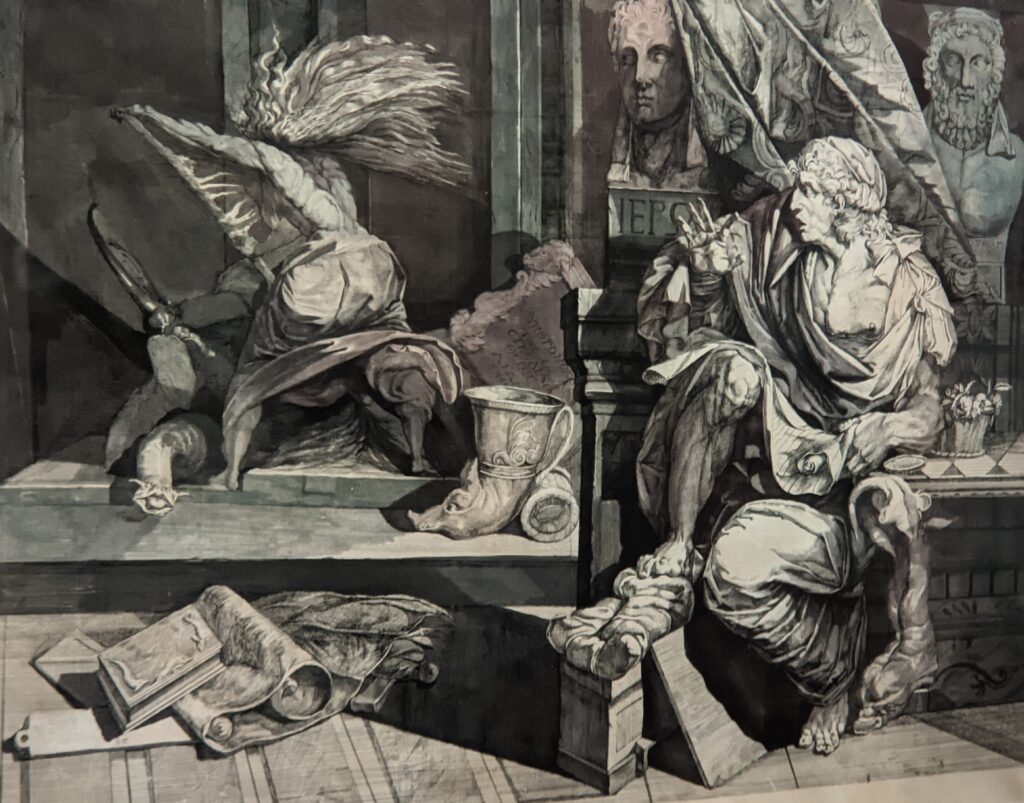
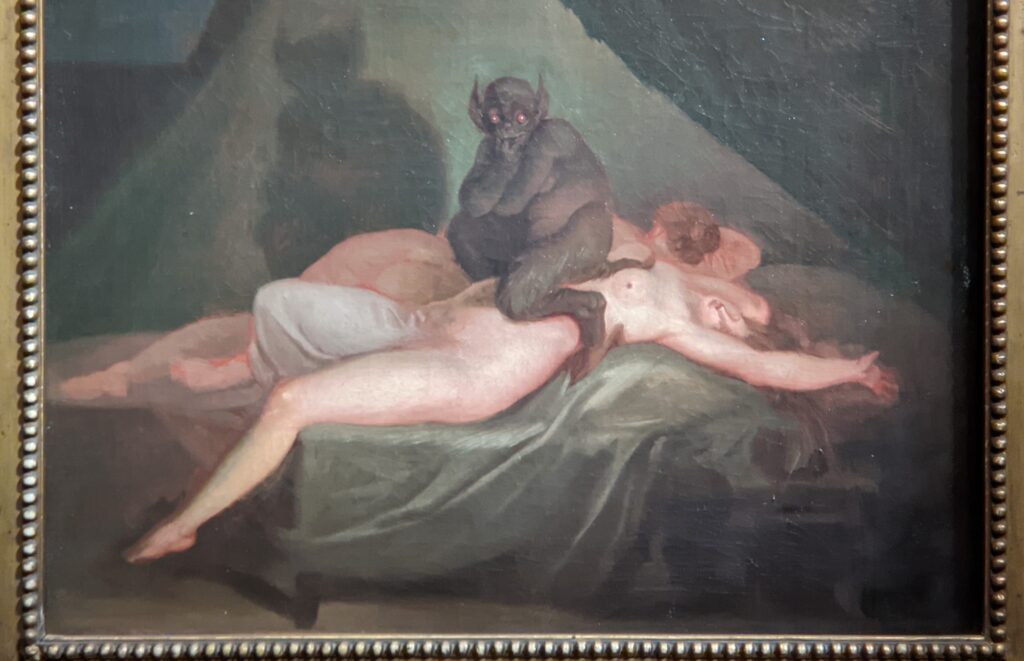
Johann Heinrich Füssli (1741 — 1825) was born in Switzerland and died in London, where he was known as Henry Fuseli. “Füssli, the Realm of Dreams and the Fantastic” was presented at the Jacquemart-André from September 16, 2022 through January 23, 2023.
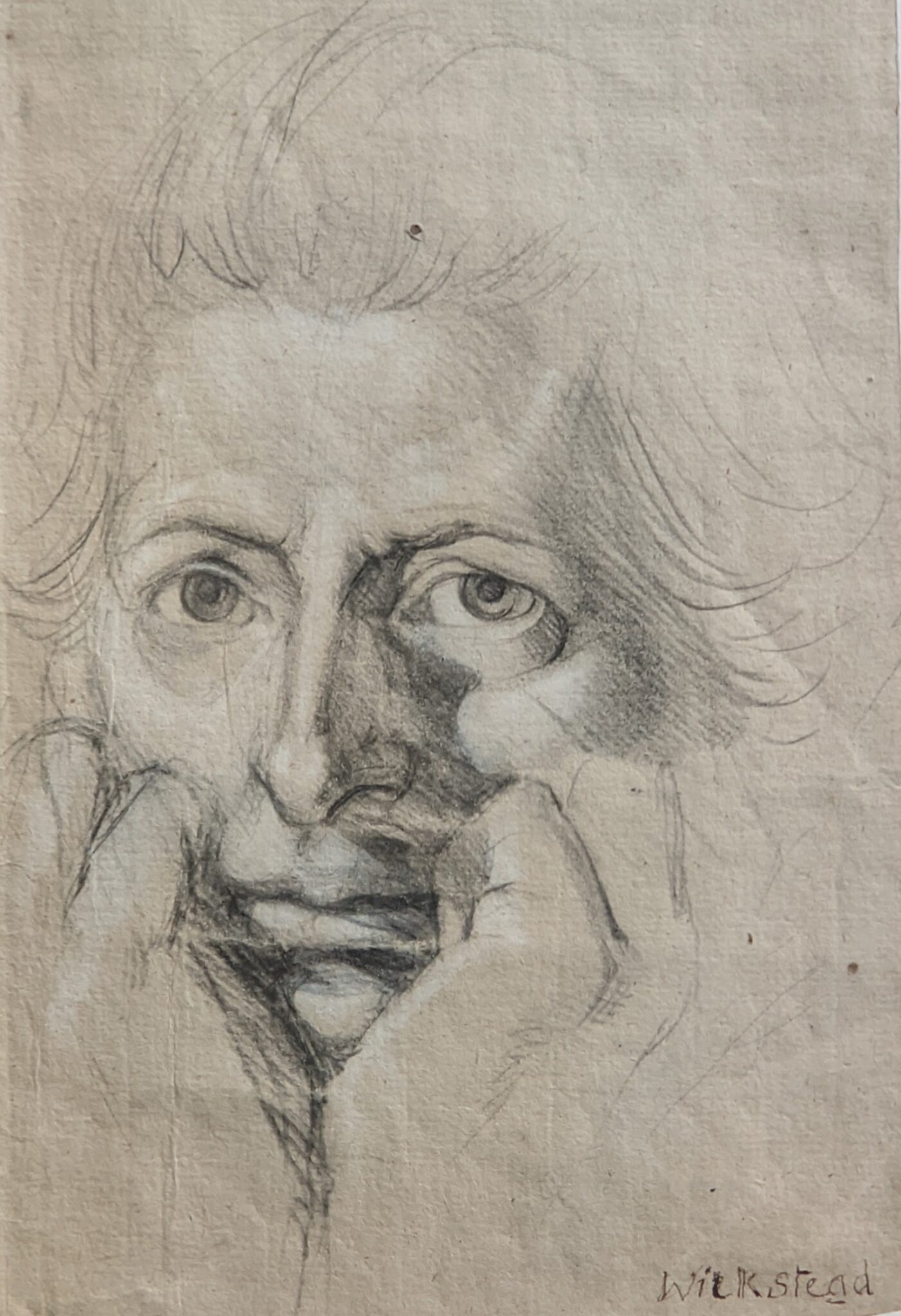
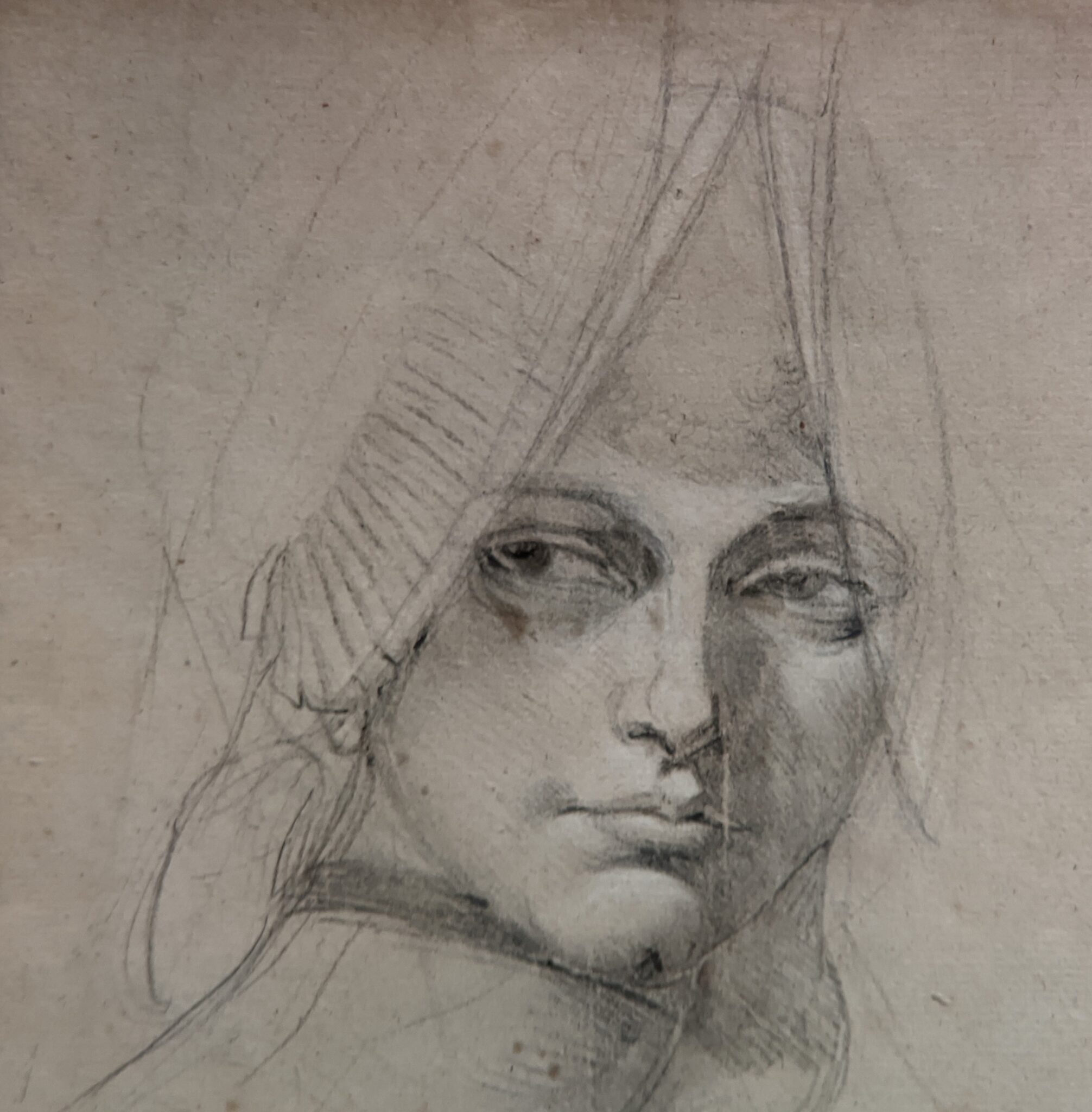
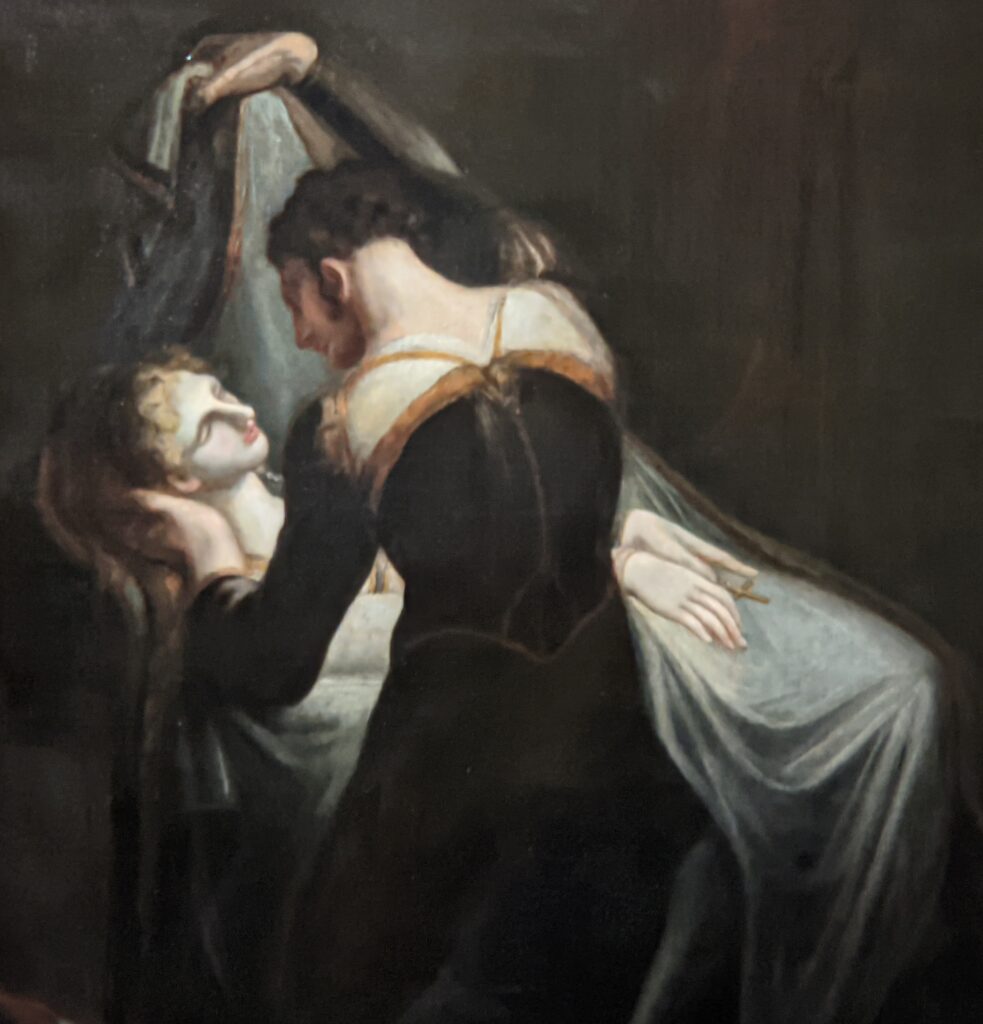
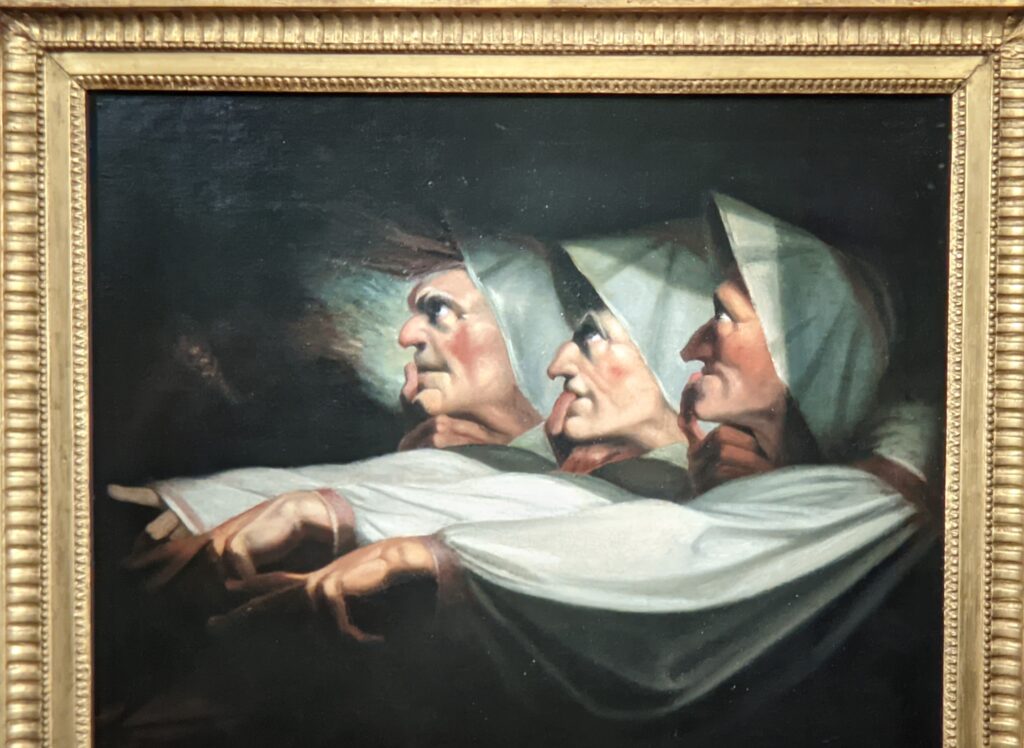
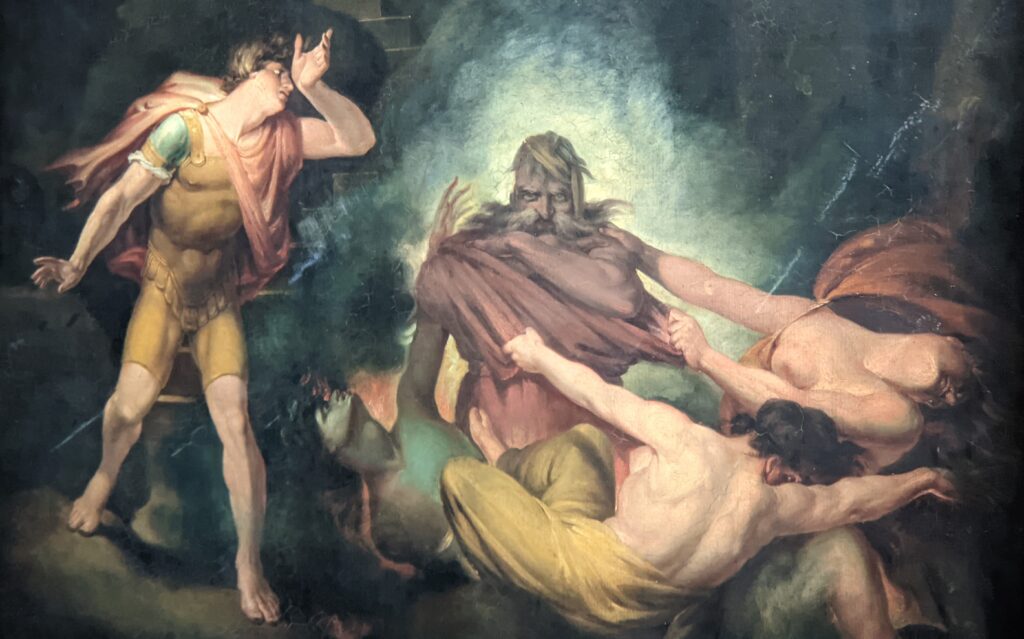
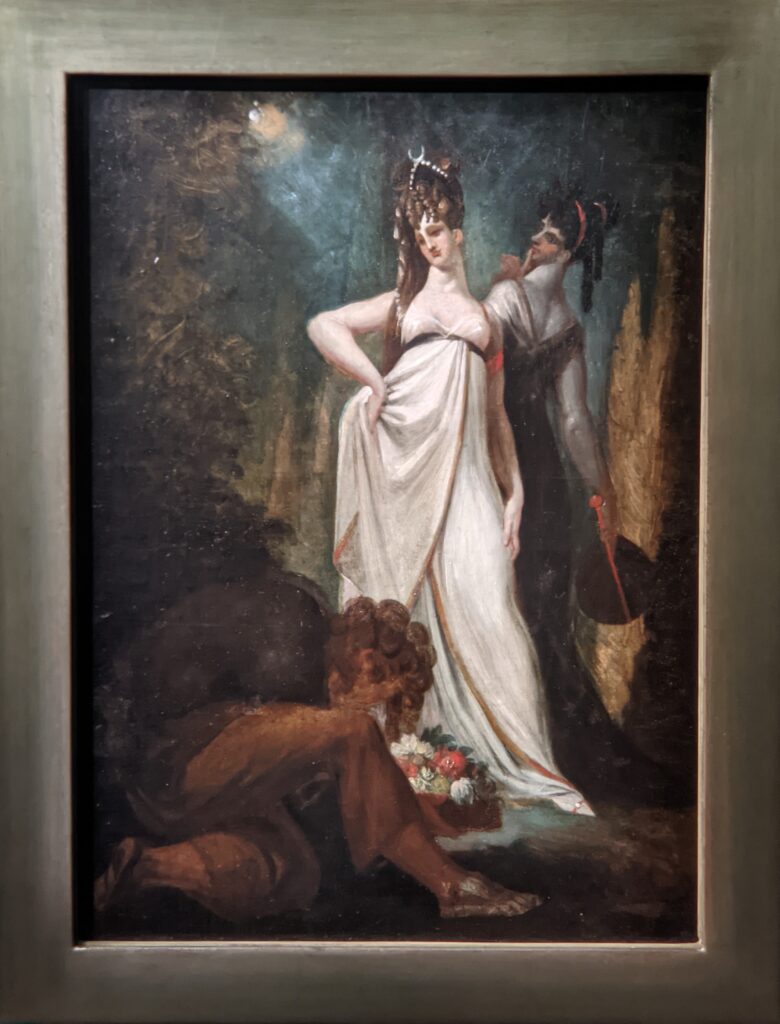
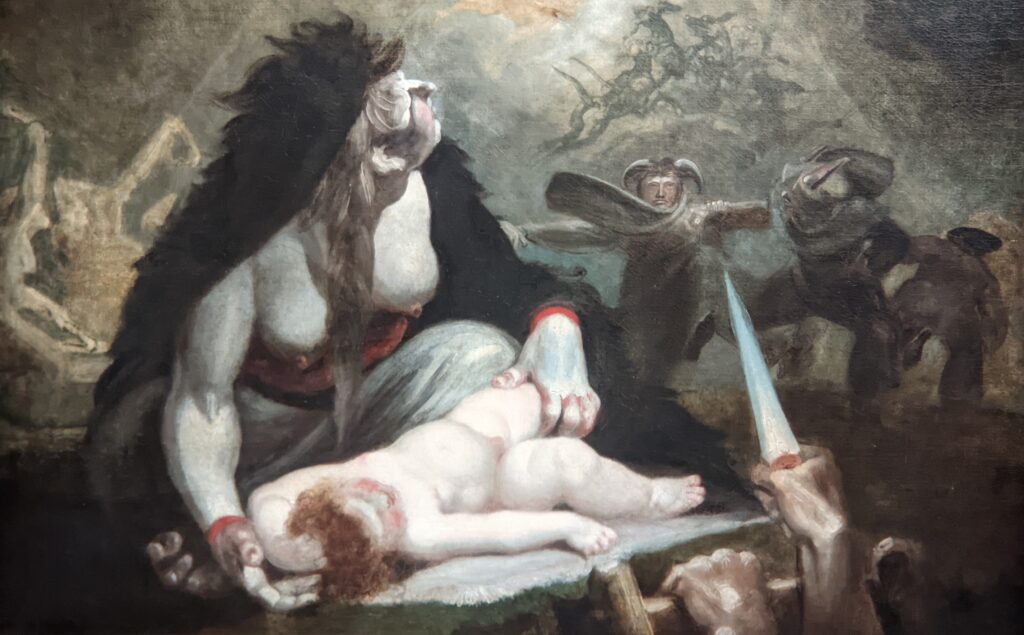
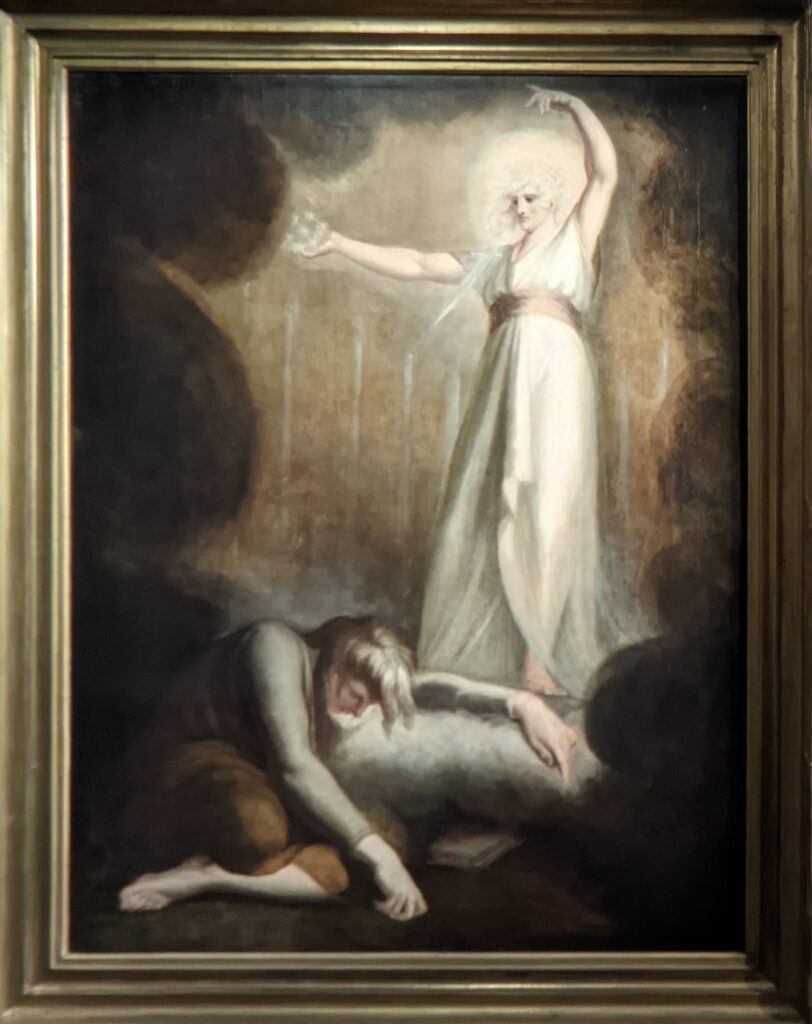
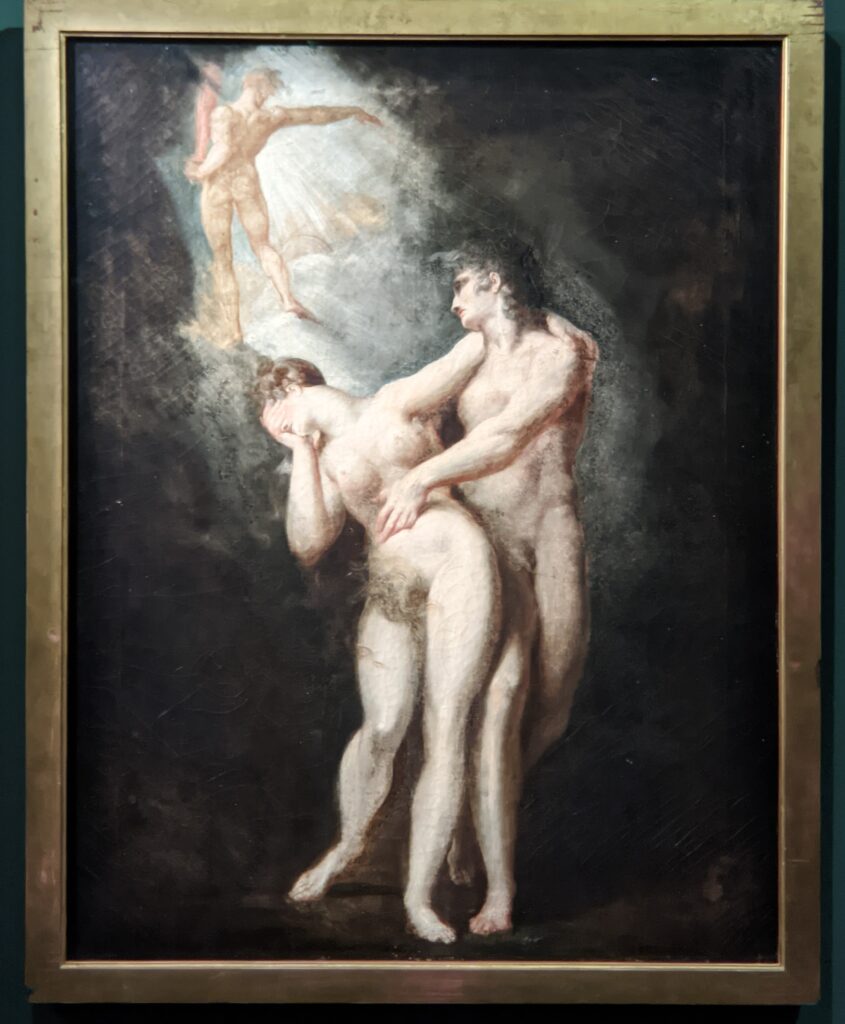
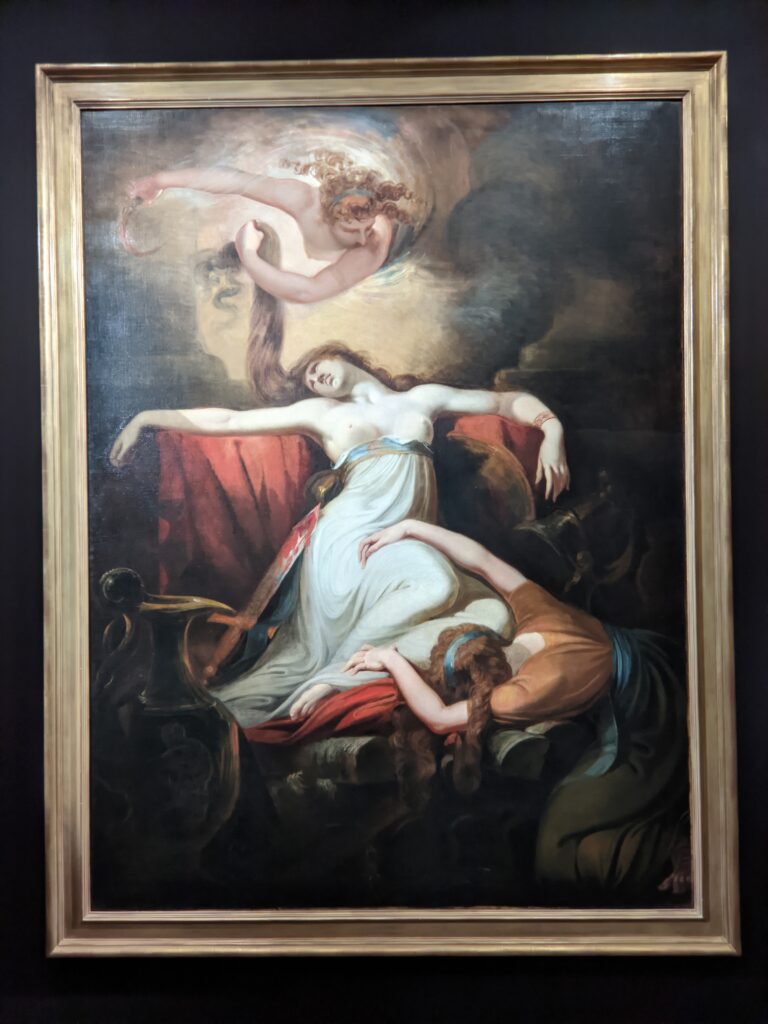














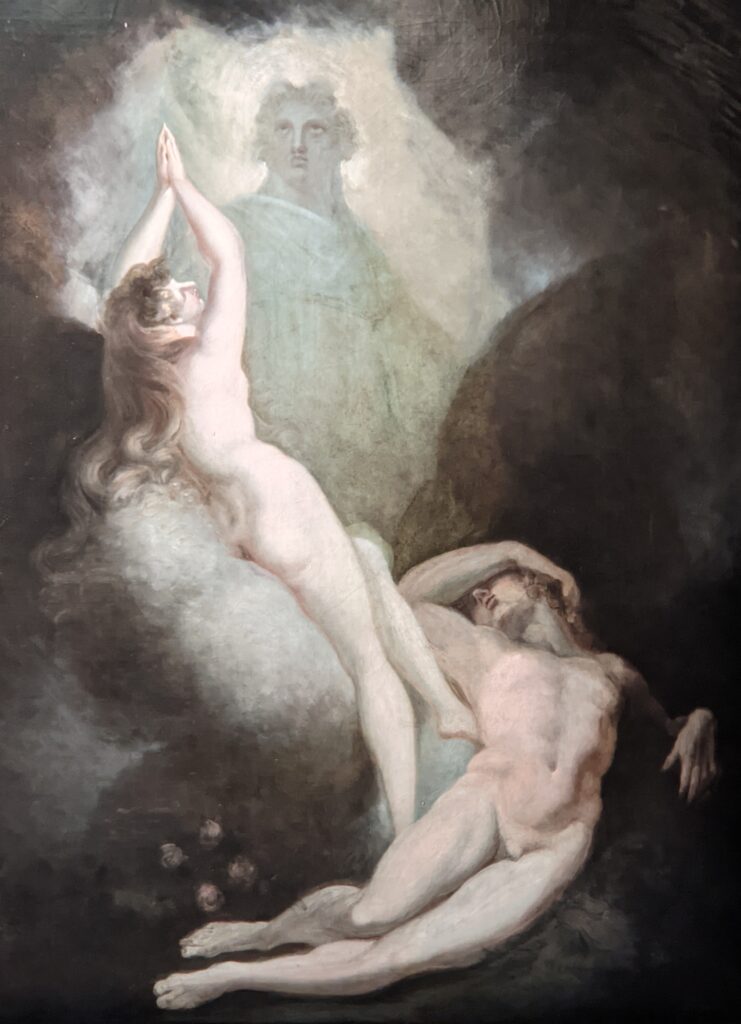








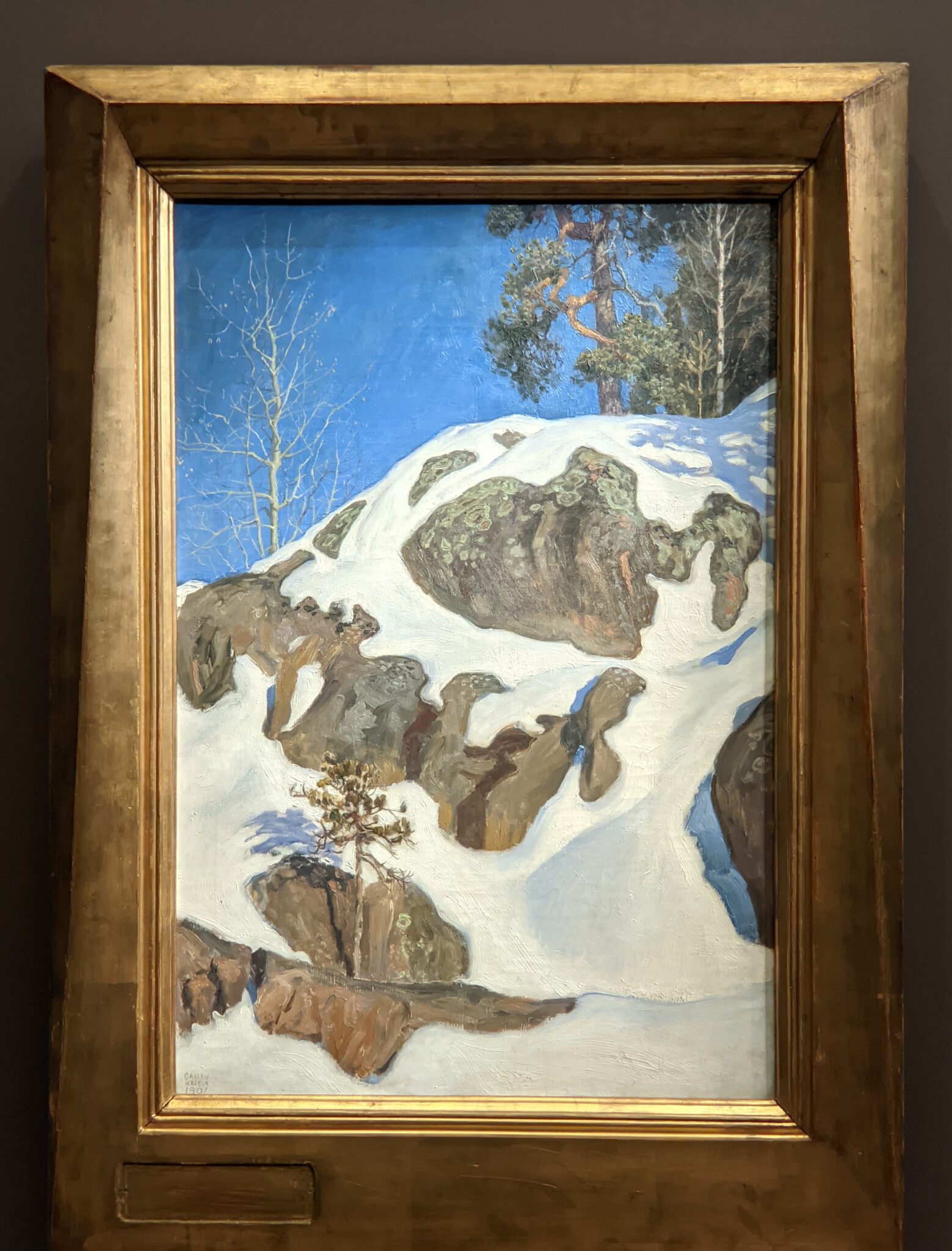
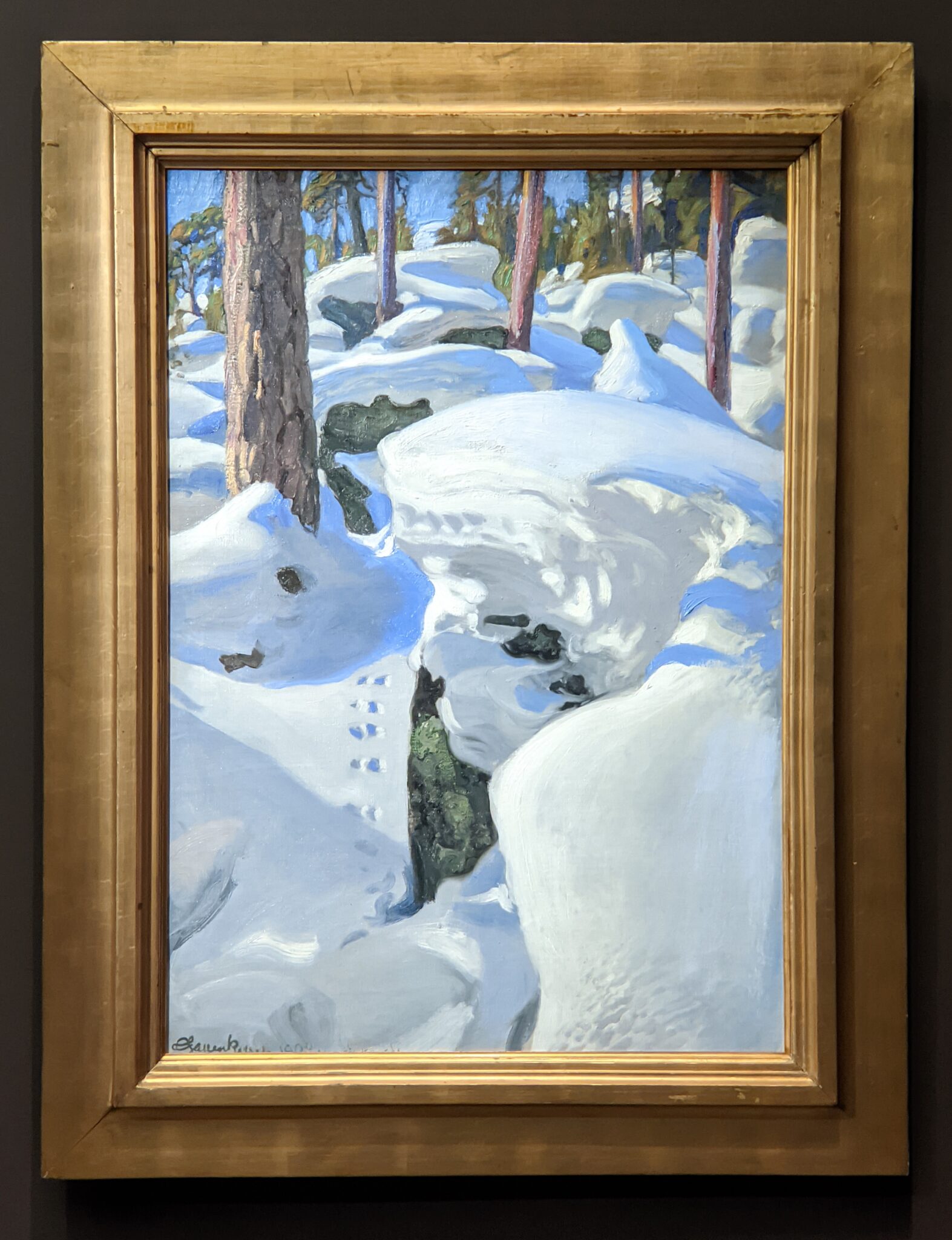
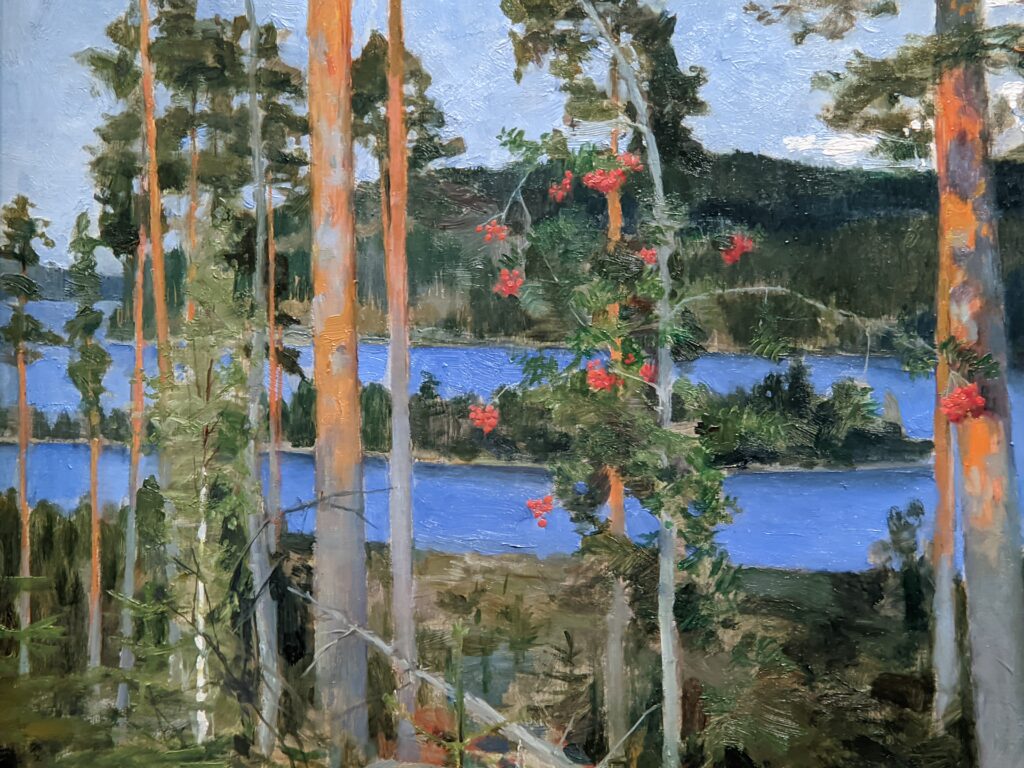
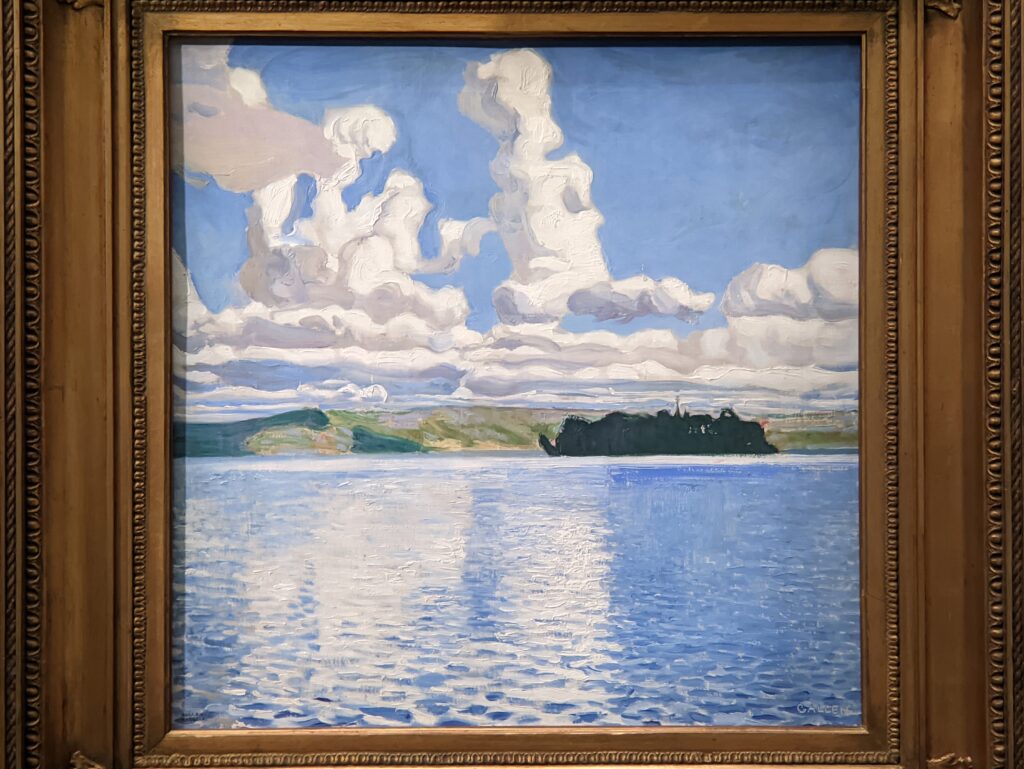
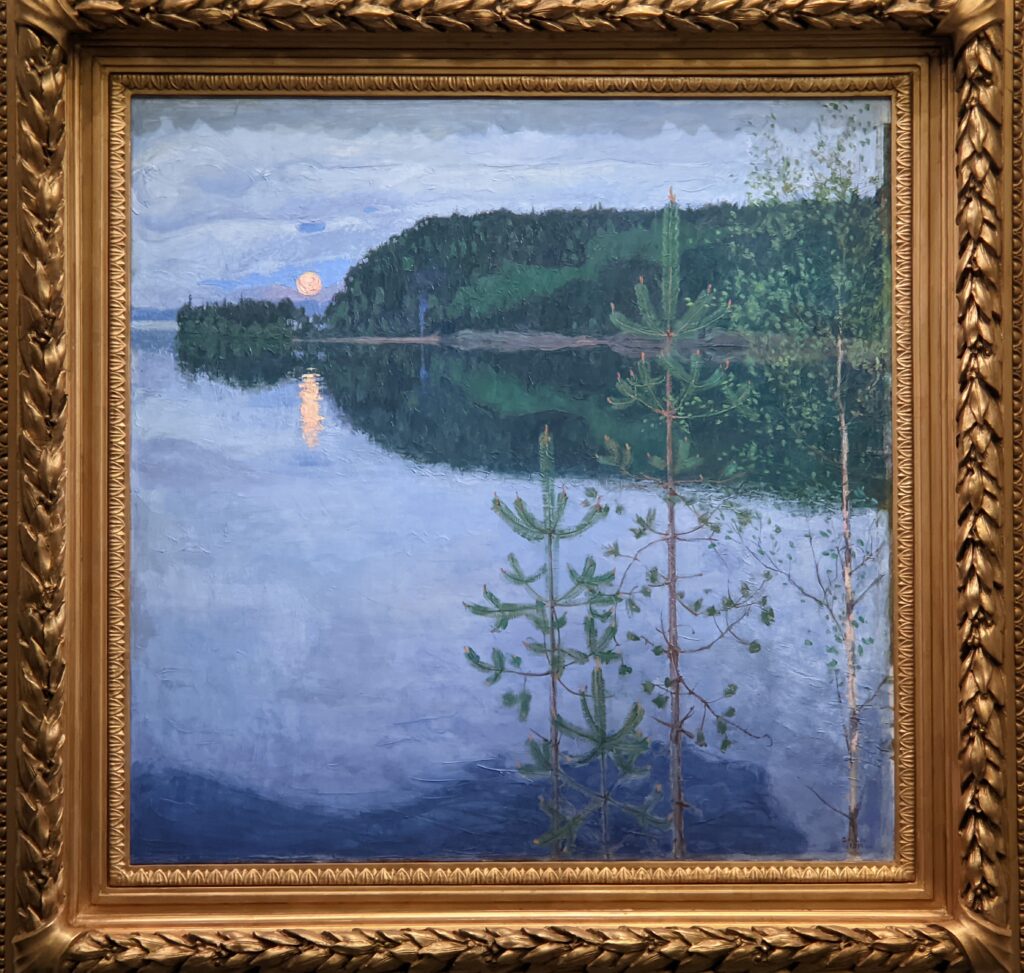
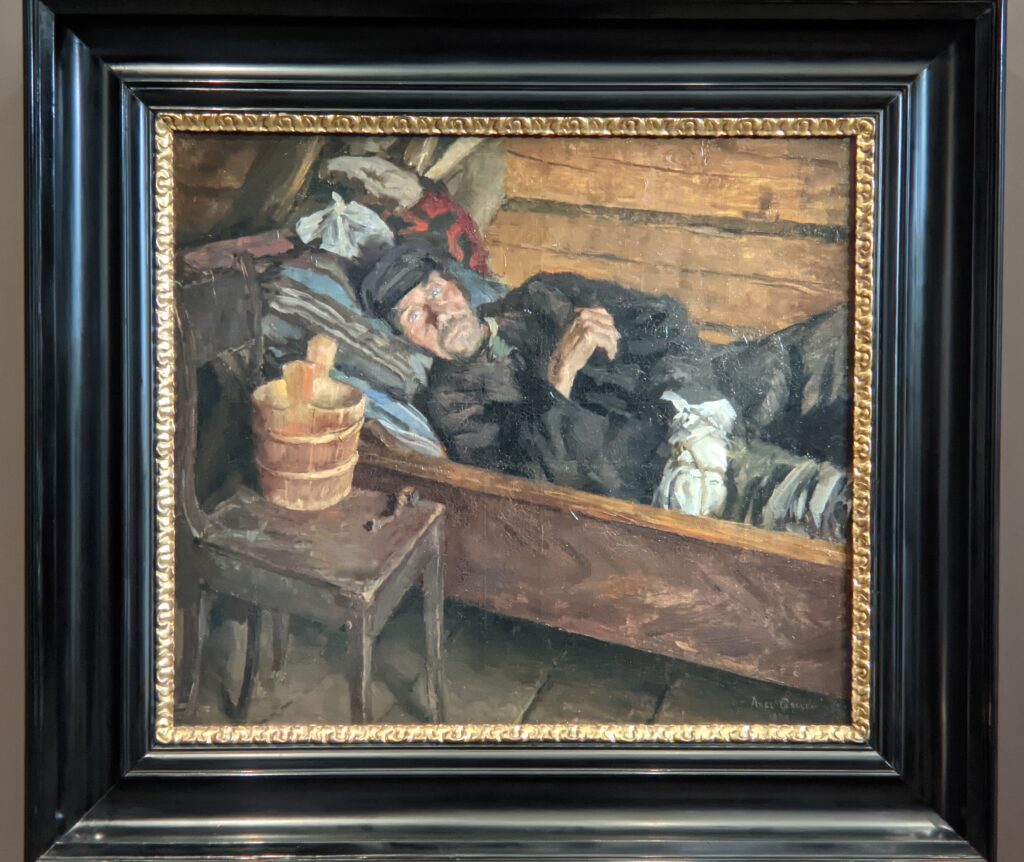
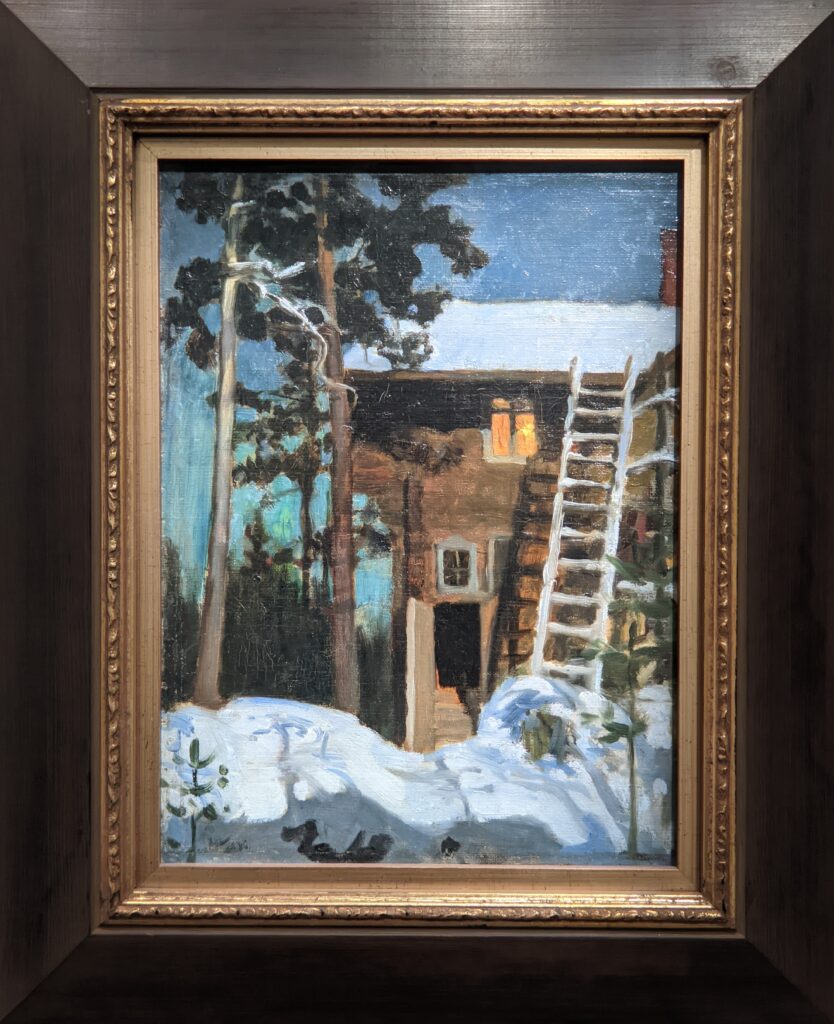
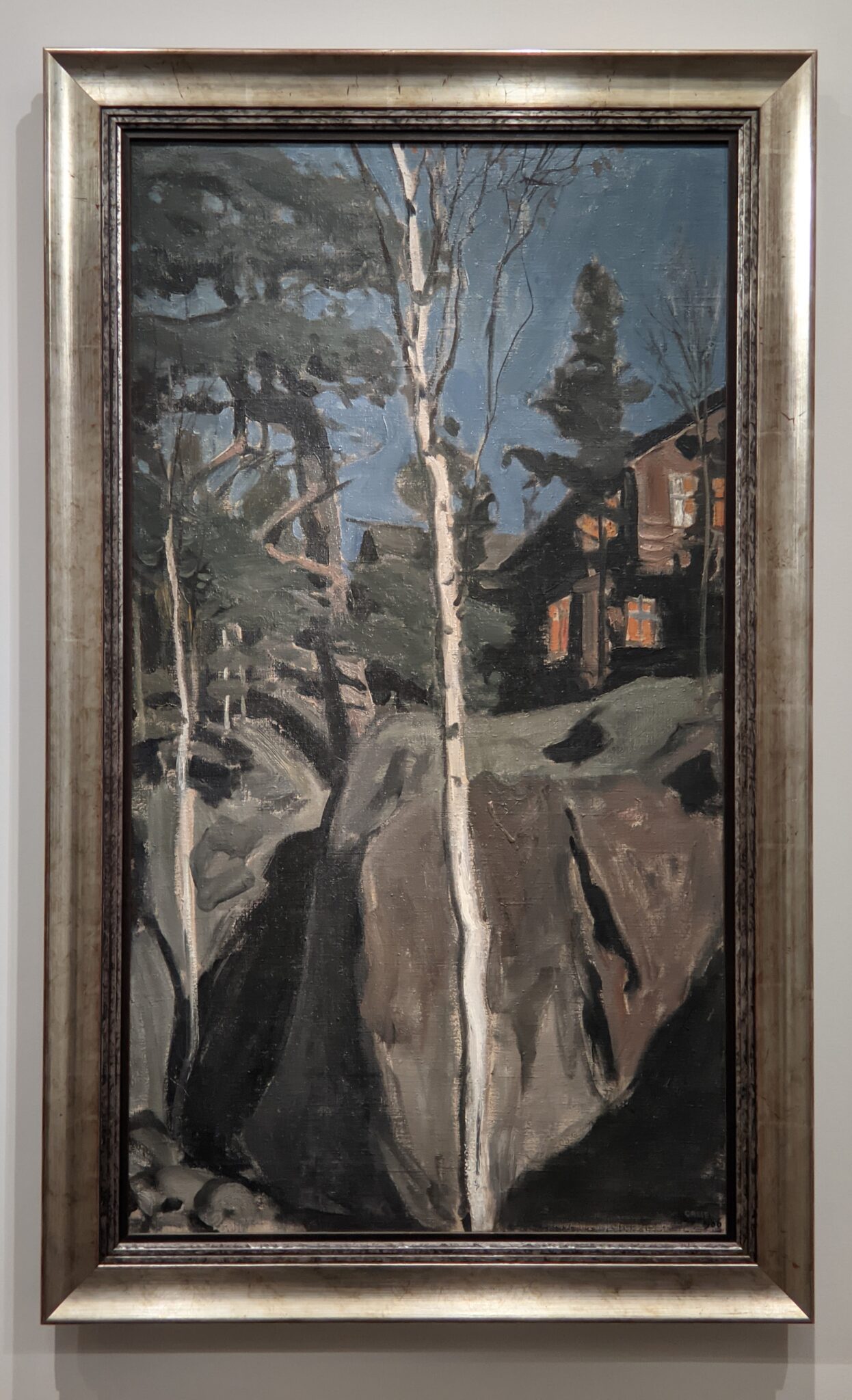
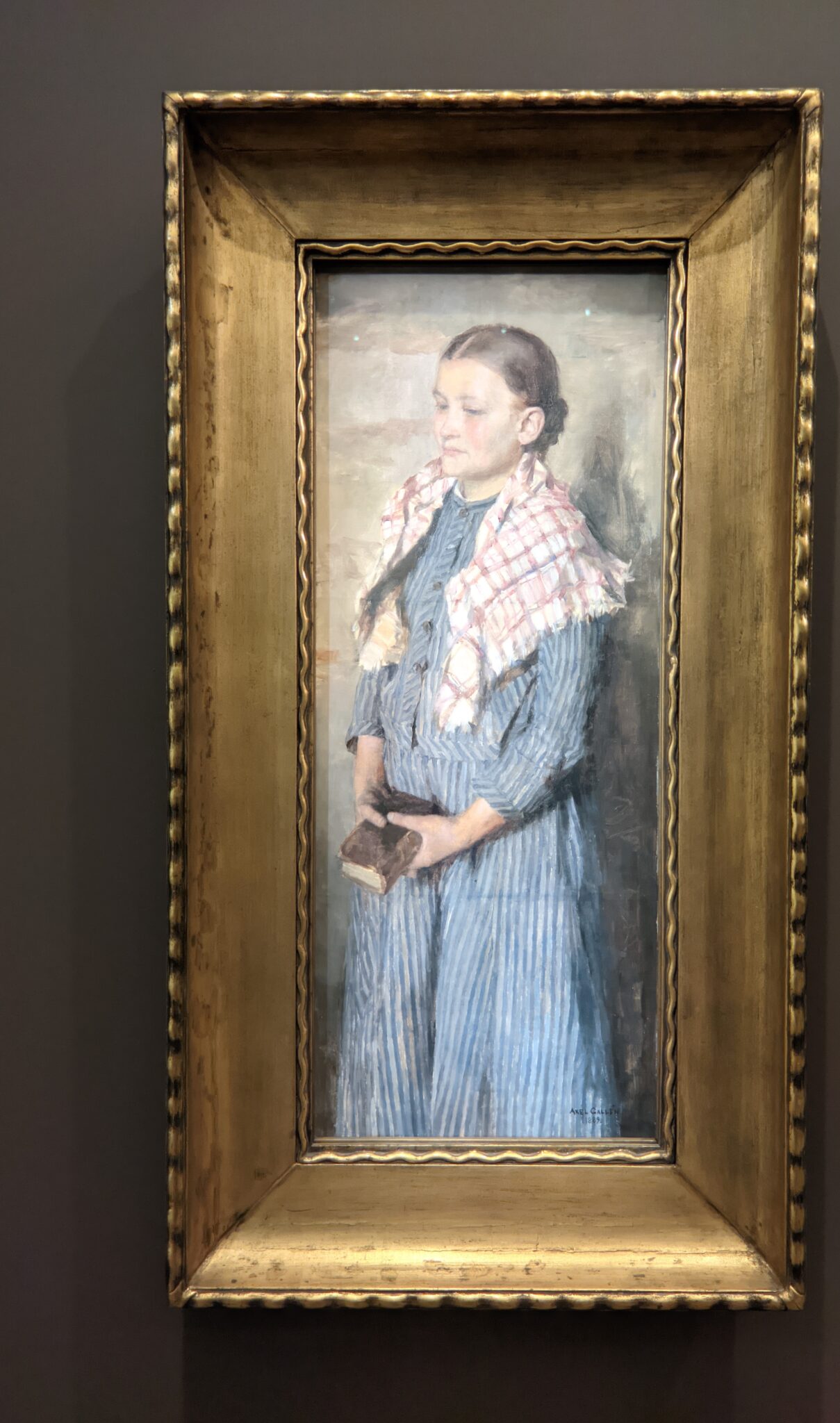
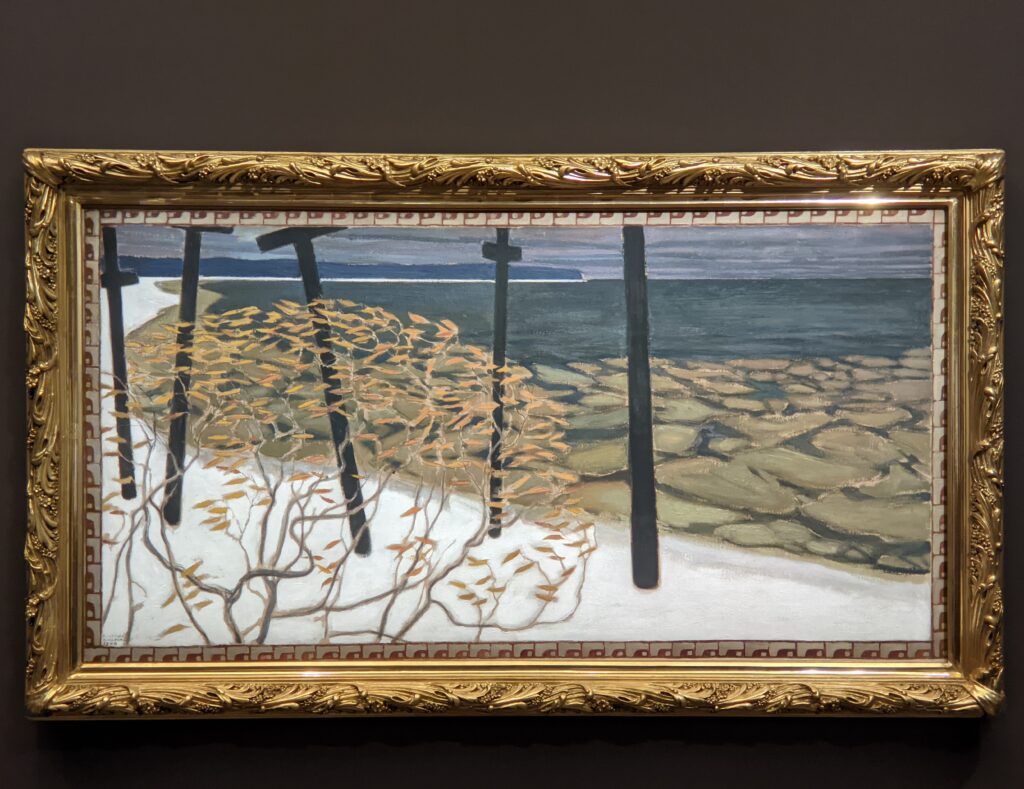
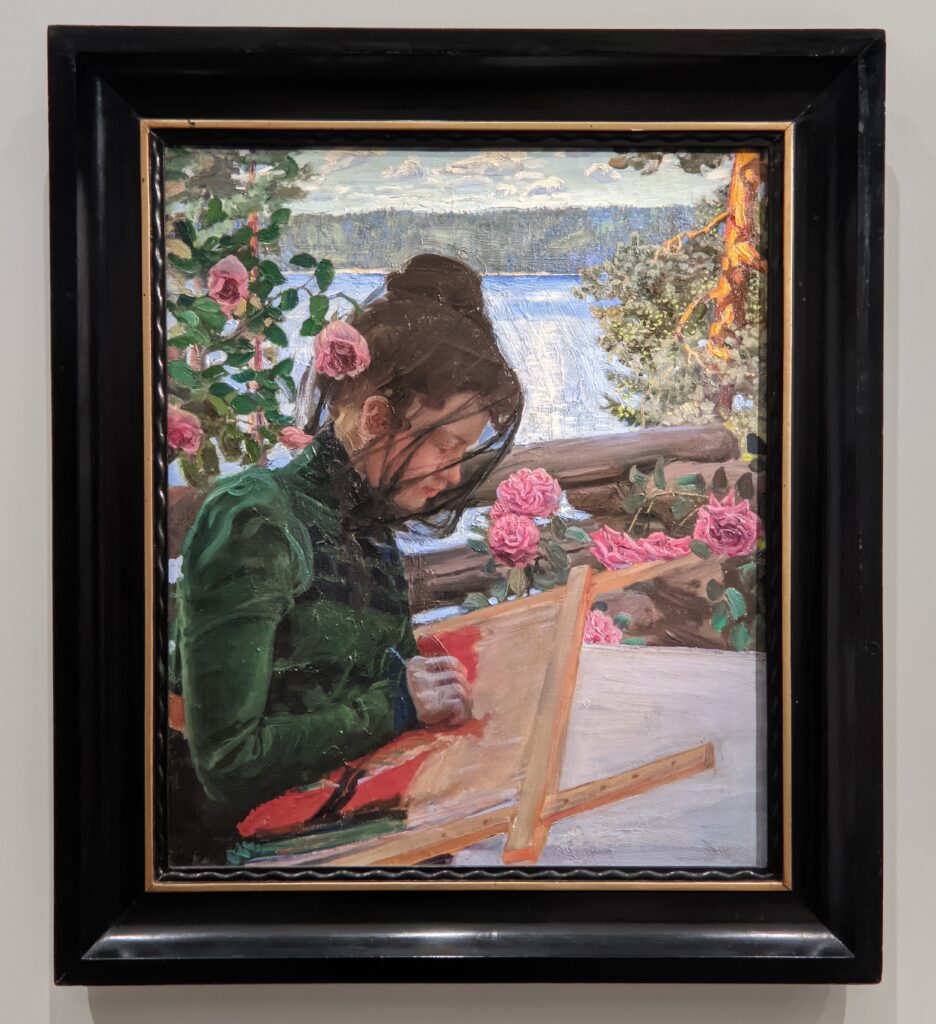
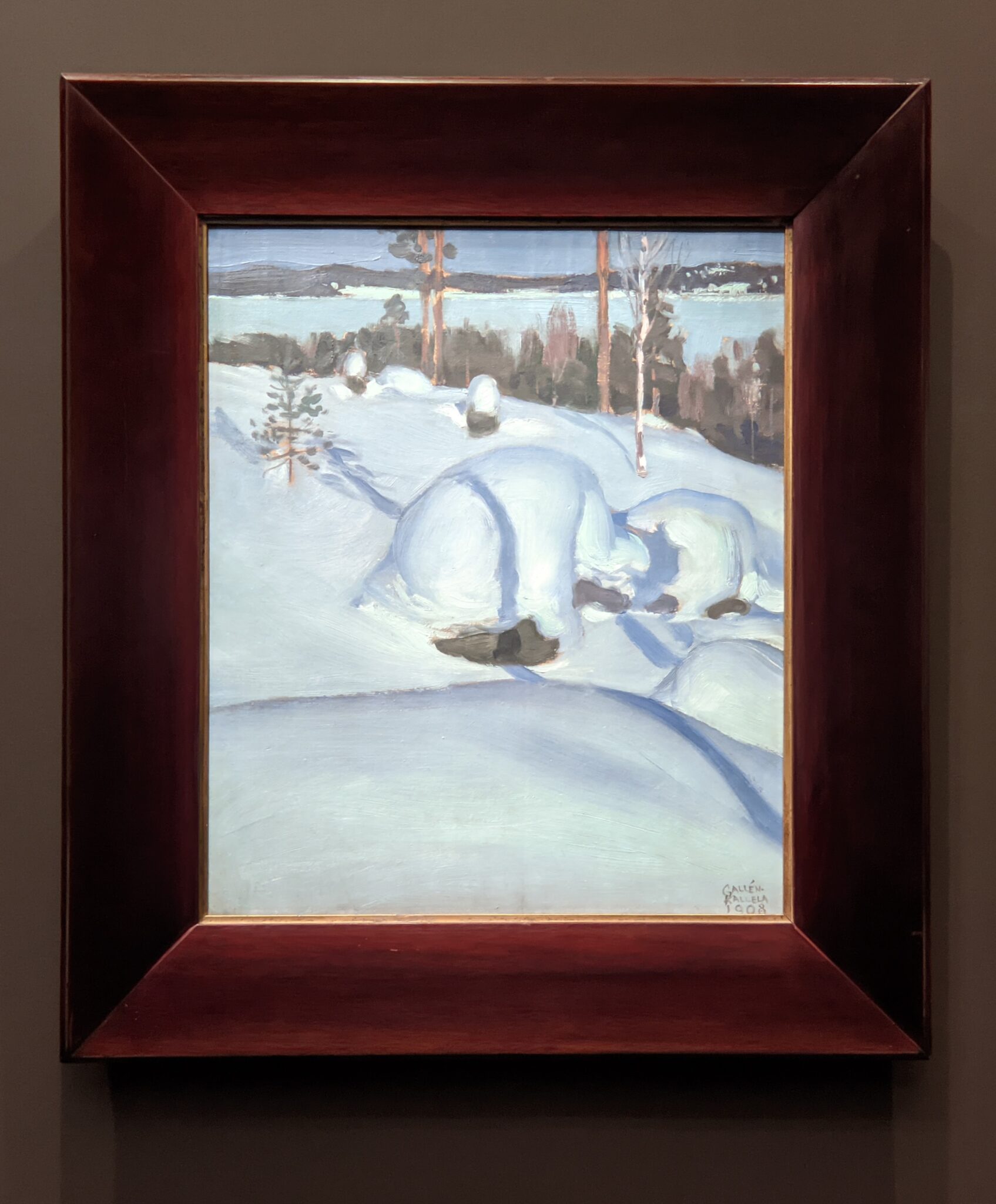
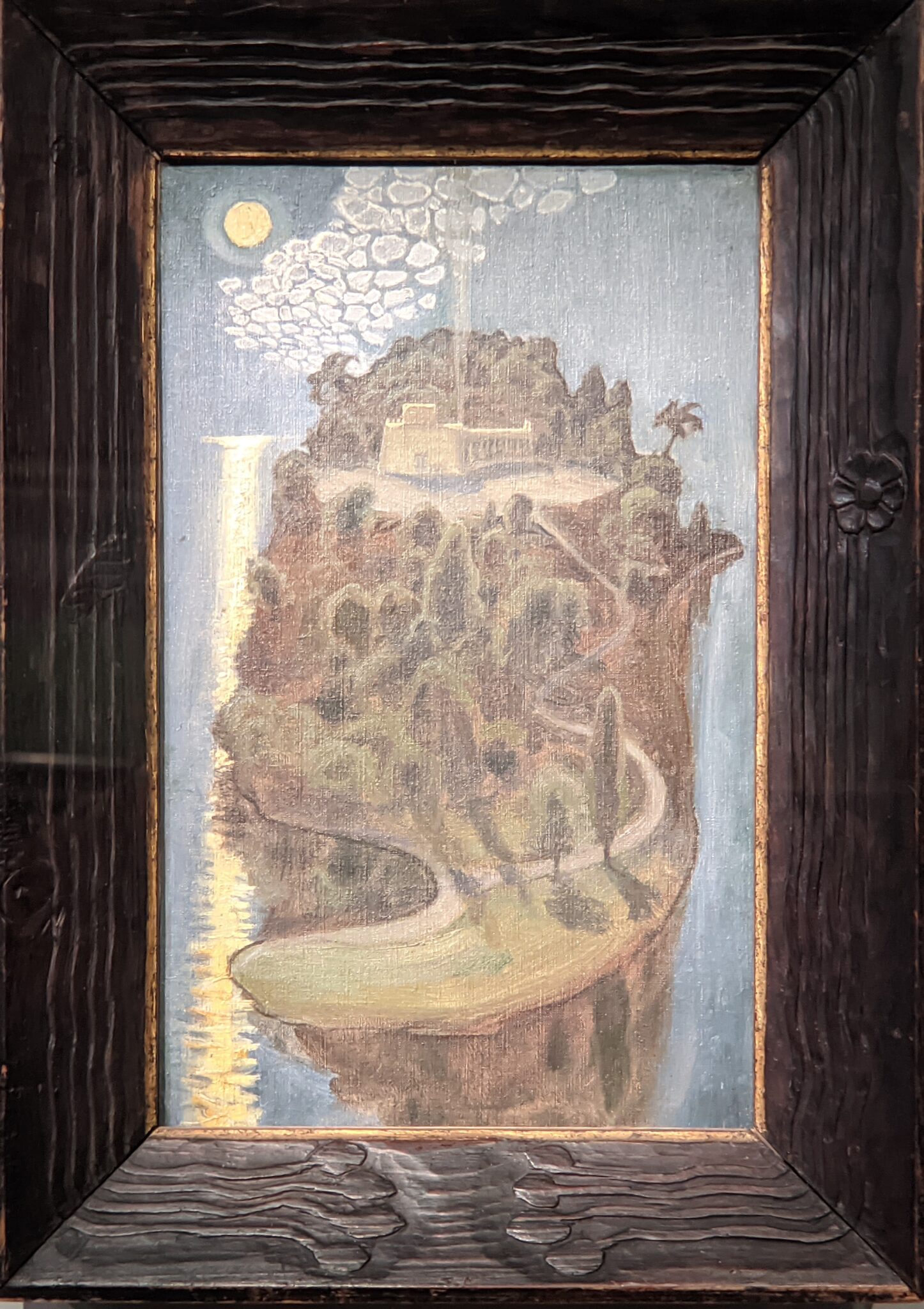
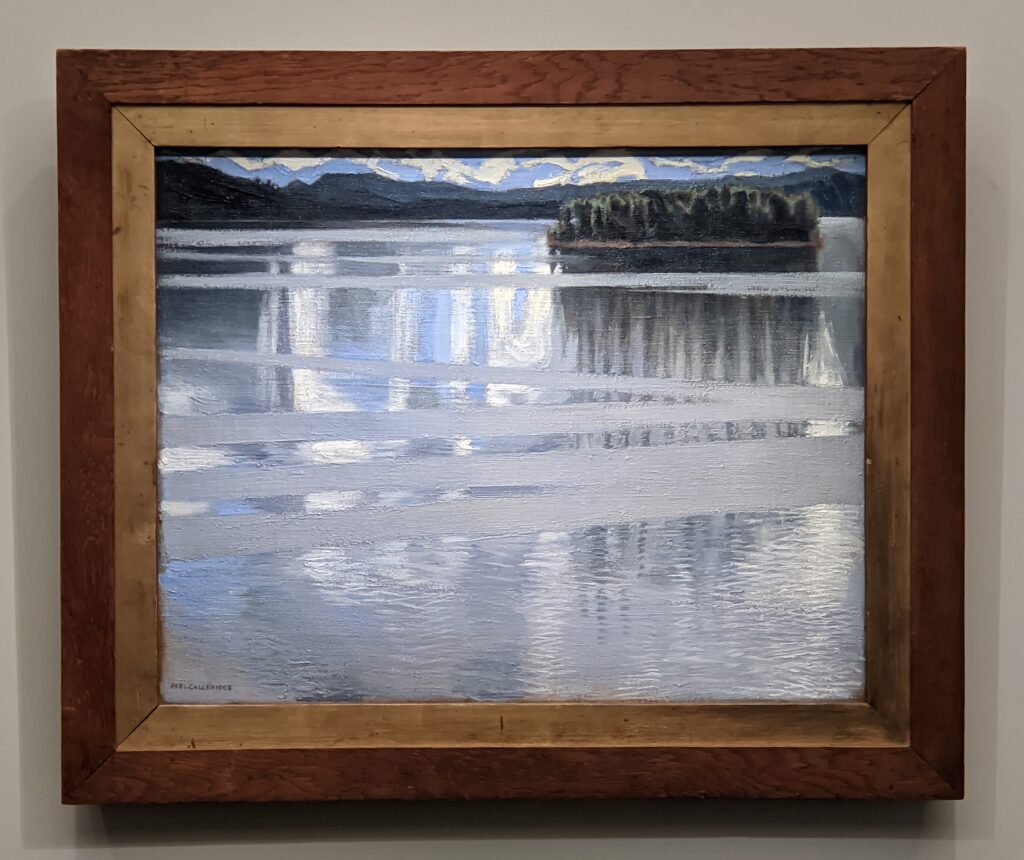
Akseli Gallen-Kallela at the Jacquemart-André Museum
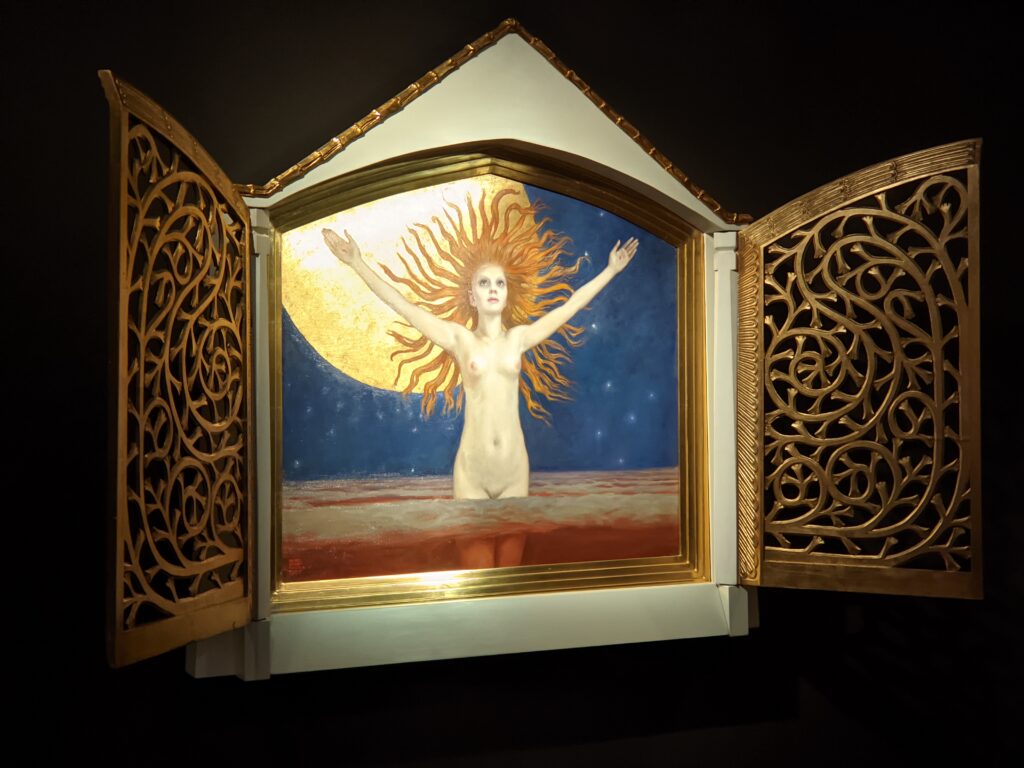
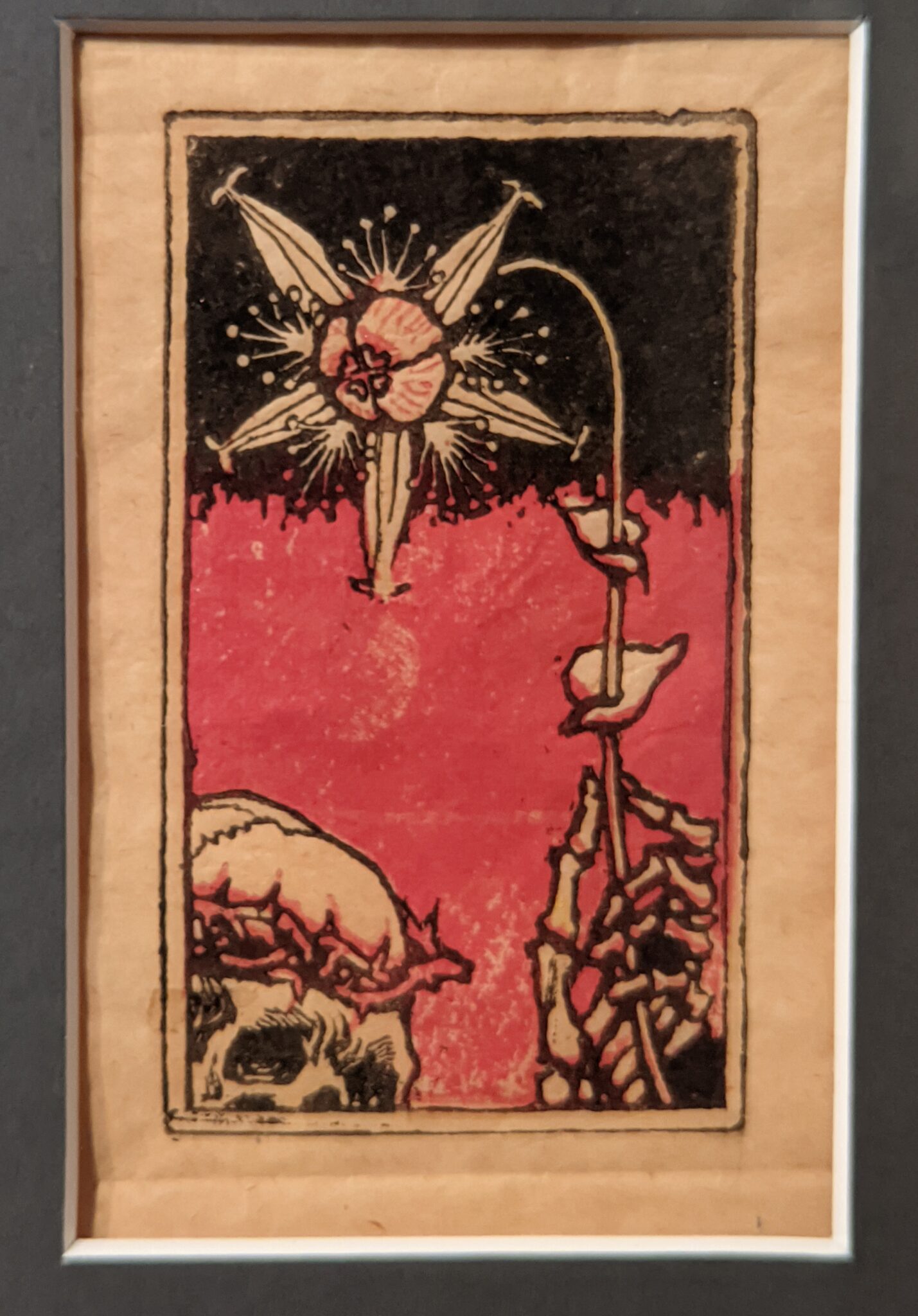
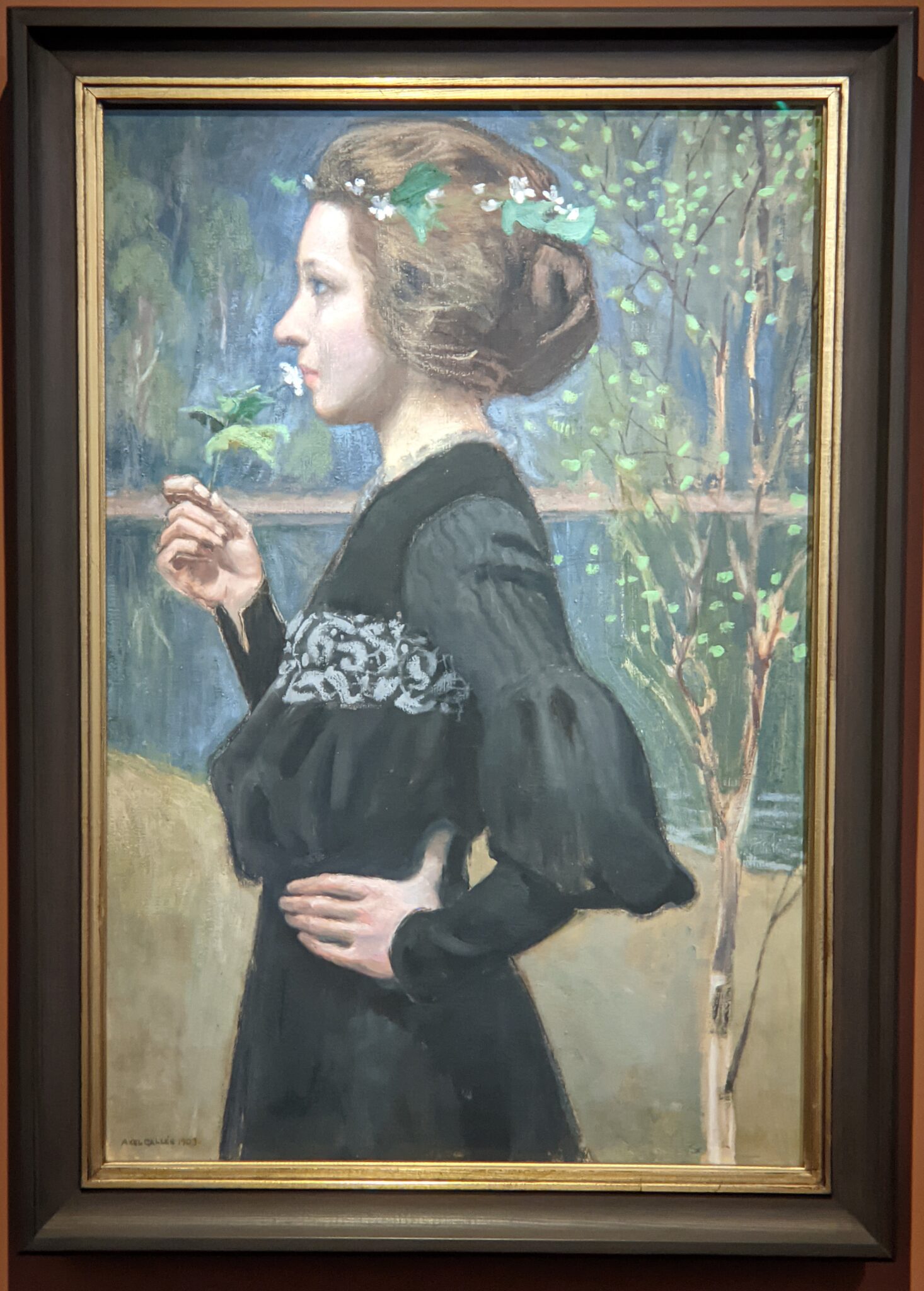
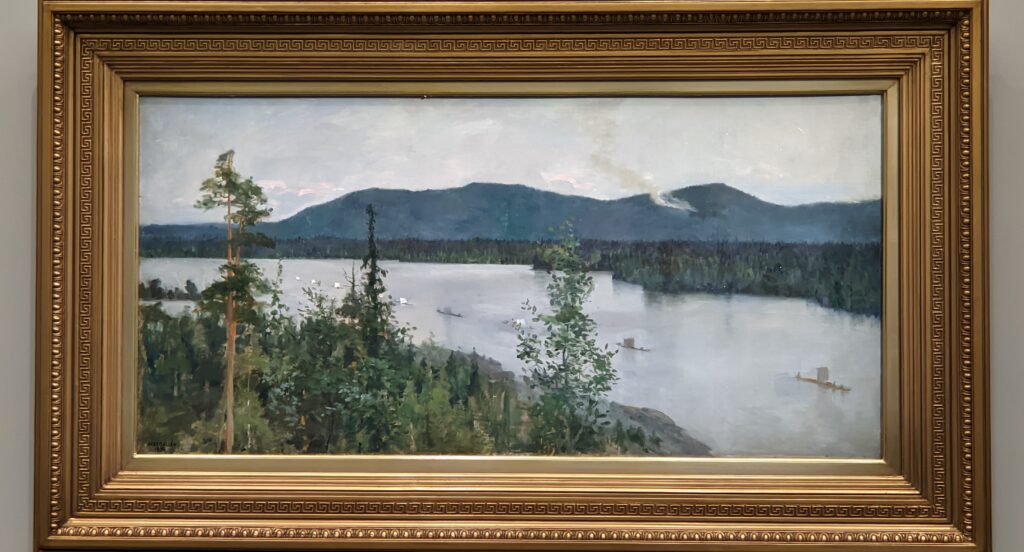




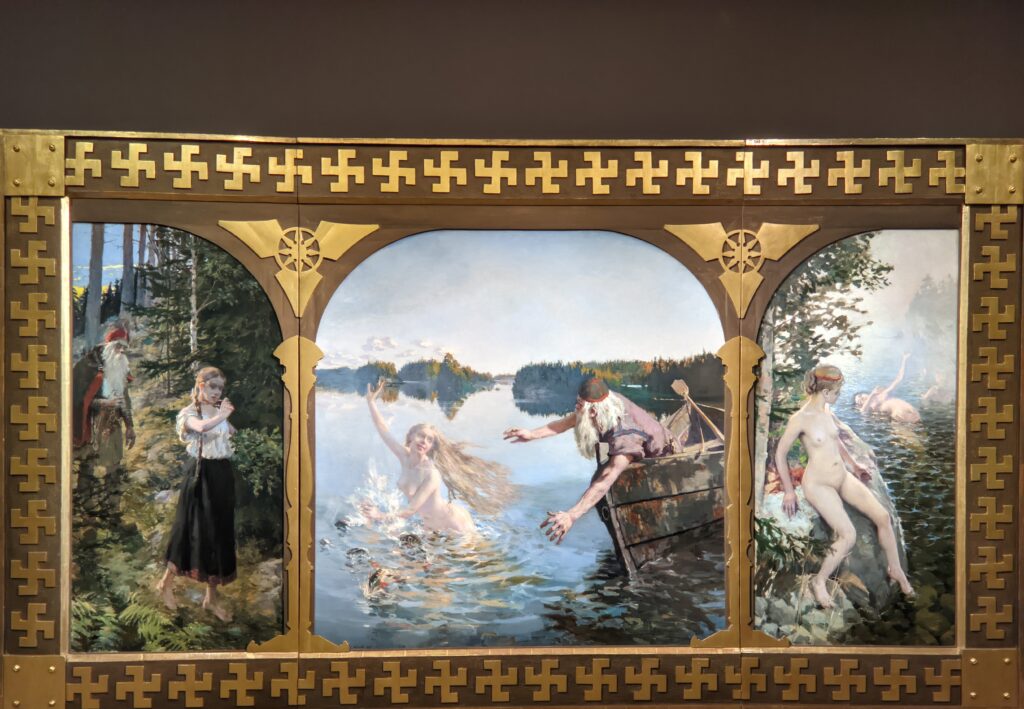
The Jacquemart-André presented a delightful retrospective devoted to Akseli Gallen-Kallela (1865 — 1931) from March 11 through July 25, 2022. Gallen-Kallela captured the solitude of the countryside in his native Finland with incomparable lyricism. His late work was marked by a shift from Naturalism to Symbolism.
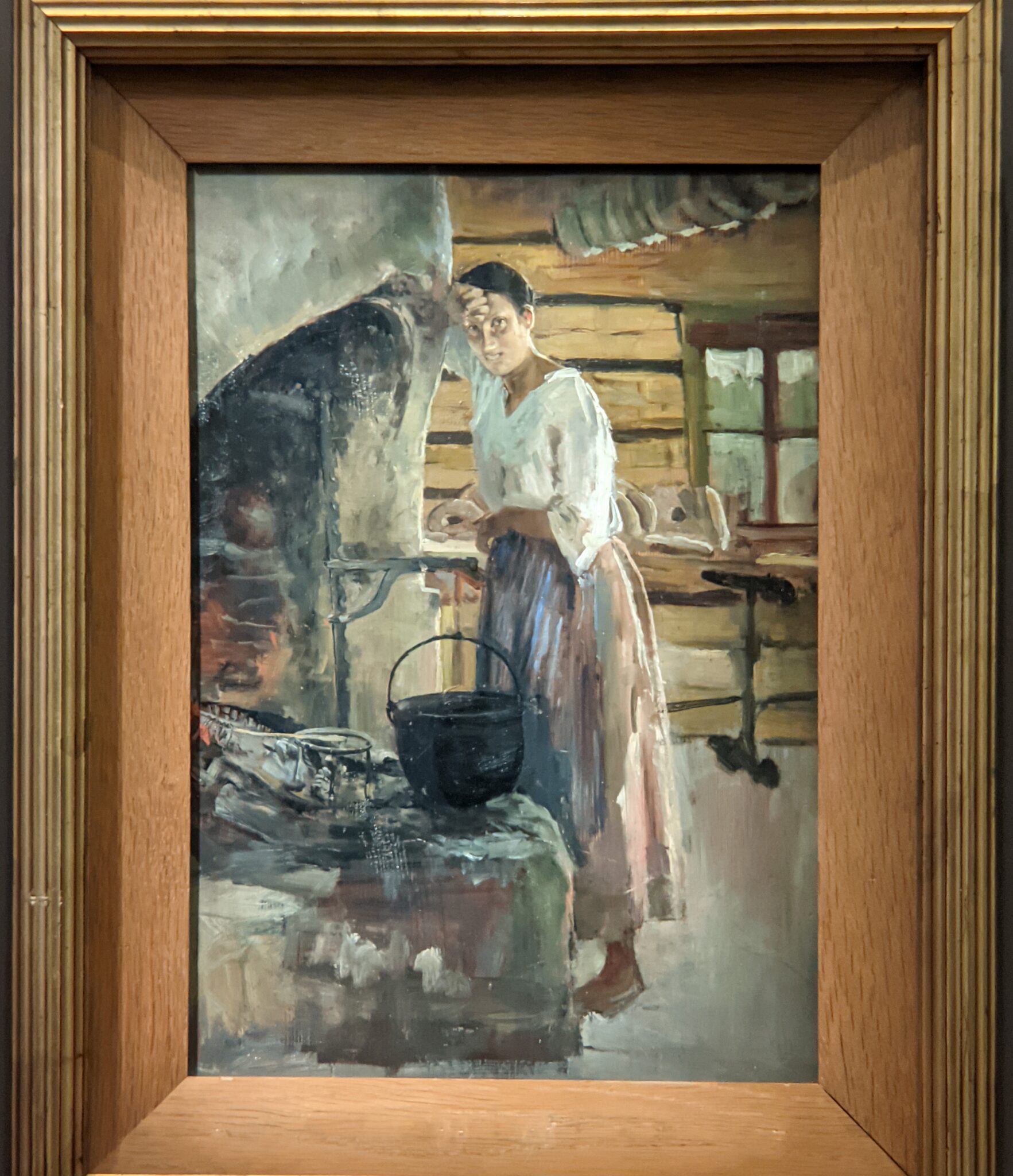
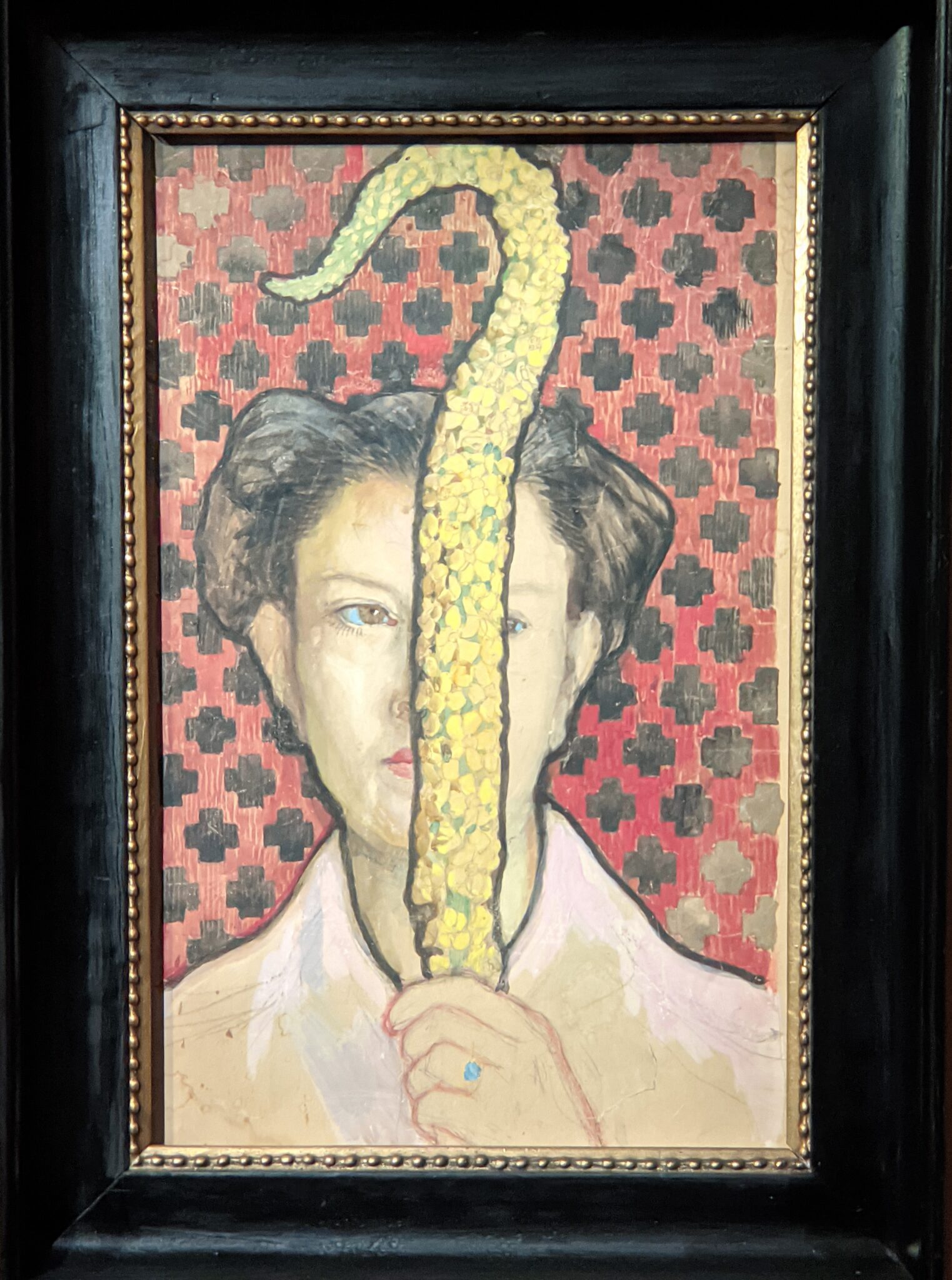
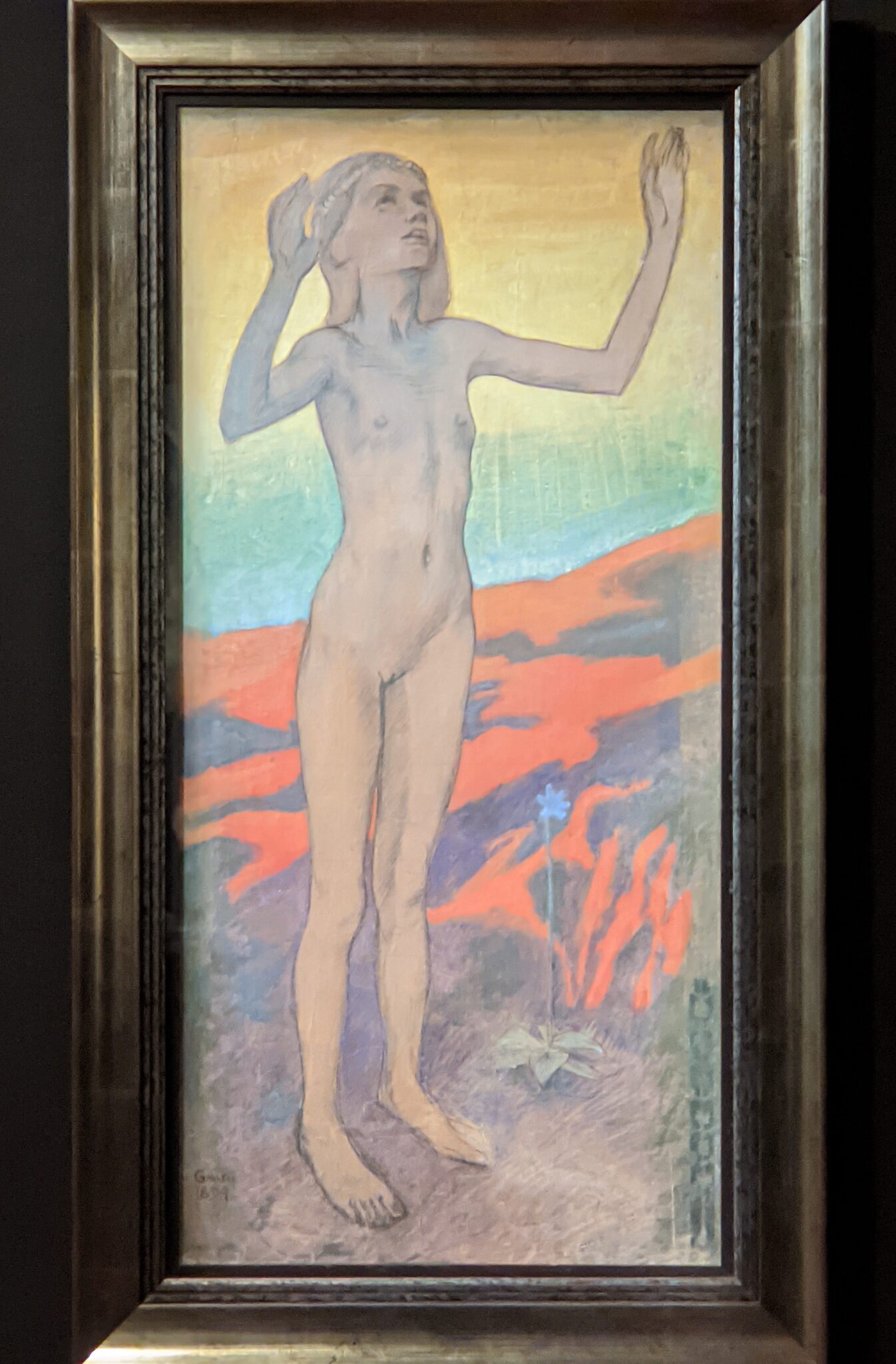
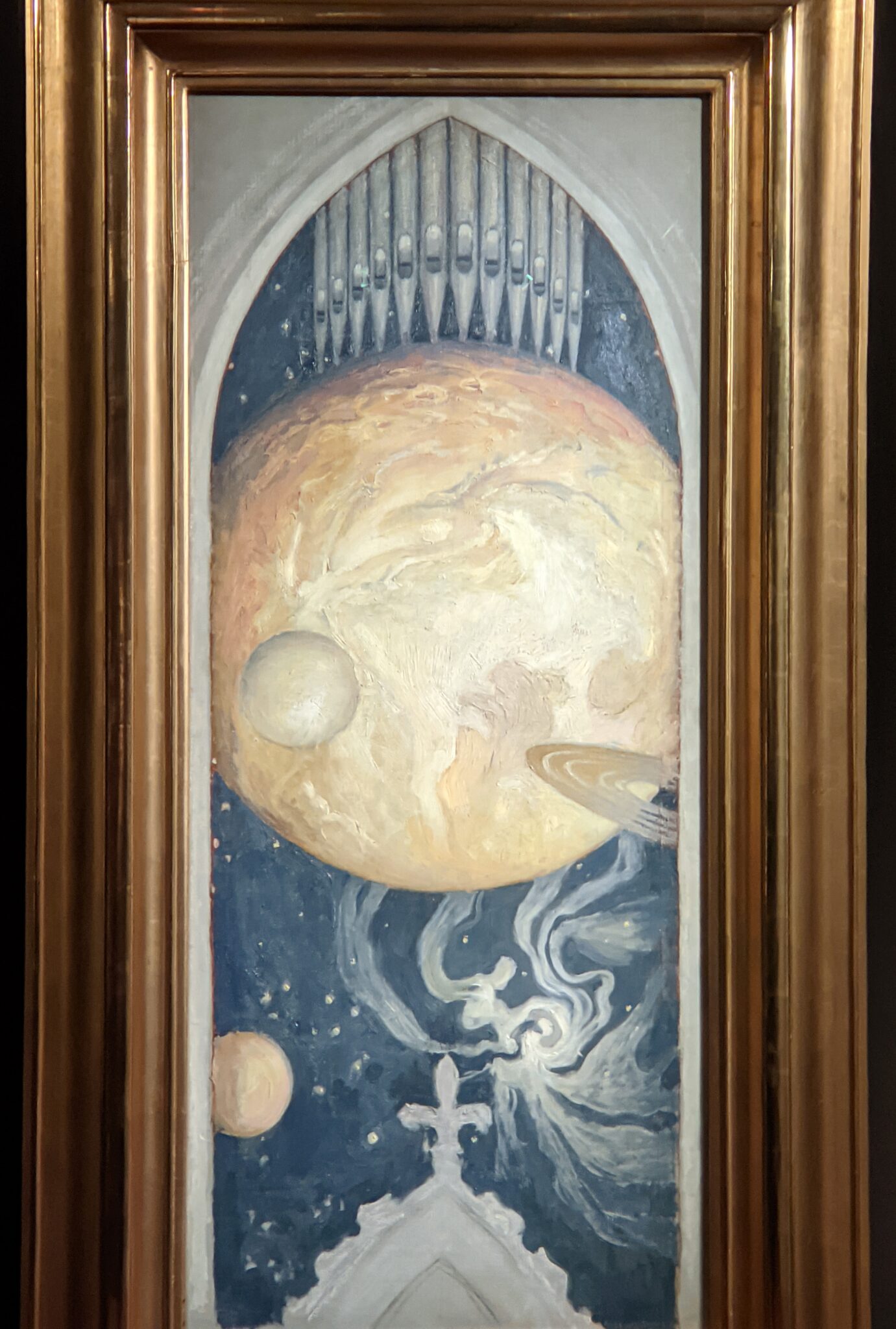
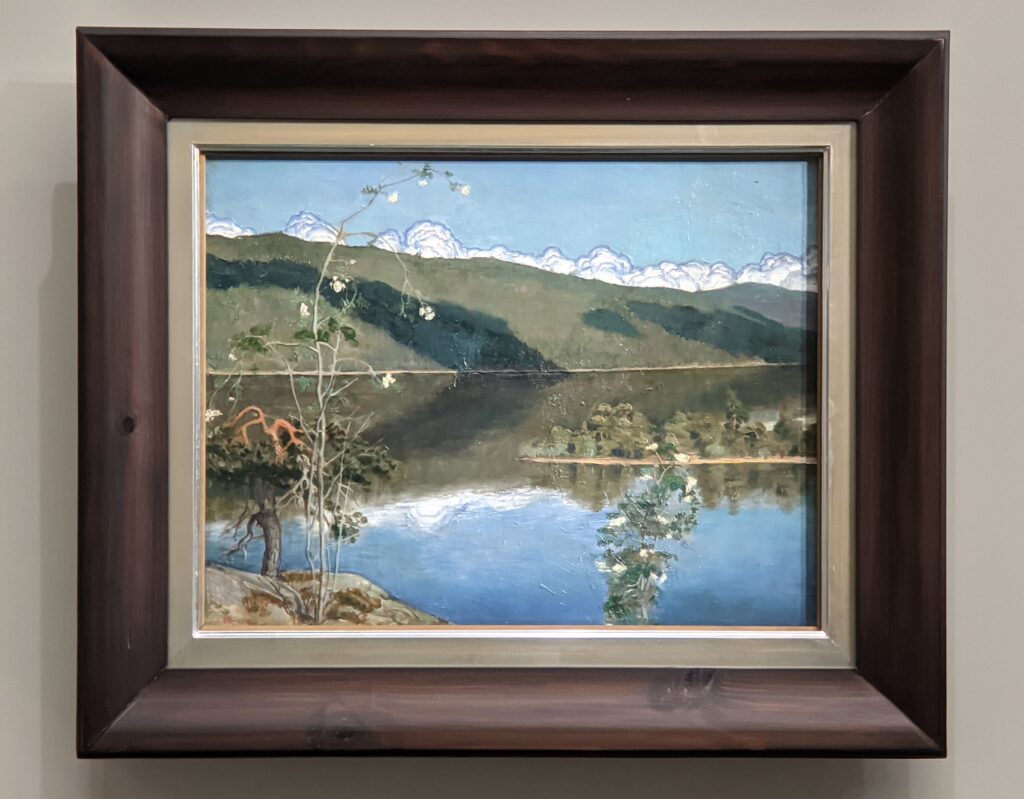
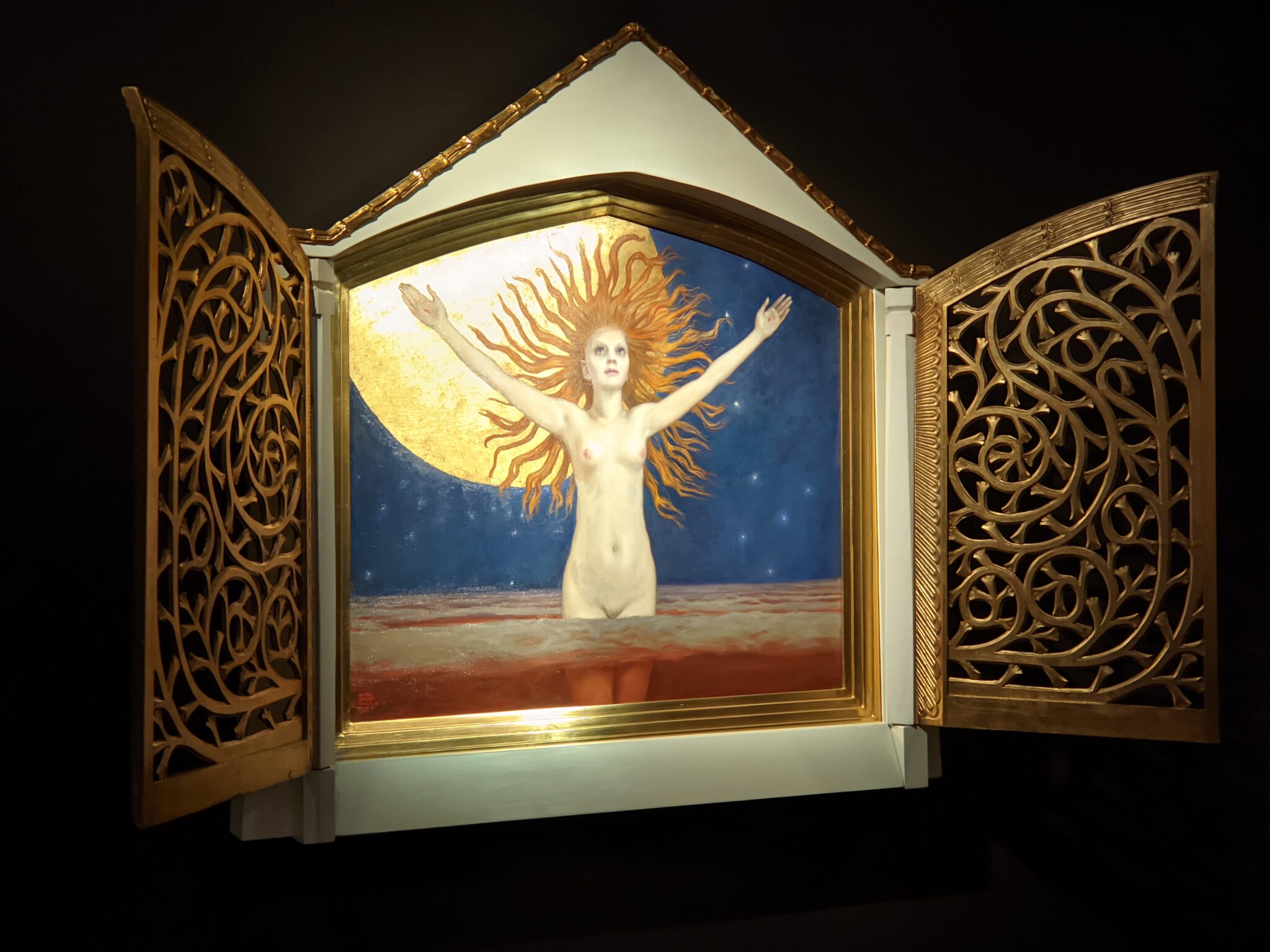
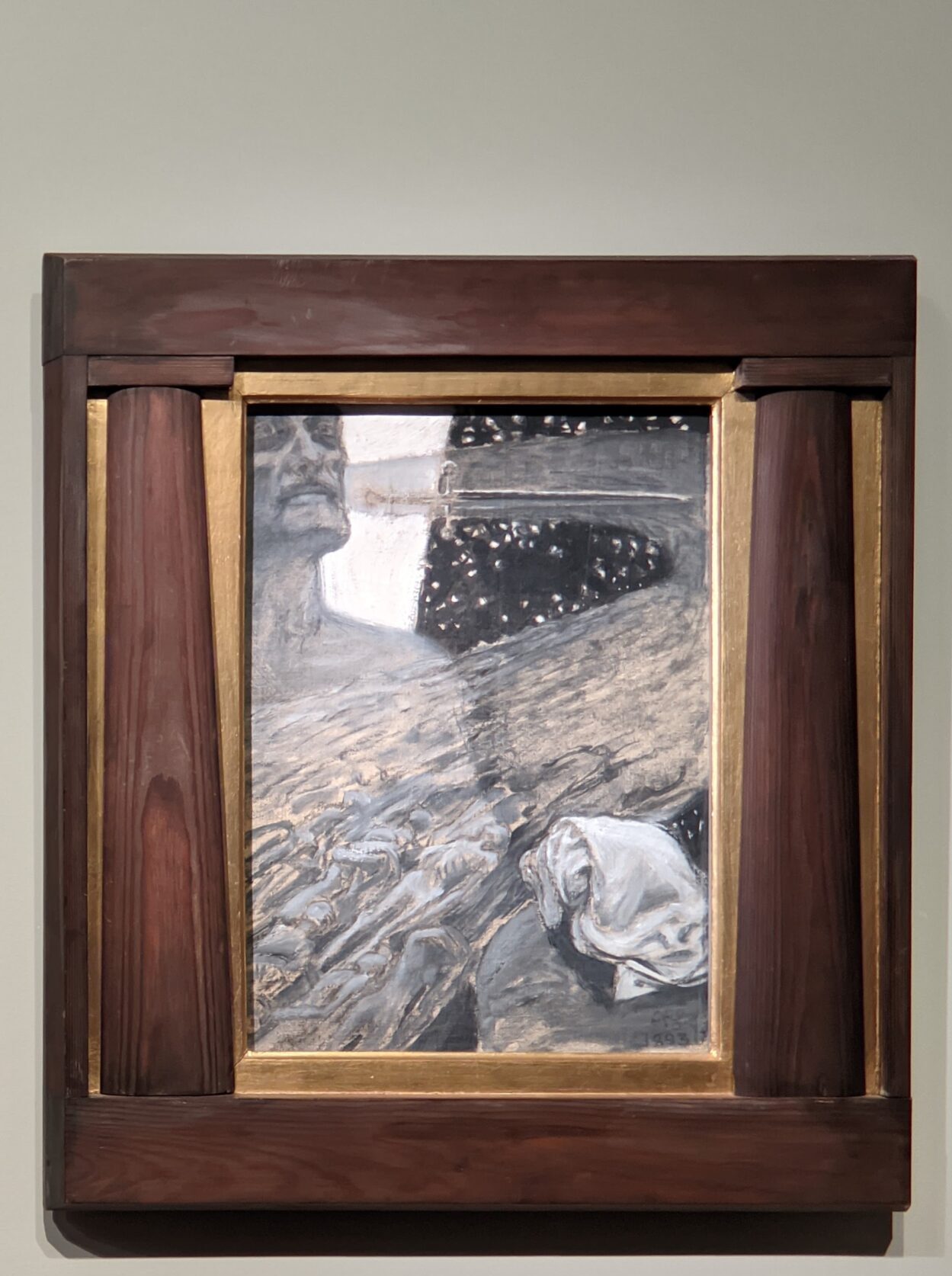
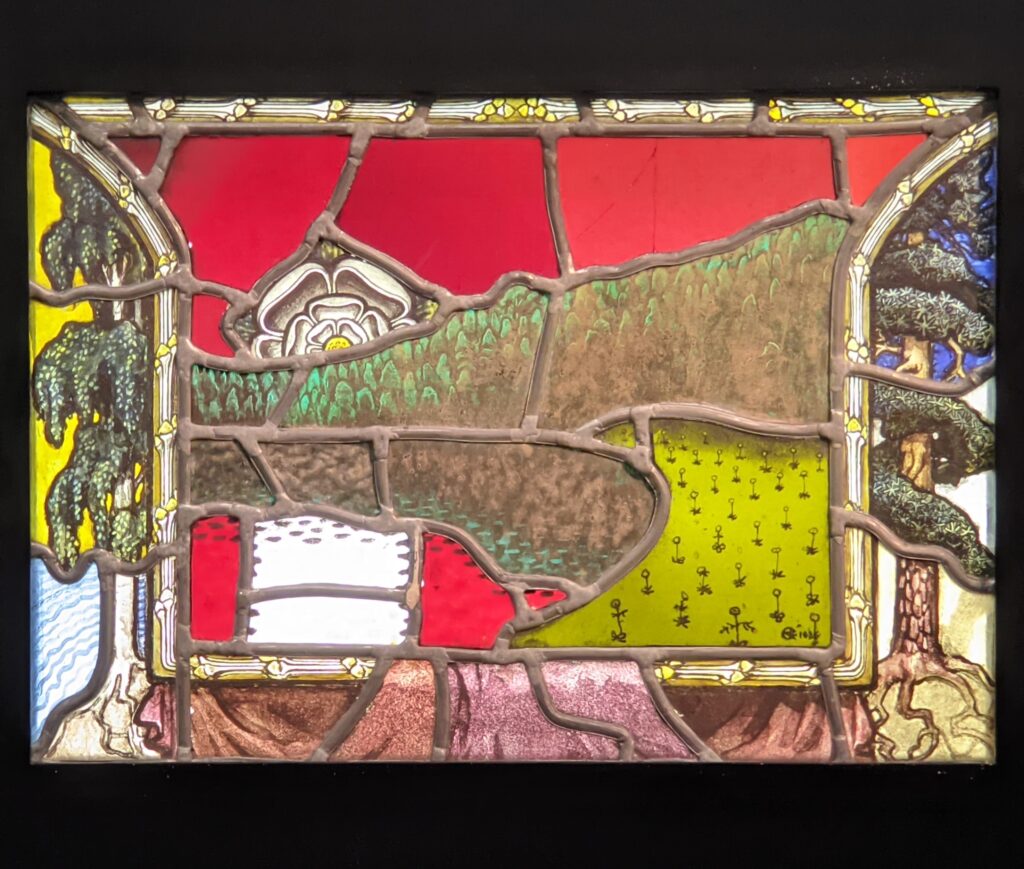
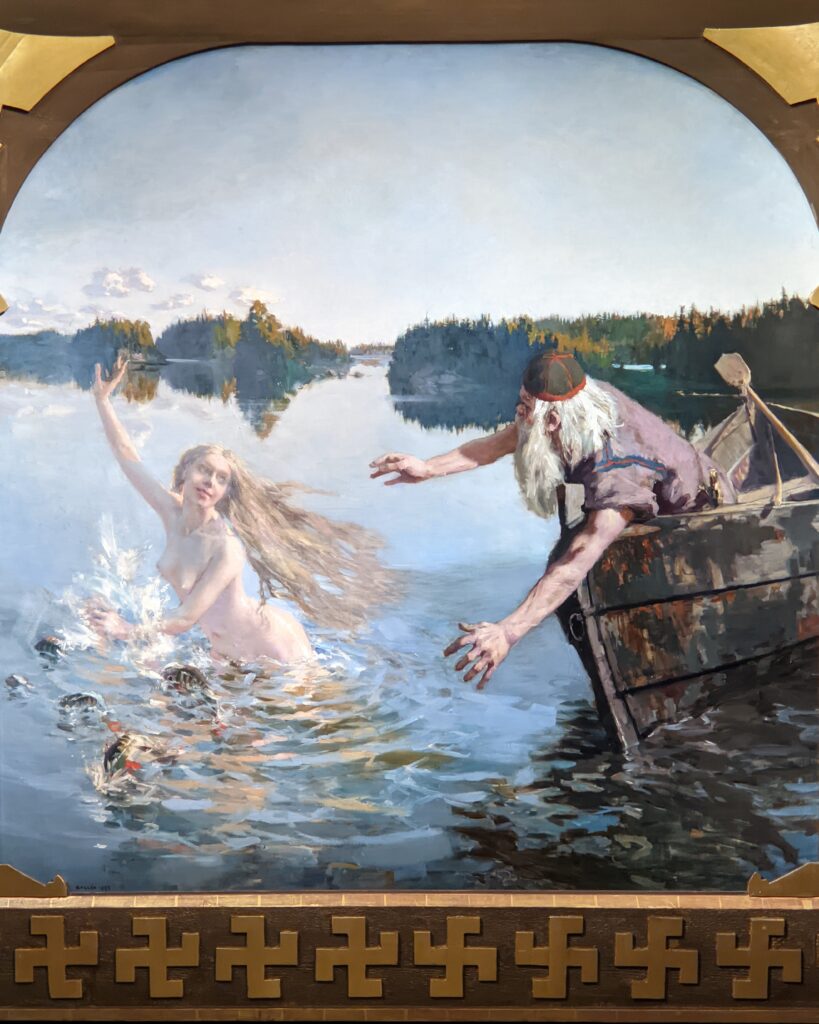
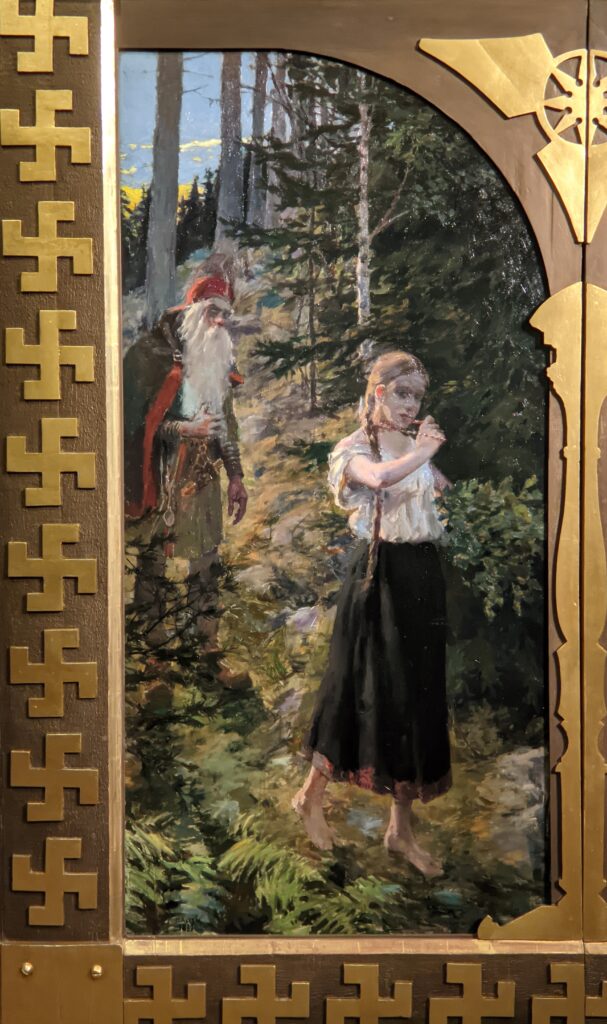
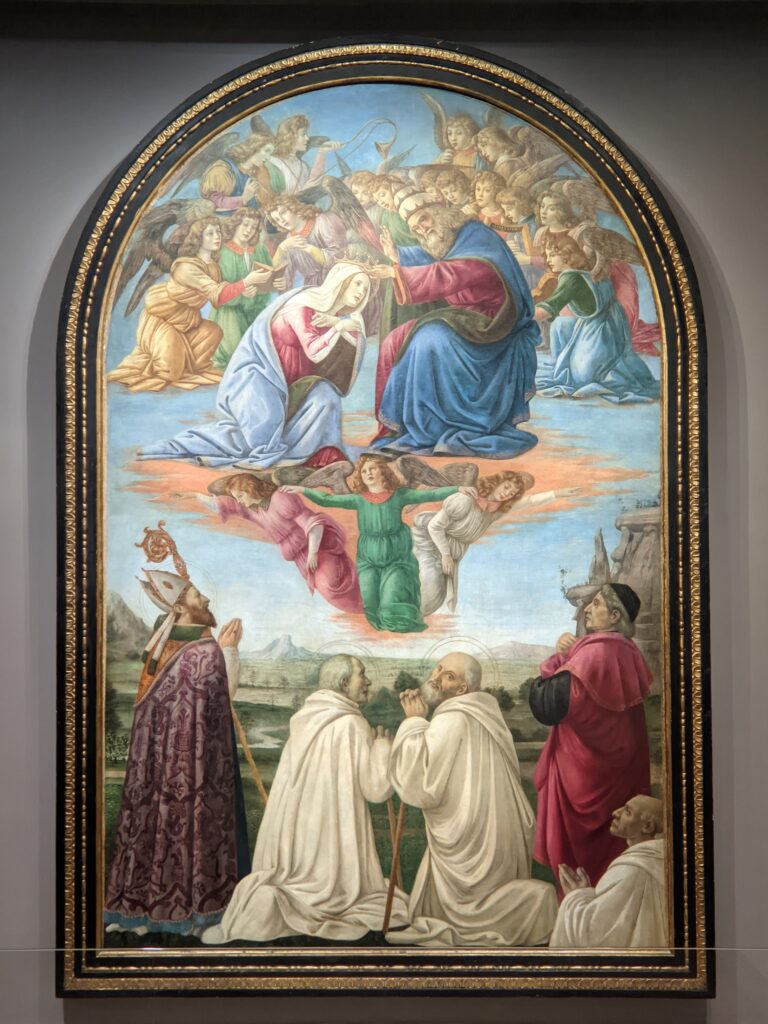





























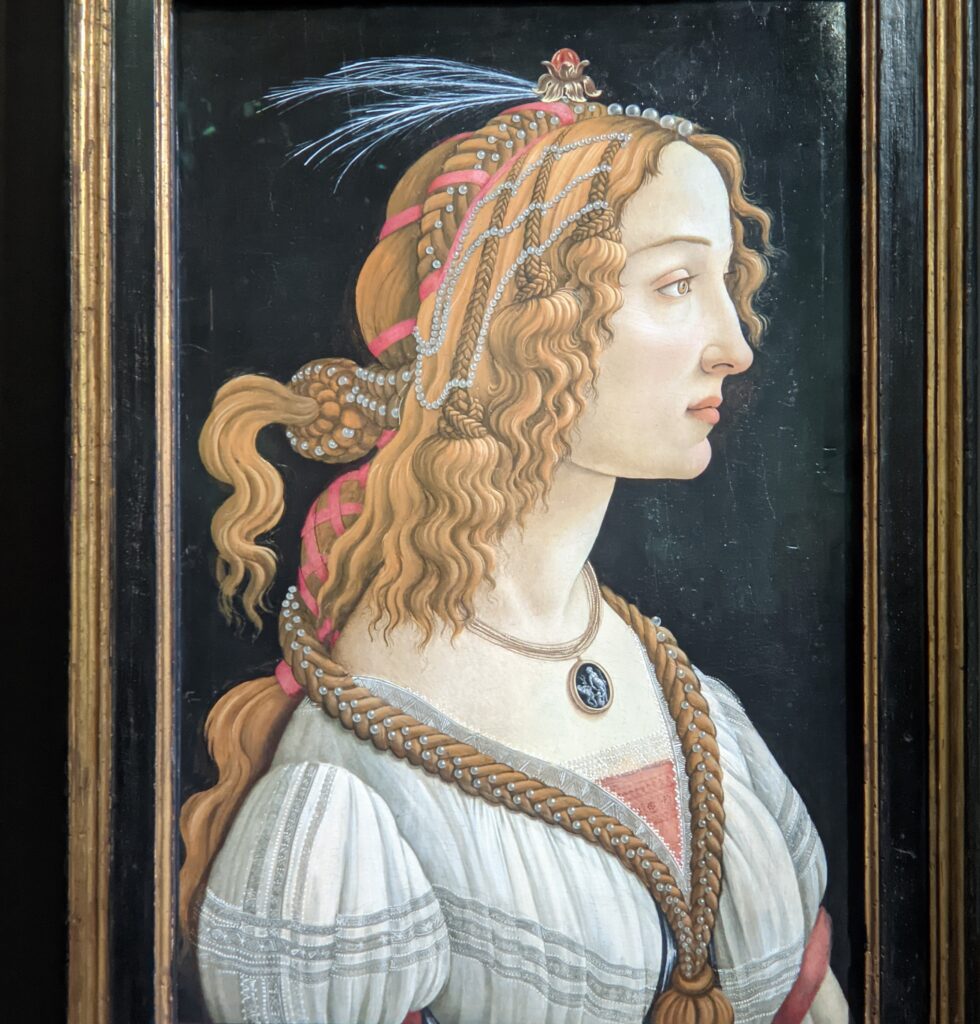
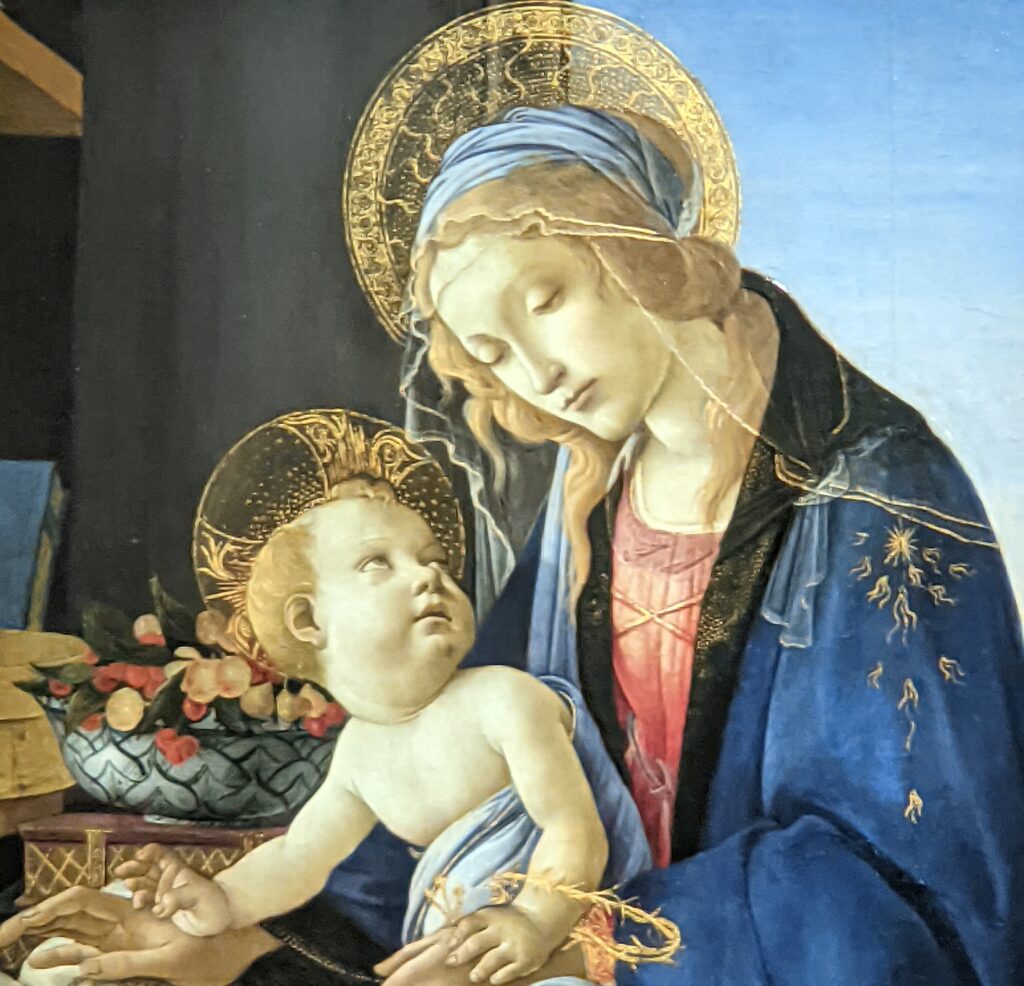
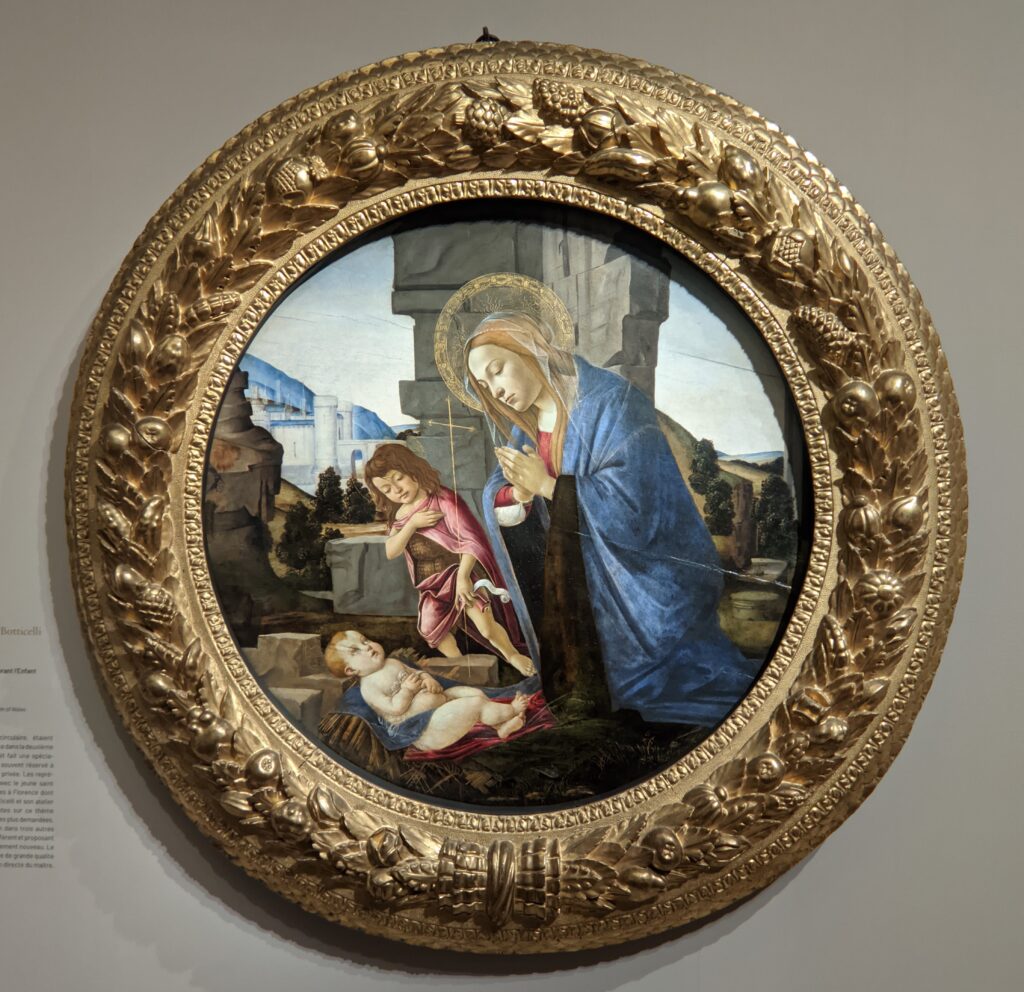
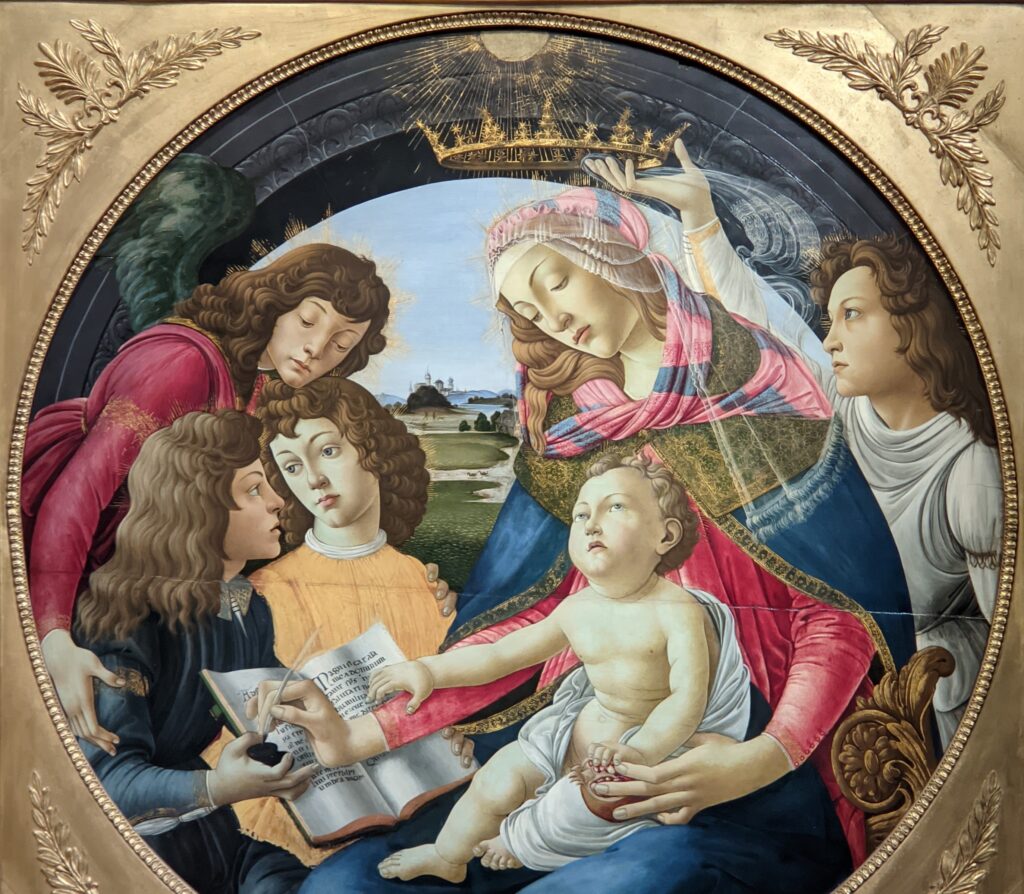
The Jacquemart-André celebrated the genius of Sandro Botticelli, a painter in whom Nélie Jacquemart was particularly interested, with a show of 40 works by the Florentine master from September 10, 2021 through January 24, 2022. Here are some of the highlights from that special exhibition.
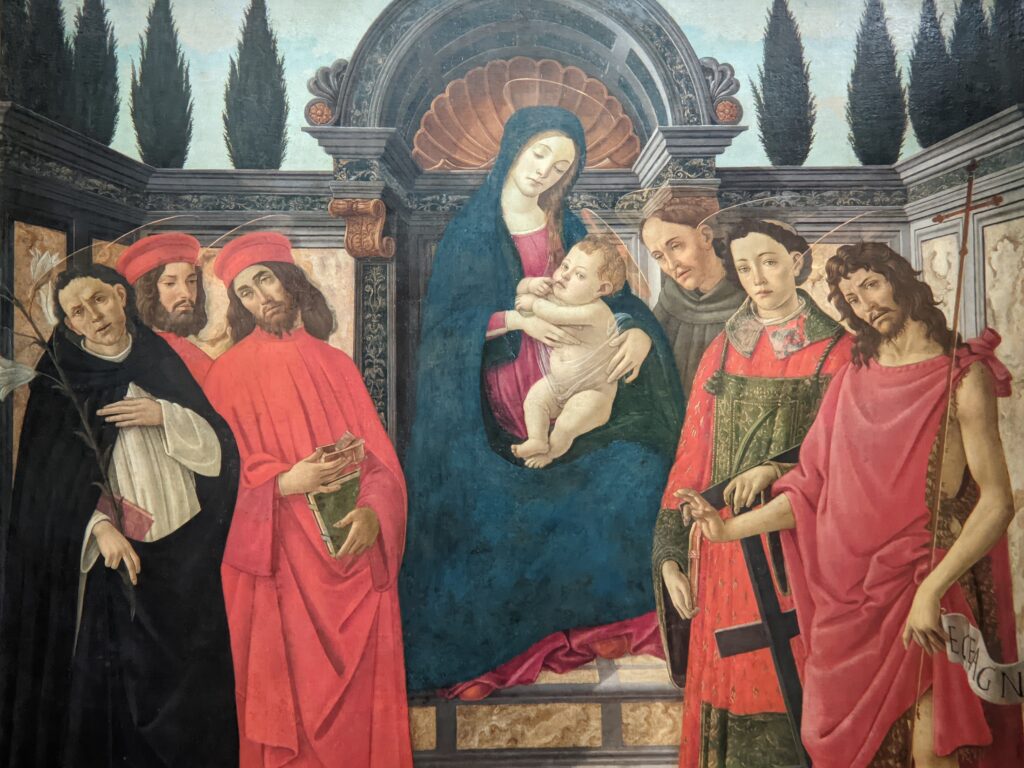
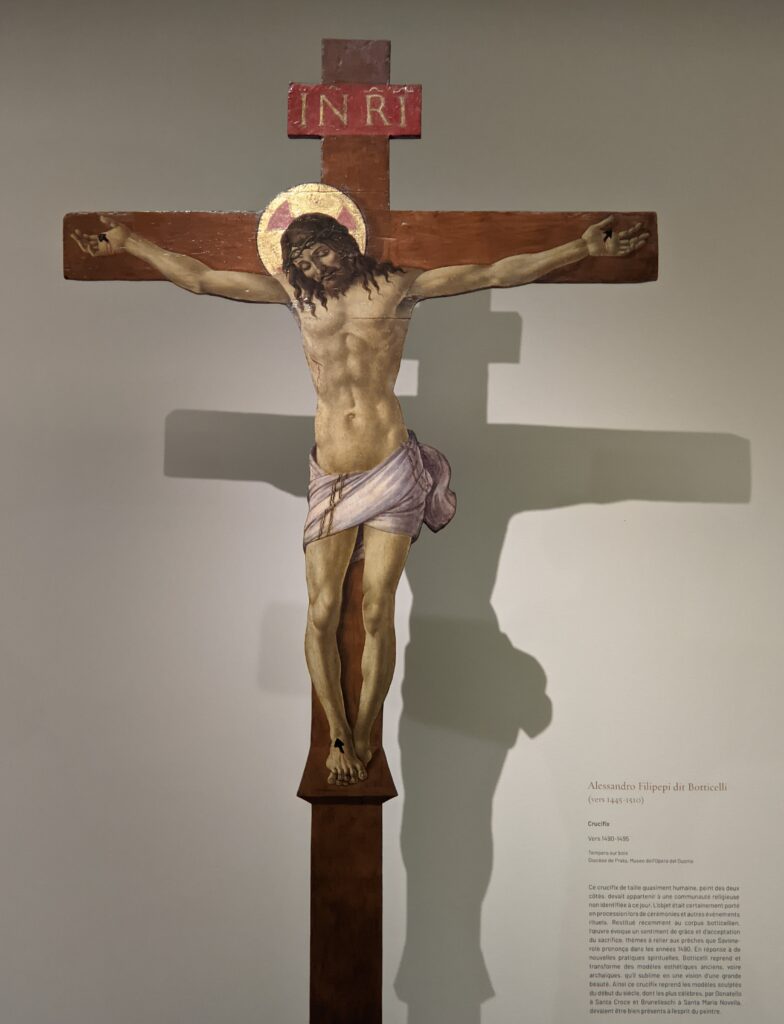
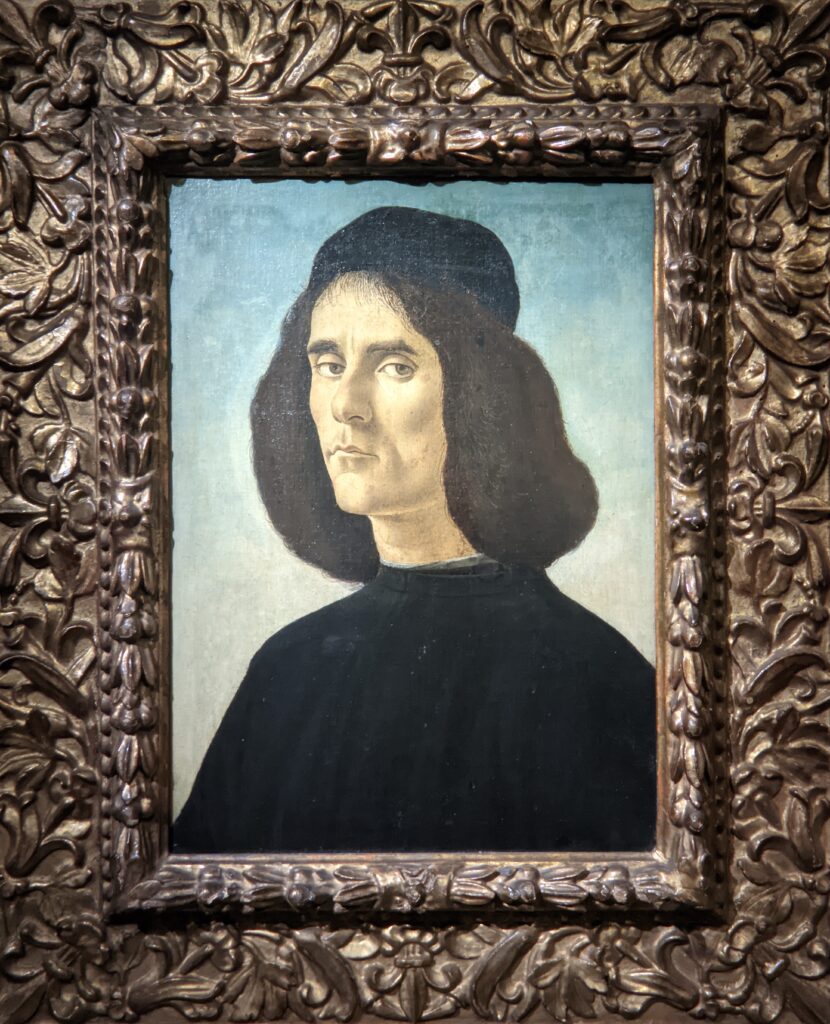
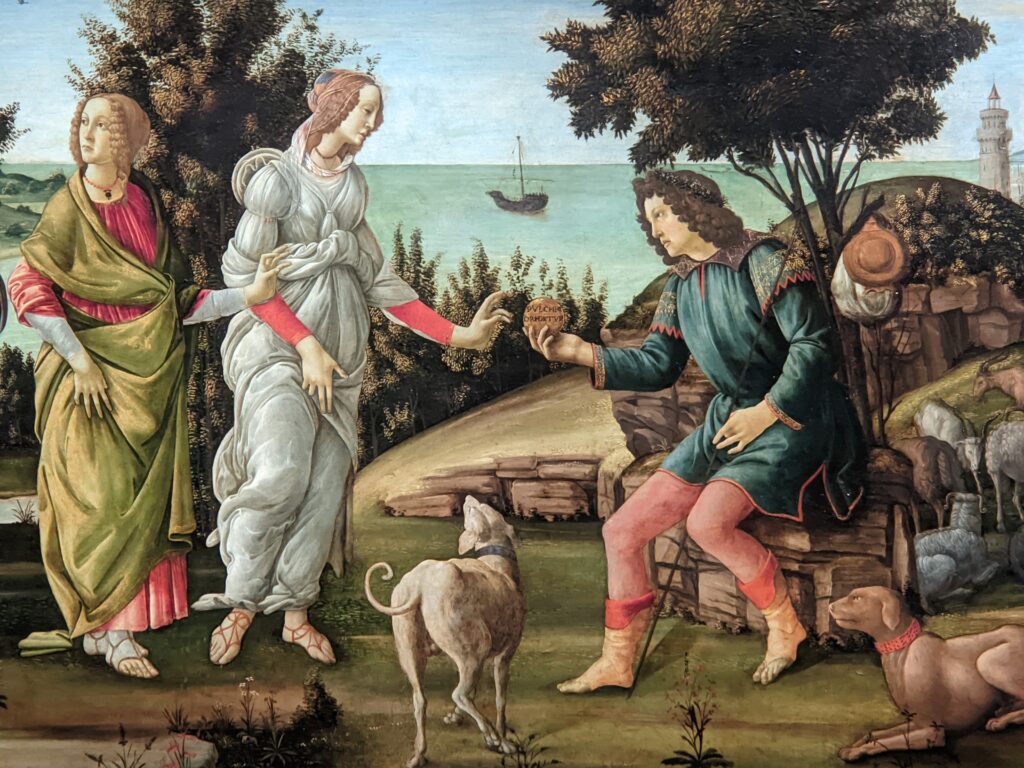

















You might choose to continue discovering the amazing cultural offerings in the French capital by reading our article “Paris — The 10 Best Art Museums.”
Thank you!











